Discussion Acknowledgments References Report Background and
... that occur during the encoding of negative stimuli. Such processes could include amygdaloid modulation of lower-level perceptual areas. Amygdaloid modulation of higher-level regions (e.g., hippocampal formation, prefrontal cortices) may also lead to better memory for negative stimuli, even in instan ...
... that occur during the encoding of negative stimuli. Such processes could include amygdaloid modulation of lower-level perceptual areas. Amygdaloid modulation of higher-level regions (e.g., hippocampal formation, prefrontal cortices) may also lead to better memory for negative stimuli, even in instan ...
Chapters 6-7 - Foundations of Human Social
... • Two-neuron networks • Negative feedback: a divisive gain control • Positive feedback: a short term memory circuit • Mutual Inhibition: a winner-take-all network ...
... • Two-neuron networks • Negative feedback: a divisive gain control • Positive feedback: a short term memory circuit • Mutual Inhibition: a winner-take-all network ...
Classical Conditioning
... • Saliva experiments on dogs • Dogs started responding prior to the meat powder • Sounds of preparation ...
... • Saliva experiments on dogs • Dogs started responding prior to the meat powder • Sounds of preparation ...
Pavlov`s Dilemma and Discovery: Classical Conditioning
... voluntarily to a stimulus that previously had no effect—or Discriminate between generalization and a very different effect—on them. The stimulus comes to discrimination. elicit, or bring forth, the response automatically. After several painful visits to the dentist, Classical conditioning was discov ...
... voluntarily to a stimulus that previously had no effect—or Discriminate between generalization and a very different effect—on them. The stimulus comes to discrimination. elicit, or bring forth, the response automatically. After several painful visits to the dentist, Classical conditioning was discov ...
vikram_slides1
... Periodicity is constant and not considered same weighing window are applied across the stimulus ...
... Periodicity is constant and not considered same weighing window are applied across the stimulus ...
Classical Conditioning PPT
... Learning: some kind of change in behavior or knowledge that is long-lasting due to an increase in one’s experience Experience is key to the learning process. Humans learn best through association - our minds naturally connect events that occur in sequence Called Associative Learning ...
... Learning: some kind of change in behavior or knowledge that is long-lasting due to an increase in one’s experience Experience is key to the learning process. Humans learn best through association - our minds naturally connect events that occur in sequence Called Associative Learning ...
sensory1
... For touch discrimination, small receptive fields allow greater accuracy in “two point discrimination” test (upcoming lab!) ...
... For touch discrimination, small receptive fields allow greater accuracy in “two point discrimination” test (upcoming lab!) ...
Difficulty (part of the hypothesis)
... We would like to know how FEF and IPS play functionally distinct roles. ...
... We would like to know how FEF and IPS play functionally distinct roles. ...
poster - Stanford University
... neuromodulation by acetylcholine is a potential mechanism for evoking synchrony during bottom-up stimulus selection. ...
... neuromodulation by acetylcholine is a potential mechanism for evoking synchrony during bottom-up stimulus selection. ...
PSY105 Neural Networks 2/5
... Hebb Rule governs changes in weights [+ other additional assumptions which are always needed when you try and make a computational recipe] • Mechanism: At least one response neuron, one unconditioned stimulus neuron and one neuron for each conditioned stimulus ...
... Hebb Rule governs changes in weights [+ other additional assumptions which are always needed when you try and make a computational recipe] • Mechanism: At least one response neuron, one unconditioned stimulus neuron and one neuron for each conditioned stimulus ...
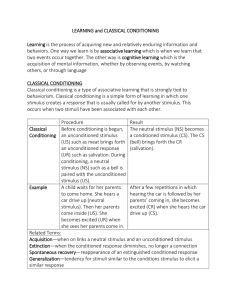
LEARNING and Classical Conditioning
... Learning is the process of acquiring new and relatively enduring information and behaviors. One way we learn is by associative learning which is when we learn that two events occur together. The other way is cognitive learning which is the acquisition of mental information, whether by observing even ...
... Learning is the process of acquiring new and relatively enduring information and behaviors. One way we learn is by associative learning which is when we learn that two events occur together. The other way is cognitive learning which is the acquisition of mental information, whether by observing even ...
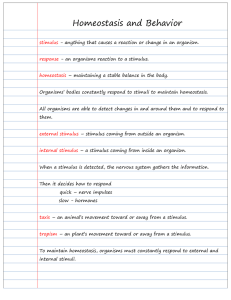
Homeostasis and Behavior
... quick – nerve impulses slow - hormones taxis – an animal’s movement toward or away from a stimulus. tropism – an plant’s movement toward or away from a stimulus. To maintain homeostasis, organisms must constantly respond to external and internal stimuli. ...
... quick – nerve impulses slow - hormones taxis – an animal’s movement toward or away from a stimulus. tropism – an plant’s movement toward or away from a stimulus. To maintain homeostasis, organisms must constantly respond to external and internal stimuli. ...
Chapter 8
... 6. For a particular person on a particular task, there is a(n) _______________ relation between response time and accuracy. 7. Stimulus onset asynchrony refers to the _______________ between the presentation of two stimuli. 8. Early in the history of psychology, _______________ was used as a systema ...
... 6. For a particular person on a particular task, there is a(n) _______________ relation between response time and accuracy. 7. Stimulus onset asynchrony refers to the _______________ between the presentation of two stimuli. 8. Early in the history of psychology, _______________ was used as a systema ...
The role of the nervous system in detecting and
... The role of the nervous system in detecting and responding to stimuli Detecting and responding in animals A complex animal may need to respond immediately to a stimulus. In many situations, it is important that a change is detected instantly and appropriate signals sent quickly to relevant parts of ...
... The role of the nervous system in detecting and responding to stimuli Detecting and responding in animals A complex animal may need to respond immediately to a stimulus. In many situations, it is important that a change is detected instantly and appropriate signals sent quickly to relevant parts of ...
Negative priming
Negative priming is an implicit memory effect in which prior exposure to a stimulus unfavorably influences the response to the same stimulus. It falls under the category of priming, which refers to the change in the response towards a stimulus due to a subconscious memory effect. Negative priming describes the slow and error-prone reaction to a stimulus that is previously ignored. For example, a subject may be imagined trying to pick a red pen from a pen holder. The red pen becomes the target of attention, so the subject responds by moving their hand towards it. At this time, they mentally block out all other pens as distractors to aid in closing in on just the red pen. After repeatedly picking the red pen over the others, switching to the blue pen results in a momentary delay picking the pen out (however, there is a decline in the negative priming effect when there is more than one nontarget item that is selected against). The slow reaction due to the change of the distractor stimulus to target stimulus is called the negative priming effect.Negative priming is believed to play a crucial role in attention and memory retrieval processes. When stimuli are perceived through the senses, all the stimuli are encoded within the brain, where each stimulus has its own internal representation. In this perceiving process, some of the stimuli receive more attention than others. Similarly, only some of them are stored in short-term memory. Negative priming is highly related to the selective nature of attention and memory.Broadly, negative priming is also known as the mechanism by which inhibitory control is applied to cognition. This refers only to the inhibition stimuli that can interfere with the current short-term goal of creating a response. The effectiveness of inhibiting the interferences depends on the cognitive control mechanism as a higher number of distractors yields higher load on working memory. Increased load on working memory can in turn result in slower perceptual processing leading to delayed reaction. Therefore, negative priming effect depends on the amount of distractors, effectiveness of the cognitive control mechanism and the availability of the cognitive control resources.