Fall Semester Review Packet
... 1. Describe the difference between a chemical change and a physical change and give three indications that a chemical change has occurred. Also, give one example of each type of change. 2. Explain the Law of Conservation of Mass. Include information about the mass of reactants and products within a ...
... 1. Describe the difference between a chemical change and a physical change and give three indications that a chemical change has occurred. Also, give one example of each type of change. 2. Explain the Law of Conservation of Mass. Include information about the mass of reactants and products within a ...
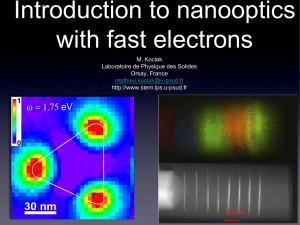
Soft-x-ray interferometer for single-shot laser linewidth measurements
... experiments were conducted in the near-IR region of the spectrum by use of a vertical-cavity surfaceemitting laser diode,14 which could be adjusted to emit in two modes of similar amplitude. Using standard 1-in. s2.54 cmd gratings of 600 groovesymm made it possible to measure the spectral separation ...
... experiments were conducted in the near-IR region of the spectrum by use of a vertical-cavity surfaceemitting laser diode,14 which could be adjusted to emit in two modes of similar amplitude. Using standard 1-in. s2.54 cmd gratings of 600 groovesymm made it possible to measure the spectral separation ...
Hybrid Dielectric/Surface Plasmon Polariton Waveguide P. David Flammer
... waveguide that can be used in either a single mode, single polarization waveguide, or in a multi-mode. When used as a single mode, the devise allows for control of propagation and confinement. Gratings may be used for coupling light into and out of the modes or for use as mirrors in the mode. When u ...
... waveguide that can be used in either a single mode, single polarization waveguide, or in a multi-mode. When used as a single mode, the devise allows for control of propagation and confinement. Gratings may be used for coupling light into and out of the modes or for use as mirrors in the mode. When u ...
Molecular energy levels - University of Lethbridge
... What happens when we have more than two atoms? In some ways, the picture isn’t that different. We can still typically treat the vibrational energy levels as if they obey equation 1, except that we have to have one such equation for each vibrational mode (each different way for the molecule to vibrat ...
... What happens when we have more than two atoms? In some ways, the picture isn’t that different. We can still typically treat the vibrational energy levels as if they obey equation 1, except that we have to have one such equation for each vibrational mode (each different way for the molecule to vibrat ...
HW / Unit 2
... 6. Fill in the missing parts of the following nuclear equations and identify the type of radiation emitted: a. 21082Pb 21083Bi + ____ b. 146C ____ + 0-1e c. 22688Ra ____ + 42He + gamma ray HW #2.7 1. Explain what each of the following scientists contributed to atomic theory. a. Niels Bohr b. E ...
... 6. Fill in the missing parts of the following nuclear equations and identify the type of radiation emitted: a. 21082Pb 21083Bi + ____ b. 146C ____ + 0-1e c. 22688Ra ____ + 42He + gamma ray HW #2.7 1. Explain what each of the following scientists contributed to atomic theory. a. Niels Bohr b. E ...
Crystal Chemistry Atoms Electrons Quantum Mechanics Orbital
... • Element = substance that can not be chemically broken down into smaller parts; has unique chemical properties • Atom = smallest subdivision of an element that still retains all of the element’s chemical properties • Protons = positively charged particles; clustered in the nucleus of the atom • Neu ...
... • Element = substance that can not be chemically broken down into smaller parts; has unique chemical properties • Atom = smallest subdivision of an element that still retains all of the element’s chemical properties • Protons = positively charged particles; clustered in the nucleus of the atom • Neu ...
slides - University of Colorado Boulder
... electrons are waves, explain with interference: e.g.: ‘The electrons were only detected at certain angles because they were interfering constructively and destructively. It was important because it meant they were acting like waves.’ electrons are waves, no explanation: e.g.: ‘The reason for this re ...
... electrons are waves, explain with interference: e.g.: ‘The electrons were only detected at certain angles because they were interfering constructively and destructively. It was important because it meant they were acting like waves.’ electrons are waves, no explanation: e.g.: ‘The reason for this re ...
CHAPTER 15. LASER AND FIBER OPTICS The laser is essentially
... the mirrors is chosen with a reflectivity as close to 100% as possible. The other is selected with a reflectivity somewhat less than 100% to allow part of the internally reflecting beam to escape and become the useful laser output beam. The fundamental mode that appears in the output laser beam is t ...
... the mirrors is chosen with a reflectivity as close to 100% as possible. The other is selected with a reflectivity somewhat less than 100% to allow part of the internally reflecting beam to escape and become the useful laser output beam. The fundamental mode that appears in the output laser beam is t ...
Chapter 4.3: How Atoms Differ
... Radiation = The _________ and ______________ emitted by ______________ materials. ...
... Radiation = The _________ and ______________ emitted by ______________ materials. ...
Monday, March 8, 2010
... 1) Very little time (nanoseconds) between arrival of light pulse and emission of electron 2) Electron energy independent of intensity of light 3) At higher frequency get higher energy electrons Minimum frequency (0) required for photoelectric effect depends on material: ...
... 1) Very little time (nanoseconds) between arrival of light pulse and emission of electron 2) Electron energy independent of intensity of light 3) At higher frequency get higher energy electrons Minimum frequency (0) required for photoelectric effect depends on material: ...
Chem MCQ for Class-9th
... 1. The atomic radii of the elements in Periodic Table: a. Incrase from left to right ina period b. Increase from top to bottom in group c. Do not change from left to right in a period d. Decrease from top to bottom in a group 2. The amount of energy given out when an electron is added to an atom is ...
... 1. The atomic radii of the elements in Periodic Table: a. Incrase from left to right ina period b. Increase from top to bottom in group c. Do not change from left to right in a period d. Decrease from top to bottom in a group 2. The amount of energy given out when an electron is added to an atom is ...
The UNCERTAINTY PRINCIPLE Uncertainty Principle II
... without friction between 2 rollers. If a particle goes through the bottom slit and back up to the screen, the plate containing the slits will recoil downwards. On the other hand it will recoil up if the particle goes through the upper slit. Then, by A 2-slit set-up where the plate with watching the ...
... without friction between 2 rollers. If a particle goes through the bottom slit and back up to the screen, the plate containing the slits will recoil downwards. On the other hand it will recoil up if the particle goes through the upper slit. Then, by A 2-slit set-up where the plate with watching the ...
1 Introduction - High Point University
... Because the states an electron occur only at discrete energy levels, they are said to be quantized. The word quantum comes from a Latin word meaning “how much.” The branch of physics that provides the current model of the Hydrogen atom is called quantum mechanics. The electron in a Hydrogen atom can ...
... Because the states an electron occur only at discrete energy levels, they are said to be quantized. The word quantum comes from a Latin word meaning “how much.” The branch of physics that provides the current model of the Hydrogen atom is called quantum mechanics. The electron in a Hydrogen atom can ...
WHAT IS A PHOTON? Spontaneous emission
... Spontaneous emission: The need for quantum field theory In these notes I would like to try and give an introduction to the quantum mechanical theory of the photon. The treatment I give is in the spirit of a treatment you can find in Dirac’s quantum mechanics monograph, The Principles of Quantum Mech ...
... Spontaneous emission: The need for quantum field theory In these notes I would like to try and give an introduction to the quantum mechanical theory of the photon. The treatment I give is in the spirit of a treatment you can find in Dirac’s quantum mechanics monograph, The Principles of Quantum Mech ...
General Introduction to Electronic Structure Theory
... Determinant 3. Solve for those orbitals which minimize the electronic energy (variational method) This winds up being mathematically equivalent to assuming each electron ...
... Determinant 3. Solve for those orbitals which minimize the electronic energy (variational method) This winds up being mathematically equivalent to assuming each electron ...
Chemistry Unit Test Study Guide (2012-2013)
... Elements in the same group or family (column) have similar physical and chemical properties based on the number of _________________ in their _______________ shell. Matching Section: ...
... Elements in the same group or family (column) have similar physical and chemical properties based on the number of _________________ in their _______________ shell. Matching Section: ...
X-ray fluorescence

X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is the emission of characteristic ""secondary"" (or fluorescent) X-rays from a material that has been excited by bombarding with high-energy X-rays or gamma rays. The phenomenon is widely used for elemental analysis and chemical analysis, particularly in the investigation of metals, glass, ceramics and building materials, and for research in geochemistry, forensic science and archaeology.