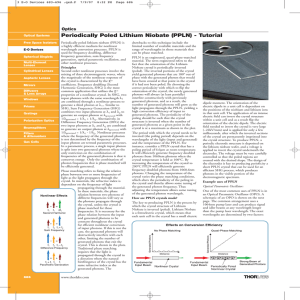
Quantum Mechanics 1 - University of Birmingham
... from the surface of a nickel crystal. Diffraction is a wave property – arises due to interference between scattered ...
... from the surface of a nickel crystal. Diffraction is a wave property – arises due to interference between scattered ...
Historical introduction to quantum mechanics
... Historical introduction to quantum mechanics Kirchhoff imagined a container – a cavity –whose walls were heated up so that they emitted radiation that was trapped in the container. Within the cavity, there is a distribution of radiation of all wavelength, λ. Intensity measures the rate at which ene ...
... Historical introduction to quantum mechanics Kirchhoff imagined a container – a cavity –whose walls were heated up so that they emitted radiation that was trapped in the container. Within the cavity, there is a distribution of radiation of all wavelength, λ. Intensity measures the rate at which ene ...
Advanced Physical Chemistry
... UHF formalism. The HF procedure works well for atoms due to spherical symmetry, but for molecules, this symmetry is not there. Must expand the spatial parts of the spinorbitals in terms of another basis set. From a set of M basis functions , obtain M linearly independent spatial wavefunctions. End u ...
... UHF formalism. The HF procedure works well for atoms due to spherical symmetry, but for molecules, this symmetry is not there. Must expand the spatial parts of the spinorbitals in terms of another basis set. From a set of M basis functions , obtain M linearly independent spatial wavefunctions. End u ...
Determining the radial distribution of the emission coefficient from a
... The purpose of this paper is to determine the radial distribution of the emission coefficient from the measured intensity distribution emitted by an extended source of radiation, particularly a plasma source. The source is assumed to be optically thin and axially symmetrical. This problem is solved ...
... The purpose of this paper is to determine the radial distribution of the emission coefficient from the measured intensity distribution emitted by an extended source of radiation, particularly a plasma source. The source is assumed to be optically thin and axially symmetrical. This problem is solved ...
THE CURRENT-VOLTAGE CHARACTERISTICS
... point in developing the modern theory for the hydrogen atom. Robert Millikan made the ...
... point in developing the modern theory for the hydrogen atom. Robert Millikan made the ...
CCD-Based Instrumentation for Radiometric
... Light is just one portion of the various electromagnetic waves flying through space. The electromagnetic spectrum covers an extremely broad range, from radio waves with wavelengths of a meter or more, down to x-rays with wavelengths of less than a billionth of a meter. Optical radiation lies between ...
... Light is just one portion of the various electromagnetic waves flying through space. The electromagnetic spectrum covers an extremely broad range, from radio waves with wavelengths of a meter or more, down to x-rays with wavelengths of less than a billionth of a meter. Optical radiation lies between ...
lecture slides of chap8
... Cation is always smaller than atom from which it is formed. This is because the nuclear charge remains the same but the reduced electron repulsion resulting from removal of electrons make the electron clouds shrink. Anion is always larger than atom from which it is formed. This is because the nuclea ...
... Cation is always smaller than atom from which it is formed. This is because the nuclear charge remains the same but the reduced electron repulsion resulting from removal of electrons make the electron clouds shrink. Anion is always larger than atom from which it is formed. This is because the nuclea ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... 51 Draw a Lewis electron-dot diagram for an atom of silicon. [1] Base your answers to questions 52 through 54 on the information below. ...
... 51 Draw a Lewis electron-dot diagram for an atom of silicon. [1] Base your answers to questions 52 through 54 on the information below. ...
ID_72_paper
... (CI) considers the mixing of wave function from the ground state configuration are taken. The CI method, in principle, has many of the desirable features being well defined, sizeconsistant and variational [2]. Møller-Plesset perturbation theory adds higher excitations to HF theory as a non-iterative ...
... (CI) considers the mixing of wave function from the ground state configuration are taken. The CI method, in principle, has many of the desirable features being well defined, sizeconsistant and variational [2]. Møller-Plesset perturbation theory adds higher excitations to HF theory as a non-iterative ...
Spectroscopy
... • Excited molecules are subjected to collisions and give up energy down to lower vibrational levels. If it survives long enough it may undergo spontaneous emission and emit remaining energy as radiation in going to the lower electronic state. The spectra has the vibrational spectra of the lower stat ...
... • Excited molecules are subjected to collisions and give up energy down to lower vibrational levels. If it survives long enough it may undergo spontaneous emission and emit remaining energy as radiation in going to the lower electronic state. The spectra has the vibrational spectra of the lower stat ...
Atomic Structure and Periodic Trends
... • Each orbital can hold a maximum of 2 electrons of opposite spin. • Pauli exclusion principle states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of 4 quantum numbers ...
... • Each orbital can hold a maximum of 2 electrons of opposite spin. • Pauli exclusion principle states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of 4 quantum numbers ...
Objective 4
... beakers. The first solution has a pH of 4, and the pH of the second solution is unknown. If the two solutions are mixed and the resulting pH is 5, the second solution must have — A fewer suspended solids B a lower temperature C more dissolved salt (NaCl) particles D a higher concentration of OH– ion ...
... beakers. The first solution has a pH of 4, and the pH of the second solution is unknown. If the two solutions are mixed and the resulting pH is 5, the second solution must have — A fewer suspended solids B a lower temperature C more dissolved salt (NaCl) particles D a higher concentration of OH– ion ...
electron configuration
... • Valence shell: outermost EL that is occupied by ein the electron cloud • Valence shell electrons: an e- that is available to be lost, gained, or shared in the outer EL – These electrons are of primary concern because they are the electrons most involved in chemical ...
... • Valence shell: outermost EL that is occupied by ein the electron cloud • Valence shell electrons: an e- that is available to be lost, gained, or shared in the outer EL – These electrons are of primary concern because they are the electrons most involved in chemical ...
Notes on Atomic Structure atoms
... numbers and types of atoms. Atoms are indivisible in chemical processes. That is, atoms are not created or destroyed in chemical reactions. A chemical reaction simply changes the way atoms are grouped together. ...
... numbers and types of atoms. Atoms are indivisible in chemical processes. That is, atoms are not created or destroyed in chemical reactions. A chemical reaction simply changes the way atoms are grouped together. ...
slides in pdf format
... • Theory: de Broglie (1924) proposes matter waves • assumes all “particles” (e.g. electrons) also have a wave associated with them with wavelength determined by its momentum, λ = h/p. • Bohr’s quantization follows because the electron in an atom is described by a “standing electron wave”. • Experime ...
... • Theory: de Broglie (1924) proposes matter waves • assumes all “particles” (e.g. electrons) also have a wave associated with them with wavelength determined by its momentum, λ = h/p. • Bohr’s quantization follows because the electron in an atom is described by a “standing electron wave”. • Experime ...
Document
... ii. Many of these symbols consist of the first letter or the first two letters of the element name. c. 3.3 Dalton’s Atomic Theory i. In the early 1800’s English scientist John Dalton came up with an explanation of how atoms combine to form compounds. ii. Dalton’s atomic theory has five main points: ...
... ii. Many of these symbols consist of the first letter or the first two letters of the element name. c. 3.3 Dalton’s Atomic Theory i. In the early 1800’s English scientist John Dalton came up with an explanation of how atoms combine to form compounds. ii. Dalton’s atomic theory has five main points: ...
the Bohr`s atom model - Latin-American Journal of Physics Education
... one electron (better say, Hydrogen) atom, Bohr have made some basic assumptions that have been resumed in three postulates, namely: i- The electron can moves only in certain and stable circular orbits about the nucleus (proton) where does not emit energy in the form of radiation. ii- Radiation is em ...
... one electron (better say, Hydrogen) atom, Bohr have made some basic assumptions that have been resumed in three postulates, namely: i- The electron can moves only in certain and stable circular orbits about the nucleus (proton) where does not emit energy in the form of radiation. ii- Radiation is em ...
Chemical Reactions
... Chemical – stored in the bonds of chemical substances Electrical – results from the movement of charged particles Mechanical – directly involved in moving matter Radiant or electromagnetic – energy traveling in waves (i.e., visible light, ultraviolet light, and X-rays) ...
... Chemical – stored in the bonds of chemical substances Electrical – results from the movement of charged particles Mechanical – directly involved in moving matter Radiant or electromagnetic – energy traveling in waves (i.e., visible light, ultraviolet light, and X-rays) ...
X-ray fluorescence

X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is the emission of characteristic ""secondary"" (or fluorescent) X-rays from a material that has been excited by bombarding with high-energy X-rays or gamma rays. The phenomenon is widely used for elemental analysis and chemical analysis, particularly in the investigation of metals, glass, ceramics and building materials, and for research in geochemistry, forensic science and archaeology.