IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS)
... via normal vaginal delivery, baby cried immediately after birth, APGAR at 1 min and 5 minutes was 9 and 10 respectively. At 2 n half hours of life, on examination child’s capillary refilling time was prolonged and child was started on ionotropes. ECHO was done, which showed Rhabdomyoma arising from ...
... via normal vaginal delivery, baby cried immediately after birth, APGAR at 1 min and 5 minutes was 9 and 10 respectively. At 2 n half hours of life, on examination child’s capillary refilling time was prolonged and child was started on ionotropes. ECHO was done, which showed Rhabdomyoma arising from ...
the circulatory system - Science with Mr. Enns
... The circulatory system (also called the cardiovascular system) consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The job of the circulatory system is to carry needed materials to cells and carries waste products away from cells. The Heart The heart is a hollow, muscular organ that pumps blood through ...
... The circulatory system (also called the cardiovascular system) consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The job of the circulatory system is to carry needed materials to cells and carries waste products away from cells. The Heart The heart is a hollow, muscular organ that pumps blood through ...
Heart
... concentration of CO2 is much higher in cells, so CO2 readily diffuses out of cells into the blood. 7% is dissolved in the plasma. 23% is carried by hemoglobin 70% reacts with water to become carbonic acid (H2CO3), which helps maintain blood pH. ...
... concentration of CO2 is much higher in cells, so CO2 readily diffuses out of cells into the blood. 7% is dissolved in the plasma. 23% is carried by hemoglobin 70% reacts with water to become carbonic acid (H2CO3), which helps maintain blood pH. ...
Slide 1 - AccessMedicine
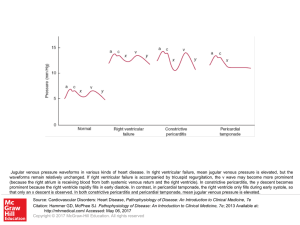
... Jugular venous pressure waveforms in various kinds of heart disease. In right ventricular failure, mean jugular venous pressure is elevated, but the waveforms remain relatively unchanged. If right ventricular failure is accompanied by tricuspid regurgitation, the v wave may become more prominent (be ...
... Jugular venous pressure waveforms in various kinds of heart disease. In right ventricular failure, mean jugular venous pressure is elevated, but the waveforms remain relatively unchanged. If right ventricular failure is accompanied by tricuspid regurgitation, the v wave may become more prominent (be ...
Circulatory System
... concentration of CO2 is much higher in cells, so CO2 readily diffuses out of cells into the blood. 7% is dissolved in the plasma. 23% is carried by hemoglobin 70% reacts with water to become carbonic acid (H2CO3), which helps maintain blood pH. ...
... concentration of CO2 is much higher in cells, so CO2 readily diffuses out of cells into the blood. 7% is dissolved in the plasma. 23% is carried by hemoglobin 70% reacts with water to become carbonic acid (H2CO3), which helps maintain blood pH. ...
Control of the Cardiac Cycle
... of_the_heart.html http://www.bbc.co.uk/learningzone/clips/the-human-heart/12225.html ...
... of_the_heart.html http://www.bbc.co.uk/learningzone/clips/the-human-heart/12225.html ...
The Transport System
... pumped to the lungs to get more oxygen. • So we say that the heart is spilt into two sections, the left and the right. ...
... pumped to the lungs to get more oxygen. • So we say that the heart is spilt into two sections, the left and the right. ...
Device treats patients with mitral valve disease who
... Aided by state-of-the-art cardiac imaging, the MitraClip is delivered via catheter to the patient’s heart and mitral valve through the femoral vein. Once positioned and implanted, the tiny clothespin-like device works by permanently clipping together a portion of the leaflets of the valve. The backf ...
... Aided by state-of-the-art cardiac imaging, the MitraClip is delivered via catheter to the patient’s heart and mitral valve through the femoral vein. Once positioned and implanted, the tiny clothespin-like device works by permanently clipping together a portion of the leaflets of the valve. The backf ...
File
... 6e) Atrial systole (atria contracting) & ventricular diastole (ventricles relaxing) Atrial systole causes the remainder of the blood to go through the AV valve to the ventricle. This is due to the fact that atrial pressure exceeds ventricle pressure, so the AV valves are pushed open and blood then ...
... 6e) Atrial systole (atria contracting) & ventricular diastole (ventricles relaxing) Atrial systole causes the remainder of the blood to go through the AV valve to the ventricle. This is due to the fact that atrial pressure exceeds ventricle pressure, so the AV valves are pushed open and blood then ...
ECG Interpretation
... The AV node delays electrical conduction so that the atria and ventricles don’t contract at the same time, and blood flows effectively from the atria to the ventricles. The delay in the AV node forms much of the PR segment on the ECG. Part of atrial repolarization can also be represented by PR segme ...
... The AV node delays electrical conduction so that the atria and ventricles don’t contract at the same time, and blood flows effectively from the atria to the ventricles. The delay in the AV node forms much of the PR segment on the ECG. Part of atrial repolarization can also be represented by PR segme ...
Lung Sternum (Breastbone) Notch Xiphoid Process (Tip of the
... Q. Clear an Airway for an Infant. ...
... Q. Clear an Airway for an Infant. ...
Unit 2
... a simple investigation based on a student developed question and write instructions others can follow to carry out the procedure. ...
... a simple investigation based on a student developed question and write instructions others can follow to carry out the procedure. ...
Top 10 Things To Know - Professional Heart Daily
... c. expansion of Class I indication to New York Heart Association (NYHA) class II (and with LBBB with QRS duration greater than or equal to 150 ms), and d. the addition of a Class IIb (may be useful) recommendation for patients who have left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) less than or equal to ...
... c. expansion of Class I indication to New York Heart Association (NYHA) class II (and with LBBB with QRS duration greater than or equal to 150 ms), and d. the addition of a Class IIb (may be useful) recommendation for patients who have left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) less than or equal to ...
ventricles.
... The cusps of the A/V valves are secured to the myocardium via papillary muscles and Chordae tendineae. In the right ventricle is the septomarginal trabecula (moderator band) which secures a large papillary muscle to the interventricular septum. The right ventricle has a smooth cone-shaped upper ...
... The cusps of the A/V valves are secured to the myocardium via papillary muscles and Chordae tendineae. In the right ventricle is the septomarginal trabecula (moderator band) which secures a large papillary muscle to the interventricular septum. The right ventricle has a smooth cone-shaped upper ...
circulatory system notes
... Condition in which fatty deposits called plaque accumulate on the inner walls of arteries 3. hypertension high blood pressure caused by hardening of arteries, stress, heredity, poor diet, cigarette smoking, aging forces heart to work harder and can result in damage to heart and vessels 4. co ...
... Condition in which fatty deposits called plaque accumulate on the inner walls of arteries 3. hypertension high blood pressure caused by hardening of arteries, stress, heredity, poor diet, cigarette smoking, aging forces heart to work harder and can result in damage to heart and vessels 4. co ...
Understanding Target Heart Rate.jpg
... ~? To truly understand target heart rate you must be aware of some important values that are necessary to obtain an appropriate target heart rate range. Heart rate is the number of times your heart beats per minute. The average resting heart rate for an adult is between 60 to 80 beats per minute, bu ...
... ~? To truly understand target heart rate you must be aware of some important values that are necessary to obtain an appropriate target heart rate range. Heart rate is the number of times your heart beats per minute. The average resting heart rate for an adult is between 60 to 80 beats per minute, bu ...
Biology 251 Fall 2015 1 TOPIC 14: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
... atrioventricular node (AV node) at base of right atrium near the septum, just above atria-ventricles junction. AP/min: 40-60. In normal conditions helps spread AP to ventricles from right atrium. ...
... atrioventricular node (AV node) at base of right atrium near the septum, just above atria-ventricles junction. AP/min: 40-60. In normal conditions helps spread AP to ventricles from right atrium. ...
Myocardial infarction

Myocardial infarction (MI) or acute myocardial infarction (AMI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow stops to a part of the heart causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Often it is in the center or left side of the chest and lasts for more than a few minutes. The discomfort may occasionally feel like heartburn. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, nausea, feeling faint, a cold sweat, or feeling tired. About 30% of people have atypical symptoms, with women more likely than men to present atypically. Among those over 75 years old, about 5% have had an MI with little or no history of symptoms. An MI may cause heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, or cardiac arrest.Most MIs occur due to coronary artery disease. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, lack of exercise, obesity, high blood cholesterol, poor diet, and excessive alcohol intake, among others. The mechanism of an MI often involves the rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque, leading to complete blockage of a coronary artery. MIs are less commonly caused by coronary artery spasms, which may be due to cocaine, significant emotional stress, and extreme cold, among others. A number of tests are useful to help with diagnosis, including electrocardiograms (ECGs), blood tests, and coronary angiography. An ECG may confirm an ST elevation MI if ST elevation is present. Commonly used blood tests include troponin and less often creatine kinase MB.Aspirin is an appropriate immediate treatment for a suspected MI. Nitroglycerin or opioids may be used to help with chest pain; however, they do not improve overall outcomes. Supplemental oxygen should be used in those with low oxygen levels or shortness of breath. In ST elevation MIs treatments which attempt to restore blood flow to the heart are typically recommended and include angioplasty, where the arteries are pushed open, or thrombolysis, where the blockage is removed using medications. People who have a non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) are often managed with the blood thinner heparin, with the additional use angioplasty in those at high risk. In people with blockages of multiple coronary arteries and diabetes, bypass surgery (CABG) may be recommended rather than angioplasty. After an MI, lifestyle modifications, along with long term treatment with aspirin, beta blockers, and statins, are typically recommended.Worldwide, more than 3 million people have ST elevation MIs and 4 million have NSTEMIs each year. STEMIs occur about twice as often in men as women. About one million people have an MI each year in the United States. In the developed world the risk of death in those who have had an STEMI is about 10%. Rates of MI for a given age have decreased globally between 1990 and 2010.