Intro to Social Psychology
... What we perceive ourselves to be Self Schemas – cognitive structures that allow people to differentiate themselves from others Social Comparison – we compare ourselves to others to form a view of ourselves Personality Identity – composed of an individual's thoughts and emotions (self-knowledge and e ...
... What we perceive ourselves to be Self Schemas – cognitive structures that allow people to differentiate themselves from others Social Comparison – we compare ourselves to others to form a view of ourselves Personality Identity – composed of an individual's thoughts and emotions (self-knowledge and e ...
XIV.Social Psychology (8–10%) This part of the course focuses on
... XIV.Social Psychology (8–10%) This part of the course focuses on how individuals relate to one another in social situations. Social psychologists study social attitudes, social influence, and other social phenomena. AP students in psychology should be able to do the following: ...
... XIV.Social Psychology (8–10%) This part of the course focuses on how individuals relate to one another in social situations. Social psychologists study social attitudes, social influence, and other social phenomena. AP students in psychology should be able to do the following: ...
Advanced Placement Psychology Learning Objectives
... Psychology Learning Objectives Topic: Social Psychology This part of the course focuses on how individuals relate to one another in social situations. Social psychologists study social attitudes, social influence, and other social phenonema. AP students in psychology should be able to do the followi ...
... Psychology Learning Objectives Topic: Social Psychology This part of the course focuses on how individuals relate to one another in social situations. Social psychologists study social attitudes, social influence, and other social phenonema. AP students in psychology should be able to do the followi ...
These are the AP Unit goals for social psychology
... cognitive dissonance (Festinger and Carlsmith) ...
... cognitive dissonance (Festinger and Carlsmith) ...
Understanding ourselves
... What factors influence the ways that we (and, by extension, others) behave in various situations? ...
... What factors influence the ways that we (and, by extension, others) behave in various situations? ...
What is Social Psychology?
... psychology The influence that people have upon the beliefs and behavior of others. ...
... psychology The influence that people have upon the beliefs and behavior of others. ...
Chapter 4
... line with expectations and existing knowledge. Perceptual set A temporary mental predisposition to perceive one thing and not another, or to perceive stimuli in a certain way. Perceptual defence bias Refers to the automatic discounting of disconfi rming stimuli and is used to protect the individual ...
... line with expectations and existing knowledge. Perceptual set A temporary mental predisposition to perceive one thing and not another, or to perceive stimuli in a certain way. Perceptual defence bias Refers to the automatic discounting of disconfi rming stimuli and is used to protect the individual ...
Psychology semester review The scientific study of behavior and
... Which view of aggression that people choose to act aggressively because they believe that aggression justified and necessary? In what kind of memory do people remember general knowledge? What psychological perspective focuses on the role thoughts in determining behavior? Psychologists who support th ...
... Which view of aggression that people choose to act aggressively because they believe that aggression justified and necessary? In what kind of memory do people remember general knowledge? What psychological perspective focuses on the role thoughts in determining behavior? Psychologists who support th ...
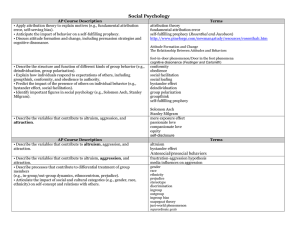
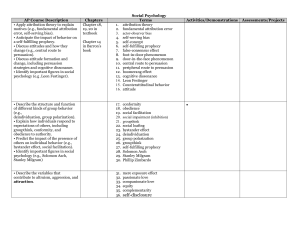
Unit 14. Social Psychology (8–10%) Apply attribution theory to
... Unit 14. Social Psychology (8–10%) 1. Apply attribution theory to explain motives (e.g., fundamental attribution error, self-serving bias). ...
... Unit 14. Social Psychology (8–10%) 1. Apply attribution theory to explain motives (e.g., fundamental attribution error, self-serving bias). ...
Ch. 3
... Deindividuation: Loss of personal sense of responsibility in a group Risky Shift: Increased willingness of individual to take risks when making decisions as a group as opposed to making decisions as individuals. Group Polarization: Shift of the group toward a more extreme position following grou ...
... Deindividuation: Loss of personal sense of responsibility in a group Risky Shift: Increased willingness of individual to take risks when making decisions as a group as opposed to making decisions as individuals. Group Polarization: Shift of the group toward a more extreme position following grou ...
Self – serving bias
... of others to internal causes Actor – observer bias – in making attributions, the tendency to attribute the behaviors of others to internal causes while attributing one’s own behaviors to external causes (situations and circumstances) Self – serving bias - the tendency to attribute success to interna ...
... of others to internal causes Actor – observer bias – in making attributions, the tendency to attribute the behaviors of others to internal causes while attributing one’s own behaviors to external causes (situations and circumstances) Self – serving bias - the tendency to attribute success to interna ...
Social Psychology – Practice Test 1. Bart complied with his friends
... 9. Using the Asch procedure, conformity to group judgments would be least likely when: A) participants announce their own answers only after the other group members have done so. B) participants are not observed by other group members when giving their answers. C) it is very difficult for anyone to ...
... 9. Using the Asch procedure, conformity to group judgments would be least likely when: A) participants announce their own answers only after the other group members have done so. B) participants are not observed by other group members when giving their answers. C) it is very difficult for anyone to ...
Social Psychology
... ◦ Forewarning Effect: Knowing that someone is attempting to persuade you may weaken the effect ◦ Ex: informing the audience that they are going to hear a persuasive speech on a particular topic may weaken the effect and attitudes of the audience ◦ Inoculation Effect: Beginning with a weak argument a ...
... ◦ Forewarning Effect: Knowing that someone is attempting to persuade you may weaken the effect ◦ Ex: informing the audience that they are going to hear a persuasive speech on a particular topic may weaken the effect and attitudes of the audience ◦ Inoculation Effect: Beginning with a weak argument a ...
2017 HRQ 14 4 Due April 10
... 4. At a conscious level, Aaron doesn't think he's prejudiced. Yet he automatically feels uncomfortable ...
... 4. At a conscious level, Aaron doesn't think he's prejudiced. Yet he automatically feels uncomfortable ...
History and Approaches
... Social Psychology Terms attribution theory fundamental attribution error actor-observer bias self-serving bias self-concept self-fulfilling prophecy false-consensus effect foot-in-door phenomenon door-in-the-face phen0menon central route to persuasion peripheral route to persuasion boomerang effect ...
... Social Psychology Terms attribution theory fundamental attribution error actor-observer bias self-serving bias self-concept self-fulfilling prophecy false-consensus effect foot-in-door phenomenon door-in-the-face phen0menon central route to persuasion peripheral route to persuasion boomerang effect ...
Social Cognition
... Social Cognition • The way we attend to, store, remember, and use information about other people and the world around us • First impressions ...
... Social Cognition • The way we attend to, store, remember, and use information about other people and the world around us • First impressions ...