Ventricular Septal Defect
... left ventricle will become greater than the pulmonary artery and closes the ductus arterosis The absent flow of blood through the umbilicus gradually closes the ductus venosus over 12 hr to 2 weeks ...
... left ventricle will become greater than the pulmonary artery and closes the ductus arterosis The absent flow of blood through the umbilicus gradually closes the ductus venosus over 12 hr to 2 weeks ...
Atrial Fibrillation in Dogs
... So, what is atrial fibrillation in dogs? Atrial fibrillation is a malfunction of the heart's electrical system. Instead of the electrical impulse originating from the SA node, the impulse originates from many different areas of the right atrium in an unorganized manner. This causes the atrial tissue ...
... So, what is atrial fibrillation in dogs? Atrial fibrillation is a malfunction of the heart's electrical system. Instead of the electrical impulse originating from the SA node, the impulse originates from many different areas of the right atrium in an unorganized manner. This causes the atrial tissue ...
Soft Foam Cross-section Human Heart Model
... • Allow students to hold the model. Ask them what observations they can make about the model and have them discuss what they already know about their heart. • Copy and enlarge the model on page 2 as a quiz or review. • Have students sit in a circle and start passing the two halves of the model in op ...
... • Allow students to hold the model. Ask them what observations they can make about the model and have them discuss what they already know about their heart. • Copy and enlarge the model on page 2 as a quiz or review. • Have students sit in a circle and start passing the two halves of the model in op ...
Patent ductus arteriosus - British Heart Foundation
... Before a baby is born the arterial duct allows blood to go around their lungs. After the baby is born and the lungs fill with air, the arterial duct is no longer needed - it usually closes by itself within the first week after birth. Sometimes the duct fails to close by itself and remains open (pate ...
... Before a baby is born the arterial duct allows blood to go around their lungs. After the baby is born and the lungs fill with air, the arterial duct is no longer needed - it usually closes by itself within the first week after birth. Sometimes the duct fails to close by itself and remains open (pate ...
Indications for Hemodynamic Monitoring
... hemodynamic monitoring is the early detection, identification, and treatment of life-threatening conditions such as heart failure and cardiac tamponade. By using invasive hemodynamic monitoring the nurse is able to evaluate the patient's immediate response to treatment such as drugs and mechanical s ...
... hemodynamic monitoring is the early detection, identification, and treatment of life-threatening conditions such as heart failure and cardiac tamponade. By using invasive hemodynamic monitoring the nurse is able to evaluate the patient's immediate response to treatment such as drugs and mechanical s ...
Slide 1
... hemodynamic monitoring is the early detection, identification, and treatment of life-threatening conditions such as heart failure and cardiac tamponade. By using invasive hemodynamic monitoring the nurse is able to evaluate the patient's immediate response to treatment such as drugs and mechanical s ...
... hemodynamic monitoring is the early detection, identification, and treatment of life-threatening conditions such as heart failure and cardiac tamponade. By using invasive hemodynamic monitoring the nurse is able to evaluate the patient's immediate response to treatment such as drugs and mechanical s ...
HERAT PHYSIOLOGY & CONDUTION SYSTEM
... ventricular action potential T wave - represents ventricular repolarization and is longer in duration than depolarization Q-T interval - represents the time of both ventricular depolarization and repolarization ...
... ventricular action potential T wave - represents ventricular repolarization and is longer in duration than depolarization Q-T interval - represents the time of both ventricular depolarization and repolarization ...
4th year biolgy test - leavingcertbiology.net
... c. Large lumen, thin wall, and valves d. Small lumen, thin wall, and no valves 33. Systole and diastole: a. Both involve relaxation of the cardiac tissue b. Involve contraction and relaxation, respectively c. Involve relaxation and contraction, respectively d. Both involve contraction of the cardiac ...
... c. Large lumen, thin wall, and valves d. Small lumen, thin wall, and no valves 33. Systole and diastole: a. Both involve relaxation of the cardiac tissue b. Involve contraction and relaxation, respectively c. Involve relaxation and contraction, respectively d. Both involve contraction of the cardiac ...
Cardiovascular System Review
... • What are the structural differences between the right and left ventricle? • The left ventricle has a thicker wall and is round, while the right ventricle has a thin wall and is pouch shaped ...
... • What are the structural differences between the right and left ventricle? • The left ventricle has a thicker wall and is round, while the right ventricle has a thin wall and is pouch shaped ...
ALTERATIONS OF CARDIAC FUNCTION
... Why is the child at greater risk of CHF? Why does the child’s heart beat faster? What are the Hct, Hgb and pulse ox concentrations appropriate for age needed for adequate oxygen transport What does cyanosis indicate? hypoxemia What is polycythemia? What labs indicate Polycythemia: What i ...
... Why is the child at greater risk of CHF? Why does the child’s heart beat faster? What are the Hct, Hgb and pulse ox concentrations appropriate for age needed for adequate oxygen transport What does cyanosis indicate? hypoxemia What is polycythemia? What labs indicate Polycythemia: What i ...
Body in Action
... State how muscle fatigue can be produced and what causes it. During continuous exercise the person will eventually have to stop due to muscle fatigue. Causing discomfort and pain. This results from a lack of oxygen to the muscle cells and the build up of a chemical called lactic acid. ...
... State how muscle fatigue can be produced and what causes it. During continuous exercise the person will eventually have to stop due to muscle fatigue. Causing discomfort and pain. This results from a lack of oxygen to the muscle cells and the build up of a chemical called lactic acid. ...
Exercise Training Benefits on the
... NUMBER and ACTIVITY LEVEL of mitochondria allows our body to actually use all the extra oxygen that we can extract due to increased capillarization. 5. Aerobic training stimulates ERYTHROPOIESIS – the formation of new red blood cells. This is a huge benefit because RBC’s contain HEMOGLOBIN, the mole ...
... NUMBER and ACTIVITY LEVEL of mitochondria allows our body to actually use all the extra oxygen that we can extract due to increased capillarization. 5. Aerobic training stimulates ERYTHROPOIESIS – the formation of new red blood cells. This is a huge benefit because RBC’s contain HEMOGLOBIN, the mole ...
ysrhythmia-Cheatsheet
... Next wave form will be on time for underlying rhythm. Wide, large QRS with no P wave ...
... Next wave form will be on time for underlying rhythm. Wide, large QRS with no P wave ...
chapter 3 - Bison Academy
... off blood flow – thereby acting as minute flow controllers. It is thought that terminal arterioles alternately open and close over time. Of course, during maximum metabolic demands the terminal arterioles can all open delivering maximum flow through the capillary network. A current hypothesis is tha ...
... off blood flow – thereby acting as minute flow controllers. It is thought that terminal arterioles alternately open and close over time. Of course, during maximum metabolic demands the terminal arterioles can all open delivering maximum flow through the capillary network. A current hypothesis is tha ...
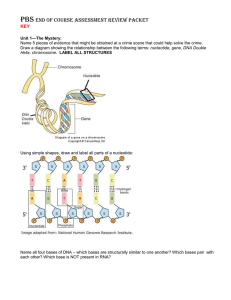
PBS End of Course Assessment Review Packet
... be different lengths. Differences are known as polymorphisms. Name and explain 3 procedures that could help treat a blockage in the heart. Angioplasty: thread a thin tube through the arm/groin to the heart with a balloon on the end; when in place the balloon is inflated to push the plaque out agains ...
... be different lengths. Differences are known as polymorphisms. Name and explain 3 procedures that could help treat a blockage in the heart. Angioplasty: thread a thin tube through the arm/groin to the heart with a balloon on the end; when in place the balloon is inflated to push the plaque out agains ...
The circulatory system
... the largest artery in the body. The aorta splits into many branches and takes blood to every body cell. The cells take food and oxygen out of the blood and put carbon dioxide and other waste into it. Then the whole process begins again. ...
... the largest artery in the body. The aorta splits into many branches and takes blood to every body cell. The cells take food and oxygen out of the blood and put carbon dioxide and other waste into it. Then the whole process begins again. ...
Circulatory systems
... Laminar blood flow is silent (pulse present). Occluded blood flow is silent (no pulse). Turbulent flow is noisy. ...
... Laminar blood flow is silent (pulse present). Occluded blood flow is silent (no pulse). Turbulent flow is noisy. ...
ASD Case for Reno Mrs. Young
... Mrs. Young is a 35 year old woman admitted to the hospital to determine the cause of her complaint of vague chest pains in stressful situations. Studies carried out at another hospital two years ago had included a chest x-ray which revealed right ventricular enlargement. A moderate systolic murmur ...
... Mrs. Young is a 35 year old woman admitted to the hospital to determine the cause of her complaint of vague chest pains in stressful situations. Studies carried out at another hospital two years ago had included a chest x-ray which revealed right ventricular enlargement. A moderate systolic murmur ...
Cardiac Electrophysiology
... A Case of Dizziness A 68 year old female arrives at the emergency room in an ambulance. That evening she had been feeling “weak and dizzy” after ingesting a handful of her “heart pills” and later passed out. Her heart rate was irregular but near 33 beats per minute. Her patient records and talks wit ...
... A Case of Dizziness A 68 year old female arrives at the emergency room in an ambulance. That evening she had been feeling “weak and dizzy” after ingesting a handful of her “heart pills” and later passed out. Her heart rate was irregular but near 33 beats per minute. Her patient records and talks wit ...
Myocardial infarction

Myocardial infarction (MI) or acute myocardial infarction (AMI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow stops to a part of the heart causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Often it is in the center or left side of the chest and lasts for more than a few minutes. The discomfort may occasionally feel like heartburn. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, nausea, feeling faint, a cold sweat, or feeling tired. About 30% of people have atypical symptoms, with women more likely than men to present atypically. Among those over 75 years old, about 5% have had an MI with little or no history of symptoms. An MI may cause heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, or cardiac arrest.Most MIs occur due to coronary artery disease. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, lack of exercise, obesity, high blood cholesterol, poor diet, and excessive alcohol intake, among others. The mechanism of an MI often involves the rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque, leading to complete blockage of a coronary artery. MIs are less commonly caused by coronary artery spasms, which may be due to cocaine, significant emotional stress, and extreme cold, among others. A number of tests are useful to help with diagnosis, including electrocardiograms (ECGs), blood tests, and coronary angiography. An ECG may confirm an ST elevation MI if ST elevation is present. Commonly used blood tests include troponin and less often creatine kinase MB.Aspirin is an appropriate immediate treatment for a suspected MI. Nitroglycerin or opioids may be used to help with chest pain; however, they do not improve overall outcomes. Supplemental oxygen should be used in those with low oxygen levels or shortness of breath. In ST elevation MIs treatments which attempt to restore blood flow to the heart are typically recommended and include angioplasty, where the arteries are pushed open, or thrombolysis, where the blockage is removed using medications. People who have a non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) are often managed with the blood thinner heparin, with the additional use angioplasty in those at high risk. In people with blockages of multiple coronary arteries and diabetes, bypass surgery (CABG) may be recommended rather than angioplasty. After an MI, lifestyle modifications, along with long term treatment with aspirin, beta blockers, and statins, are typically recommended.Worldwide, more than 3 million people have ST elevation MIs and 4 million have NSTEMIs each year. STEMIs occur about twice as often in men as women. About one million people have an MI each year in the United States. In the developed world the risk of death in those who have had an STEMI is about 10%. Rates of MI for a given age have decreased globally between 1990 and 2010.