Document
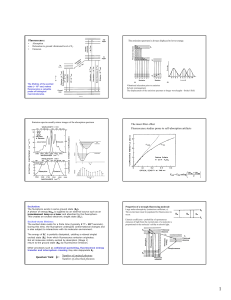
... “Electron Volt” – energy gained by charge +1e when accelerated by 1 Volt: U qV 1e = 1.610–19 C, so 1 eV = 1.610–19 J Planck constant: h = 6.626 10–34 J∙s Speed of light: c = 3 108 m/s Electron mass: m = 9.1 10–31 kg ...
... “Electron Volt” – energy gained by charge +1e when accelerated by 1 Volt: U qV 1e = 1.610–19 C, so 1 eV = 1.610–19 J Planck constant: h = 6.626 10–34 J∙s Speed of light: c = 3 108 m/s Electron mass: m = 9.1 10–31 kg ...
Unit 9: Atomic Structure, Periodicity and Chemical Bonding
... • Photoelectron spectroscopy determines the energy needed to eject electrons from the material. Measurement of these energies provides a method to deduce the shell structure of an atom. The intensity of the photoelectron signal at a given energy is a measure of the number of electrons in that energy ...
... • Photoelectron spectroscopy determines the energy needed to eject electrons from the material. Measurement of these energies provides a method to deduce the shell structure of an atom. The intensity of the photoelectron signal at a given energy is a measure of the number of electrons in that energy ...
Chapter 1 Chemistry: The Study of Matter
... definite volume nor shape. Gases have this characteristic because they are composed of particles that move very rapidly and are at great distances from one another. At these distances, the attractive forces are very weak. A gas will expand to fill any size container and take the shape of that contai ...
... definite volume nor shape. Gases have this characteristic because they are composed of particles that move very rapidly and are at great distances from one another. At these distances, the attractive forces are very weak. A gas will expand to fill any size container and take the shape of that contai ...
UNIT 3 VOCABULARY MATCHING and mole problems
... ____ 2.) equal to the number of protons in an atom; whole number on the Periodic Table ____ 3.) equal to the number of protons plus the number of neutrons in an atom ____ 4.) discovered the electron using a cathode ray tube ____ 5.) atoms of the same element, but have different masses ____ 6.) negat ...
... ____ 2.) equal to the number of protons in an atom; whole number on the Periodic Table ____ 3.) equal to the number of protons plus the number of neutrons in an atom ____ 4.) discovered the electron using a cathode ray tube ____ 5.) atoms of the same element, but have different masses ____ 6.) negat ...
Honors Chemistry Final Review
... electronegativity difference that is ___________ which means that the two combining elements will be further apart on the _________________ In fact, the further apart, the more ionic! A covalent bond forms from the combination of ______________________, including ___________ It has an electronegativ ...
... electronegativity difference that is ___________ which means that the two combining elements will be further apart on the _________________ In fact, the further apart, the more ionic! A covalent bond forms from the combination of ______________________, including ___________ It has an electronegativ ...
1s + 2p
... “Atom in a Box” can be used to show: (1) Spectral transitions for H atom (levels, energy, wavelength) (2) Static shift of e-density from mixing 2s with 2p (same energy) (3) Oscillation of e-density from mixing orbitals with different energy because of change in relative phase* with time (add, then ...
... “Atom in a Box” can be used to show: (1) Spectral transitions for H atom (levels, energy, wavelength) (2) Static shift of e-density from mixing 2s with 2p (same energy) (3) Oscillation of e-density from mixing orbitals with different energy because of change in relative phase* with time (add, then ...
solutions - The University of Sydney
... surfactant, which results in a varying surface tension. Long molecules become aligned and harder to separate when the film is stretched, so increasing ! as r increases. Likewise, on relaxing the tension the molecules are more randomised, reducing the surface tension. Hence Laplace’s law still applie ...
... surfactant, which results in a varying surface tension. Long molecules become aligned and harder to separate when the film is stretched, so increasing ! as r increases. Likewise, on relaxing the tension the molecules are more randomised, reducing the surface tension. Hence Laplace’s law still applie ...
Unit 1 – Physical Science and Chemical Reactions
... - Period number = Number of energy levels occupied by electrons - The first three energy levels will have 2, 8, and 8 structures of electrons ...
... - Period number = Number of energy levels occupied by electrons - The first three energy levels will have 2, 8, and 8 structures of electrons ...
Optical Gain Experiment Manual
... From the previous study in physics of semiconductors, there are two types of semiconductors classified according the energy band distribution in wavenumber space, i.e. direct semiconductors such as Si and Ge and indirect band gap semiconductors such as GaAs. Fig. 2-(a) shows the band energy diagram ...
... From the previous study in physics of semiconductors, there are two types of semiconductors classified according the energy band distribution in wavenumber space, i.e. direct semiconductors such as Si and Ge and indirect band gap semiconductors such as GaAs. Fig. 2-(a) shows the band energy diagram ...
Magnetotransport of Topological Insulators
... In order to learn some of the basic properties of our TIs, which were grown in the MBE lab at Notre Dame, we performed magnetotransport on Bi2Se3, Bi2Te3, and Bi2(TeSe)3. We accomplished this by soldering samples of various materials, size, and thickness to a sample holder. The sample holder was wir ...
... In order to learn some of the basic properties of our TIs, which were grown in the MBE lab at Notre Dame, we performed magnetotransport on Bi2Se3, Bi2Te3, and Bi2(TeSe)3. We accomplished this by soldering samples of various materials, size, and thickness to a sample holder. The sample holder was wir ...
Long Distance, Unconditional Teleportation of Atomic States V 87, N
... by the process of teleportation [2]. Quantum information processing needs only to be performed locally. The scheme should allow reliable transmission of quantum information between quantum microcomputers separated by distances of tens of kilometers, without using entanglement purification or quantum ...
... by the process of teleportation [2]. Quantum information processing needs only to be performed locally. The scheme should allow reliable transmission of quantum information between quantum microcomputers separated by distances of tens of kilometers, without using entanglement purification or quantum ...
ppt
... “Electron Volt” – energy gained by charge +1e when accelerated by 1 Volt: U qV 1e = 1.610–19 C, so 1 eV = 1.610–19 J Planck constant: h = 6.626 10–34 J∙s Speed of light: c = 3 108 m/s Electron mass: m = 9.1 10–31 kg ...
... “Electron Volt” – energy gained by charge +1e when accelerated by 1 Volt: U qV 1e = 1.610–19 C, so 1 eV = 1.610–19 J Planck constant: h = 6.626 10–34 J∙s Speed of light: c = 3 108 m/s Electron mass: m = 9.1 10–31 kg ...
Periodic Properties of the Elements Effective Nuclear Charge, Zeff
... 3. Electrons for which n is one less than n for the electron of interest contribute 0.85 to the value of S, while those with even smaller values of n contribute 1.00. ...
... 3. Electrons for which n is one less than n for the electron of interest contribute 0.85 to the value of S, while those with even smaller values of n contribute 1.00. ...
Lecture 20: Polyelectronic Atoms
... • Aufbau is German for “Building Up”. We are building a multielectronic atom from the rules for the 1 electron atom (so a few things get modified), but it works pretty well. ...
... • Aufbau is German for “Building Up”. We are building a multielectronic atom from the rules for the 1 electron atom (so a few things get modified), but it works pretty well. ...
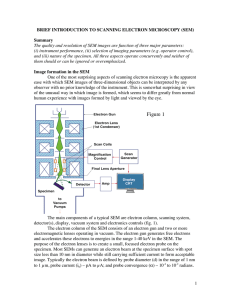
Introduction to Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
... In order to produce images the electron beam is focused into a fine probe, which is scanned across the surface of the specimen with the help of scanning coils (fig. 1). Each point on the specimen that is struck by the accelerated electrons emits signal in the form of electromagnetic radiation. Sele ...
... In order to produce images the electron beam is focused into a fine probe, which is scanned across the surface of the specimen with the help of scanning coils (fig. 1). Each point on the specimen that is struck by the accelerated electrons emits signal in the form of electromagnetic radiation. Sele ...
7 - Mona Shores Blogs
... 34. Which of the following metals cannot displace hydrogen from water? a. Mg b. Ba c. Li d. Ag 35. Copper does not react with hydrochloric acid whereas manganese does? This means that a. copper is more active than hydrogen b. manganese is less active than hydrogen c. chloride ion will react with cop ...
... 34. Which of the following metals cannot displace hydrogen from water? a. Mg b. Ba c. Li d. Ag 35. Copper does not react with hydrochloric acid whereas manganese does? This means that a. copper is more active than hydrogen b. manganese is less active than hydrogen c. chloride ion will react with cop ...
A high-speed tunable beam splitter for feed
... Femtosecond laser pulses from a Ti:Sapphire oscillator are up-converted with a 0.7 mm β barium borate crystal (BBO1) cut for type-I phase-matching. This produces vertically polarized second harmonic pulses. The up-converted pulses and the remaining fundamental pulses are separated with six dichroic ...
... Femtosecond laser pulses from a Ti:Sapphire oscillator are up-converted with a 0.7 mm β barium borate crystal (BBO1) cut for type-I phase-matching. This produces vertically polarized second harmonic pulses. The up-converted pulses and the remaining fundamental pulses are separated with six dichroic ...
The Atomic Theory, and the Structure of Matter
... Writing Balanced Chemical Equations 1. Write the chemical formula for each reactant and product followed by the state of each: solid (s); liquid (l); gas (g); ...
... Writing Balanced Chemical Equations 1. Write the chemical formula for each reactant and product followed by the state of each: solid (s); liquid (l); gas (g); ...
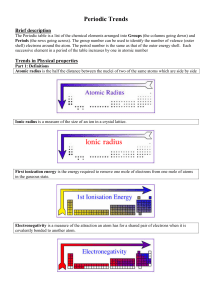
Topic 3 Periodicity notes SL - Chemical Minds
... Going down a group, the atomic radius and ionic radius increase due to an increase in the number of electron shells surrounding the nucleus. The ionisation energy and electronegativity decrease because i) there is a decrease in the electrostatic attraction between the positive protons in the nucleus ...
... Going down a group, the atomic radius and ionic radius increase due to an increase in the number of electron shells surrounding the nucleus. The ionisation energy and electronegativity decrease because i) there is a decrease in the electrostatic attraction between the positive protons in the nucleus ...
X-ray fluorescence

X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is the emission of characteristic ""secondary"" (or fluorescent) X-rays from a material that has been excited by bombarding with high-energy X-rays or gamma rays. The phenomenon is widely used for elemental analysis and chemical analysis, particularly in the investigation of metals, glass, ceramics and building materials, and for research in geochemistry, forensic science and archaeology.