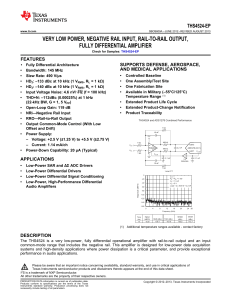
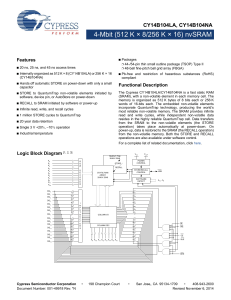
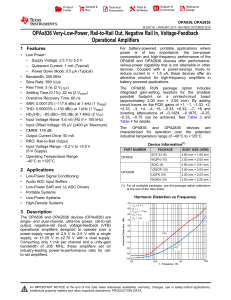
VERY LOW POWER, NEGATIVE RAIL INPUT, RAIL-TO-RAIL OUTPUT, FULLY DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER THS4521 THS4522
... range that includes the negative rail. These amplifiers are designed for low-power data acquisition systems and high-density applications where power dissipation is a critical parameter, and provide exceptional performance in audio applications. The family includes single (THS4521), (THS4522), and q ...
... range that includes the negative rail. These amplifiers are designed for low-power data acquisition systems and high-density applications where power dissipation is a critical parameter, and provide exceptional performance in audio applications. The family includes single (THS4521), (THS4522), and q ...
MT-060 TUTORIAL Choosing Between Voltage Feedback (VFB)
... The output offset voltage due to the input bias currents can be nulled by making the effective source resistance equal in both the inverting and non-inverting inputs. This scheme will not work with bias-current compensated VFB op amps which have additional current generators on their inputs. In this ...
... The output offset voltage due to the input bias currents can be nulled by making the effective source resistance equal in both the inverting and non-inverting inputs. This scheme will not work with bias-current compensated VFB op amps which have additional current generators on their inputs. In this ...
2-GBPS Differential Repeater EVM
... Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, modifications, enhancements, improvements, and other changes to its products and services at any time and to discontinue any product or service without notice. Customers should obtain the latest relevant ...
... Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, modifications, enhancements, improvements, and other changes to its products and services at any time and to discontinue any product or service without notice. Customers should obtain the latest relevant ...
MAX9100/MAX9101 +1.0V Micropower SOT23 Comparators General Description ____________________________Features
... optimized for single-cell systems, and are fully specified for operation from a single supply of 1.0V to 5.5V. This ultra-low voltage operation, 5µA quiescent current consumption, and small footprint make the MAX9100/MAX9101 ideal for use in battery-powered systems. A wide-input common-mode range th ...
... optimized for single-cell systems, and are fully specified for operation from a single supply of 1.0V to 5.5V. This ultra-low voltage operation, 5µA quiescent current consumption, and small footprint make the MAX9100/MAX9101 ideal for use in battery-powered systems. A wide-input common-mode range th ...
BR34E02FVT-3
... and acknowledge is always required after each byte. I C BUS data communication with several devices is possible by connecting with 2 communication lines: serial data (SDA) and serial clock (SCL). Among the devices, there should be a “master” that generates clock and control communication start and e ...
... and acknowledge is always required after each byte. I C BUS data communication with several devices is possible by connecting with 2 communication lines: serial data (SDA) and serial clock (SCL). Among the devices, there should be a “master” that generates clock and control communication start and e ...
Reset circuit - STMicroelectronics
... Negative-going VCC transients The STM1001 is relatively immune to negative-going VCC transients (glitches). Figure 10 on page 10 shows typical transient duration versus reset comparator overdrive (for which the STM1001 will NOT generate a reset pulse). The graph was generated using a negative pulse ...
... Negative-going VCC transients The STM1001 is relatively immune to negative-going VCC transients (glitches). Figure 10 on page 10 shows typical transient duration versus reset comparator overdrive (for which the STM1001 will NOT generate a reset pulse). The graph was generated using a negative pulse ...
SDIO101A 1. General description SD/SDIO/MMC/CE-ATA host controller
... transmissions on the SD/SDIO/MMC/CE-ATA port. The SDIO101A offers separate pins for SD/SDIO/MMC/CE-ATA port supply voltage, host interface supply voltage and core supply voltage. The SD/SDIO/MMC/CE-ATA port can operate at a wide voltage range (1.8 V to 3.6 V) which allows the device to interface to ...
... transmissions on the SD/SDIO/MMC/CE-ATA port. The SDIO101A offers separate pins for SD/SDIO/MMC/CE-ATA port supply voltage, host interface supply voltage and core supply voltage. The SD/SDIO/MMC/CE-ATA port can operate at a wide voltage range (1.8 V to 3.6 V) which allows the device to interface to ...
THS1031 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... For more design flexibility, the internal reference can be bypassed to use an external reference to suit the dc accuracy and temperature drift requirements of the application. The out-of-range output indicates any out-of-range condition in THS1031’s input signal. The format of digital output can be ...
... For more design flexibility, the internal reference can be bypassed to use an external reference to suit the dc accuracy and temperature drift requirements of the application. The out-of-range output indicates any out-of-range condition in THS1031’s input signal. The format of digital output can be ...
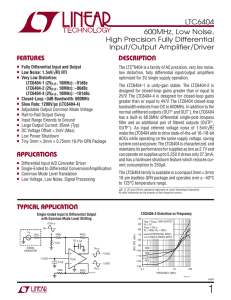
LTC6404 - 600MHz, Low Noise, High Precision Fully Differential
... designed for closed-loop gains greater than or equal to 2V/V. The LTC6404-4 is designed for closed-loop gains greater than or equal to 4V/V. The LTC6404 closed-loop bandwidth extends from DC to 600MHz. In addition to the normal unfiltered outputs (OUT+ and OUT–), the LTC6404 has a built-in 88.5MHz di ...
... designed for closed-loop gains greater than or equal to 2V/V. The LTC6404-4 is designed for closed-loop gains greater than or equal to 4V/V. The LTC6404 closed-loop bandwidth extends from DC to 600MHz. In addition to the normal unfiltered outputs (OUT+ and OUT–), the LTC6404 has a built-in 88.5MHz di ...
P R O B L E M S
... (b) If an input difference signal is applied that is large enough to steer the current entirely to one side of the pair, what is the change in voltage at each collector (from the condition for which v = 0)? (c) If the available power supply V is 5 V, what value of IR should you choose in order to al ...
... (b) If an input difference signal is applied that is large enough to steer the current entirely to one side of the pair, what is the change in voltage at each collector (from the condition for which v = 0)? (c) If the available power supply V is 5 V, what value of IR should you choose in order to al ...
CD4027BC Dual J-K Master/Slave Flip
... 16-Lead Plastic Dual-In-Line Package (PDIP), JEDEC MS-001, 0.300" Wide Package Number N16E ...
... 16-Lead Plastic Dual-In-Line Package (PDIP), JEDEC MS-001, 0.300" Wide Package Number N16E ...
Real-Time Computing Without Stable States
... particular feature, the multiple recurrent loops that form an immensely complicated network using as many as 80% of all the synapses within a functional neocortical column, has presented an intractable problem both for computational models inspired by current artificial computing machinery (Savage, ...
... particular feature, the multiple recurrent loops that form an immensely complicated network using as many as 80% of all the synapses within a functional neocortical column, has presented an intractable problem both for computational models inspired by current artificial computing machinery (Savage, ...
OPAx836 Very-Low-Power, Rail-to-Rail Out, Negative
... dual-channel, ultralow power, rail-to-rail output, negative-rail input, voltage-feedback operational amplifiers designed to operate over a power-supply range of 2.5 V to 5.5 V (single supply), or ±1.25 V to ±2.75 V (dual supply). Consuming only 1 mA per channel and a unity gain bandwidth of 205 MHz, ...
... dual-channel, ultralow power, rail-to-rail output, negative-rail input, voltage-feedback operational amplifiers designed to operate over a power-supply range of 2.5 V to 5.5 V (single supply), or ±1.25 V to ±2.75 V (dual supply). Consuming only 1 mA per channel and a unity gain bandwidth of 205 MHz, ...
Kinetis KL26: 48MHz Cortex-M0+ 32-128KB Flash 32-64pin
... 1. PTB0, PTB1, PTD6, and PTD7 I/O have both high drive and normal drive capability selected by the associated PTx_PCRn[DSE] control bit. All other GPIOs are normal drive only. 2. The reset pin only contains an active pull down device when configured as the RESET signal or as a GPIO. When configured ...
... 1. PTB0, PTB1, PTD6, and PTD7 I/O have both high drive and normal drive capability selected by the associated PTx_PCRn[DSE] control bit. All other GPIOs are normal drive only. 2. The reset pin only contains an active pull down device when configured as the RESET signal or as a GPIO. When configured ...
Transistor–transistor logic (TTL)
... 2-input NAND Gate This CMOS gate example contains 3 N-channel MOSFET’s, one for each input FET1 and FET2 and one for the output FET3. When both the inputs A and B are at logic level “0”, FET1 and FET2 are both switched “OFF” giving an output logic “1” from the source of FET3. When one or both of the ...
... 2-input NAND Gate This CMOS gate example contains 3 N-channel MOSFET’s, one for each input FET1 and FET2 and one for the output FET3. When both the inputs A and B are at logic level “0”, FET1 and FET2 are both switched “OFF” giving an output logic “1” from the source of FET3. When one or both of the ...
Flip-flop (electronics)
In electronics, a flip-flop or latch is a circuit that has two stable states and can be used to store state information. A flip-flop is a bistable multivibrator. The circuit can be made to change state by signals applied to one or more control inputs and will have one or two outputs. It is the basic storage element in sequential logic. Flip-flops and latches are a fundamental building block of digital electronics systems used in computers, communications, and many other types of systems.Flip-flops and latches are used as data storage elements. A flip-flop stores a single bit (binary digit) of data; one of its two states represents a ""one"" and the other represents a ""zero"". Such data storage can be used for storage of state, and such a circuit is described as sequential logic. When used in a finite-state machine, the output and next state depend not only on its current input, but also on its current state (and hence, previous inputs). It can also be used for counting of pulses, and for synchronizing variably-timed input signals to some reference timing signal.Flip-flops can be either simple (transparent or opaque) or clocked (synchronous or edge-triggered). Although the term flip-flop has historically referred generically to both simple and clocked circuits, in modern usage it is common to reserve the term flip-flop exclusively for discussing clocked circuits; the simple ones are commonly called latches.Using this terminology, a latch is level-sensitive, whereas a flip-flop is edge-sensitive. That is, when a latch is enabled it becomes transparent, while a flip flop's output only changes on a single type (positive going or negative going) of clock edge.