CPR Course
... • In SCA, ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation causes the heart to beat too fast. ● Ventricular tachycardia (VT), a dangerously fast rhythm in the lower two chambers of the heart. ● Ventricular fibrillation (VF), a rapid and chaotic quivering of the ventricles, which can be triggered ...
... • In SCA, ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation causes the heart to beat too fast. ● Ventricular tachycardia (VT), a dangerously fast rhythm in the lower two chambers of the heart. ● Ventricular fibrillation (VF), a rapid and chaotic quivering of the ventricles, which can be triggered ...
Combined Aortic and Pulmonic Stenosis
... In -May 1958, the child was operated upon by mneans of extracorporeal circulation. The right ventriele was opened and, in effect, a single ventricle was encountered. A diaphragmatie obstruction in the pullmloonary outflow tract was relieved by cutting- out fibromuscular tissue. Then a finger could e ...
... In -May 1958, the child was operated upon by mneans of extracorporeal circulation. The right ventriele was opened and, in effect, a single ventricle was encountered. A diaphragmatie obstruction in the pullmloonary outflow tract was relieved by cutting- out fibromuscular tissue. Then a finger could e ...
EGANSChapter_09
... • Respond to volume changes Baroreceptor output is directly proportional to vessel stretch • Negative feedback system, so greater stretch causes venodilation and decreased heart rate and contractility. ...
... • Respond to volume changes Baroreceptor output is directly proportional to vessel stretch • Negative feedback system, so greater stretch causes venodilation and decreased heart rate and contractility. ...
Cardiogenic Shock
... At the conclusion of this program, the participants will be able to: Identify the signs and symptoms of cardiogenic shock Identify two factors that place a patient at risk for developing cardiogenic shock Discuss what is currently being stated in the literature regarding the usefulness of IABC ...
... At the conclusion of this program, the participants will be able to: Identify the signs and symptoms of cardiogenic shock Identify two factors that place a patient at risk for developing cardiogenic shock Discuss what is currently being stated in the literature regarding the usefulness of IABC ...
Beacon2002Q2 - Med
... tighten, and air cannot move freely. Less air causes a person to feel short of breath, and the air moving through the tightened airways causes a whistling sound known as wheezing. ...
... tighten, and air cannot move freely. Less air causes a person to feel short of breath, and the air moving through the tightened airways causes a whistling sound known as wheezing. ...
Input Impedance of the Systemic Circulation in Man
... settings used in this study, measured by applying an appropriate electrical input signal to the system," was constant in amplitude (±5%) from 0 to 32 Hz. Phase shift was approximately linear and equivalent to a time delay of 17 msec. This response is adequate for accurate measurement of pulsatile ve ...
... settings used in this study, measured by applying an appropriate electrical input signal to the system," was constant in amplitude (±5%) from 0 to 32 Hz. Phase shift was approximately linear and equivalent to a time delay of 17 msec. This response is adequate for accurate measurement of pulsatile ve ...
Regulation of Cardiac Output by Stroke Volume and Heart Rate in
... equivalent increase in cardiac output by distending the ventricle and increasing stroke volume."7 Indeed, in the present study, in dogs anesthetized and with an open chest, the increased cardiac output observed with volume loading occurred entirely through increases in stroke volume (Fig. 3). This i ...
... equivalent increase in cardiac output by distending the ventricle and increasing stroke volume."7 Indeed, in the present study, in dogs anesthetized and with an open chest, the increased cardiac output observed with volume loading occurred entirely through increases in stroke volume (Fig. 3). This i ...
Progressive Dystrophic Pathology in Diaphragm and Impairment of
... Total protein was extracted from heart and diaphragm muscles using TX-100 buffer (1% Triton X-100, 50mM Tris pH8.0, 150mM NaCl, 0.1% SDS) supplemented with protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche, Germany). Samples were homogenized in TX-100 buffer and the supernatants were collected by centrifugation at ...
... Total protein was extracted from heart and diaphragm muscles using TX-100 buffer (1% Triton X-100, 50mM Tris pH8.0, 150mM NaCl, 0.1% SDS) supplemented with protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche, Germany). Samples were homogenized in TX-100 buffer and the supernatants were collected by centrifugation at ...
Right Ventricular Bifocal Stimulation in the Treatment of Dilated
... In dilated cardiomyopathy some degree of delay occurs in myocardial stimulus conduction, which causes QRS widening. Associated lesions in the conduction system also often cause QRS widening. In these cases, when a cardiac pacemaker is necessary, paced QRS is more enlarged, easily achieving 200 ms or ...
... In dilated cardiomyopathy some degree of delay occurs in myocardial stimulus conduction, which causes QRS widening. Associated lesions in the conduction system also often cause QRS widening. In these cases, when a cardiac pacemaker is necessary, paced QRS is more enlarged, easily achieving 200 ms or ...
Назва наукового напрямку (модуля): Семестр: 4 Модуль 4 Цикл
... During registration of the ECG in V1 lead, an active electrode was set on the patient in II intercostal region to the left of breastbone(sternum),that is not correct. Where is an electrode supposed to be placed in this case? In II intercostal region to the right of breastbone In IV intercostal regio ...
... During registration of the ECG in V1 lead, an active electrode was set on the patient in II intercostal region to the left of breastbone(sternum),that is not correct. Where is an electrode supposed to be placed in this case? In II intercostal region to the right of breastbone In IV intercostal regio ...
Cardiac MRI: Part 1, Cardiovascular Shunts
... The foramen ovale is a flaplike opening between the septum primum and septum secundum at the level of the fossa ovalis that usually closes by the first or second year of life but that remains patent (patent foramen ovale [PFO]) in 25–30% of the population. It is not a true “defect” because septal ti ...
... The foramen ovale is a flaplike opening between the septum primum and septum secundum at the level of the fossa ovalis that usually closes by the first or second year of life but that remains patent (patent foramen ovale [PFO]) in 25–30% of the population. It is not a true “defect” because septal ti ...
Assessment of Heart Rates and Blood Pressure in
... and joints of the body are exercised byrecitation. There is also a need to increase the blood flow to the face, tongue, the sensory and motor areas of the mouth, and the upper pre-motor cortex of the brain during recitation. Thus, heart rate would have increased during creative speech, but once the ...
... and joints of the body are exercised byrecitation. There is also a need to increase the blood flow to the face, tongue, the sensory and motor areas of the mouth, and the upper pre-motor cortex of the brain during recitation. Thus, heart rate would have increased during creative speech, but once the ...
Recent Studies in the Pre-Excitation Syndrome
... QRS duration associated with a delta wave. Both of these reflect the presence of ventricular fusion caused by activity being conducted simultaneously over the accessory A-V pathway and normal A-V conduction system. The degree of fusion is influenced by the relative conduction times over the two A-V ...
... QRS duration associated with a delta wave. Both of these reflect the presence of ventricular fusion caused by activity being conducted simultaneously over the accessory A-V pathway and normal A-V conduction system. The degree of fusion is influenced by the relative conduction times over the two A-V ...
No Job Name - IMP. Erlangen
... and validated dedicated cardiac reconstruction algorithms for imaging the heart with subsecond multi-slice spiral CT utilizing electrocardiogram ~ECG! information. The single-slice cardiac z-interpolation algorithms 180°CI and 180°CD @Med. Phys. 25, 2417–2431 ~1998!# were generalized to allow imagin ...
... and validated dedicated cardiac reconstruction algorithms for imaging the heart with subsecond multi-slice spiral CT utilizing electrocardiogram ~ECG! information. The single-slice cardiac z-interpolation algorithms 180°CI and 180°CD @Med. Phys. 25, 2417–2431 ~1998!# were generalized to allow imagin ...
Obtaining a High Quality ECG and Basic ECG
... “rabbit ears” in V1. This is a frequent normal variant. ...
... “rabbit ears” in V1. This is a frequent normal variant. ...
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation by Chest Compression Alone: A
... after 4-10 min of resuscitation, irrespective of attempts at ventilation.56,66 Furthermore, ventilation may occur during CO-CPR through active and passive mechanisms. After a non-hypoxic cardiac arrest, patients usually continue to breath actively for some short period, before the respiratory centre ...
... after 4-10 min of resuscitation, irrespective of attempts at ventilation.56,66 Furthermore, ventilation may occur during CO-CPR through active and passive mechanisms. After a non-hypoxic cardiac arrest, patients usually continue to breath actively for some short period, before the respiratory centre ...
Differentiation of Muscarinic Receptors Mediating Negative
... nate in the absence of pathology. Vasoconstriction becomes the dominant effect in patients with atherosclerosis or hypertension due to reduction or loss of endothelium-dependent vasodilation. The physiological significance of muscarinic receptors in the coronary vasculature is currently unknown, but ...
... nate in the absence of pathology. Vasoconstriction becomes the dominant effect in patients with atherosclerosis or hypertension due to reduction or loss of endothelium-dependent vasodilation. The physiological significance of muscarinic receptors in the coronary vasculature is currently unknown, but ...
The Effect of Temperature Acclimation and Adrenaline on the
... in a manneridentical to thatof series I, except thatthere was no adrenalinefree perfusion. The heart received perfusate containing 5 nmol adrenaline - L-1 during surgery.This initial adrenaline concentrationwas established in partbecause adrenaline-freeperfusion at 5 C in series I produced slow and ...
... in a manneridentical to thatof series I, except thatthere was no adrenalinefree perfusion. The heart received perfusate containing 5 nmol adrenaline - L-1 during surgery.This initial adrenaline concentrationwas established in partbecause adrenaline-freeperfusion at 5 C in series I produced slow and ...
HEART IN NORMAL MAN output of the heart per unit of time. This
... The output of the heart per minute under ordinary conditions of life is a constantly changing value. It changes with position, with temperature, and it changes tremendously with increased oxygen consumption during exercise. It is therefore somewhat surprising that digitalis, which affects cardiac ac ...
... The output of the heart per minute under ordinary conditions of life is a constantly changing value. It changes with position, with temperature, and it changes tremendously with increased oxygen consumption during exercise. It is therefore somewhat surprising that digitalis, which affects cardiac ac ...
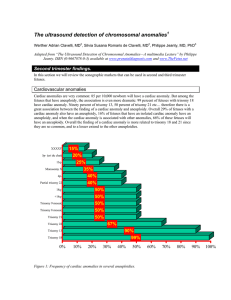
The ultrasound detection of chromosomal anomalies
... Doug Brown was the first to bring to the attention of the ultrasound community, the association between echogenic foci and trisomy 214. Subsequent papers have demonstrated that about 5% of midtrimester pregnancies have an echogenic foci in the heart. Different authors have reported association betwe ...
... Doug Brown was the first to bring to the attention of the ultrasound community, the association between echogenic foci and trisomy 214. Subsequent papers have demonstrated that about 5% of midtrimester pregnancies have an echogenic foci in the heart. Different authors have reported association betwe ...
PPT - The Citadel
... Obesity — People with a body mass index (BMI) of 30.0 or higher are more likely to develop high blood pressure. Eating too much salt — A high sodium intake increases blood pressure in some people. Drinking too much alcohol — Heavy and regular use of alcohol can increase blood pressure dramatically. ...
... Obesity — People with a body mass index (BMI) of 30.0 or higher are more likely to develop high blood pressure. Eating too much salt — A high sodium intake increases blood pressure in some people. Drinking too much alcohol — Heavy and regular use of alcohol can increase blood pressure dramatically. ...
Accuracy of Chest Radiography plus Electrocardiogram in
... Hypertrophy diagnosis compared to echocardiogram. This one, however, is not available in primary health care centers to all hypertensive population. Objective: To evaluate whether the association chest radiography-electrocardiogram provides the accuracy to justify its use in left ventricular hypertr ...
... Hypertrophy diagnosis compared to echocardiogram. This one, however, is not available in primary health care centers to all hypertensive population. Objective: To evaluate whether the association chest radiography-electrocardiogram provides the accuracy to justify its use in left ventricular hypertr ...
“Double Density” of left atrial enlargement When the LA enlarges, it
... Even though we are on the right side of the heart, we can see left atrial enlargement. Normally the left atrium sits right in the middle of the heart posteriorly and does not form a normal border on the frontal film. ...
... Even though we are on the right side of the heart, we can see left atrial enlargement. Normally the left atrium sits right in the middle of the heart posteriorly and does not form a normal border on the frontal film. ...
Ruptured Aneurysm of the Right Sinus of Valsalva Into the Right
... ASVs are classified as congenital or acquired. Congenital ASVs are caused by separation or failed fusion of the aortic media with the fibrosus annulus of the aortic valve. Acquired ASVs can develop as the result of injury1, endocarditis2, syphilis3, Behcet's disease4 and Marfan syndrome. Isolated AS ...
... ASVs are classified as congenital or acquired. Congenital ASVs are caused by separation or failed fusion of the aortic media with the fibrosus annulus of the aortic valve. Acquired ASVs can develop as the result of injury1, endocarditis2, syphilis3, Behcet's disease4 and Marfan syndrome. Isolated AS ...
Combined Heart and Liver Transplantation
... hypercholesterolemia and coronary artery disease with her unfortunate death after 10 weeks [5]. There was another setback due to the demise of 2 patients at the time of admission with complications of familial hypercholesterolemia and coronary artery disease in one and biliary hypoplasia and cardiom ...
... hypercholesterolemia and coronary artery disease with her unfortunate death after 10 weeks [5]. There was another setback due to the demise of 2 patients at the time of admission with complications of familial hypercholesterolemia and coronary artery disease in one and biliary hypoplasia and cardiom ...
Myocardial infarction

Myocardial infarction (MI) or acute myocardial infarction (AMI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow stops to a part of the heart causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Often it is in the center or left side of the chest and lasts for more than a few minutes. The discomfort may occasionally feel like heartburn. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, nausea, feeling faint, a cold sweat, or feeling tired. About 30% of people have atypical symptoms, with women more likely than men to present atypically. Among those over 75 years old, about 5% have had an MI with little or no history of symptoms. An MI may cause heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, or cardiac arrest.Most MIs occur due to coronary artery disease. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, lack of exercise, obesity, high blood cholesterol, poor diet, and excessive alcohol intake, among others. The mechanism of an MI often involves the rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque, leading to complete blockage of a coronary artery. MIs are less commonly caused by coronary artery spasms, which may be due to cocaine, significant emotional stress, and extreme cold, among others. A number of tests are useful to help with diagnosis, including electrocardiograms (ECGs), blood tests, and coronary angiography. An ECG may confirm an ST elevation MI if ST elevation is present. Commonly used blood tests include troponin and less often creatine kinase MB.Aspirin is an appropriate immediate treatment for a suspected MI. Nitroglycerin or opioids may be used to help with chest pain; however, they do not improve overall outcomes. Supplemental oxygen should be used in those with low oxygen levels or shortness of breath. In ST elevation MIs treatments which attempt to restore blood flow to the heart are typically recommended and include angioplasty, where the arteries are pushed open, or thrombolysis, where the blockage is removed using medications. People who have a non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) are often managed with the blood thinner heparin, with the additional use angioplasty in those at high risk. In people with blockages of multiple coronary arteries and diabetes, bypass surgery (CABG) may be recommended rather than angioplasty. After an MI, lifestyle modifications, along with long term treatment with aspirin, beta blockers, and statins, are typically recommended.Worldwide, more than 3 million people have ST elevation MIs and 4 million have NSTEMIs each year. STEMIs occur about twice as often in men as women. About one million people have an MI each year in the United States. In the developed world the risk of death in those who have had an STEMI is about 10%. Rates of MI for a given age have decreased globally between 1990 and 2010.