Chapter 18: Social Behavior
... 1. Social roles are the expected behavior patterns associated with particular social positions (student, daughter, worker, etc) 2. Fundamental Attribution Error is the tendency to attribute the behavior of others to internal causes (personality, likes, etc) 3. A Secure attachment base is when someon ...
... 1. Social roles are the expected behavior patterns associated with particular social positions (student, daughter, worker, etc) 2. Fundamental Attribution Error is the tendency to attribute the behavior of others to internal causes (personality, likes, etc) 3. A Secure attachment base is when someon ...
Psychology 101: Introduction to Psychology
... B) The presence of others increases the likelihood that someone will choose to help. C) In ambiguous situations, people are less likely to offer help than in clear-cut ...
... B) The presence of others increases the likelihood that someone will choose to help. C) In ambiguous situations, people are less likely to offer help than in clear-cut ...
Fundamentals of Management 4e.
... Perception • Organizing & interpreting sensory input • Gives meaning to one’s environment • Judgment ...
... Perception • Organizing & interpreting sensory input • Gives meaning to one’s environment • Judgment ...
Social Psychology
... other groups but recognize how greatly we differ from others in our group Other-race effect: tendency to recall faces of one’s own race more accurately than faces of other races ...
... other groups but recognize how greatly we differ from others in our group Other-race effect: tendency to recall faces of one’s own race more accurately than faces of other races ...
Chapter 5: Managerial Ethics & Corporate Social Responsibility
... attending to some parts more than others) » External Factors (i.e., in physical envir.) – Similarity – Size – Nearness – Motion » Internal Factors – Experience – Motivation ...
... attending to some parts more than others) » External Factors (i.e., in physical envir.) – Similarity – Size – Nearness – Motion » Internal Factors – Experience – Motivation ...
Behavioral
... • The scientific study of the ways in which the thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of one individual are influenced by the real, imagined, or inferred behavior or characteristics of other people ...
... • The scientific study of the ways in which the thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of one individual are influenced by the real, imagined, or inferred behavior or characteristics of other people ...
Chapter 18: Social Behavior
... -public distance 12 feet or more -lectures Social perception Attribution: process of making inferences about the causes of one’s own behavior and that of others Attribution Theory -consistency (behavior changes little across occasions) -distinctiveness (behavior occurs only in specific circumstances ...
... -public distance 12 feet or more -lectures Social perception Attribution: process of making inferences about the causes of one’s own behavior and that of others Attribution Theory -consistency (behavior changes little across occasions) -distinctiveness (behavior occurs only in specific circumstances ...
Autism
... Autism occurs in children with all levels of intelligence (gifted to mental retardation) 72% have some type of limited cognitive ...
... Autism occurs in children with all levels of intelligence (gifted to mental retardation) 72% have some type of limited cognitive ...
Thinking/Influences Unit Guide
... o Social dilemmas – situations in which selfish behavior that benefits individuals in the short run may spell disaster for an entire group in the long run “The prisoner’s dilemma”: 2 people separated immediately after arrested for a serious crime – DA believes they are guilty but lacks evidence – ...
... o Social dilemmas – situations in which selfish behavior that benefits individuals in the short run may spell disaster for an entire group in the long run “The prisoner’s dilemma”: 2 people separated immediately after arrested for a serious crime – DA believes they are guilty but lacks evidence – ...
Unit 7: Study Guide Social Psychology
... Students also learn the basic concepts of social cognition. One of these is attribution, the ways in which individuals form judgments about other individuals’ behavior and about their own. Attributions of behavior are a blend of situational and dispositional factors. The influence of stereotypes on ...
... Students also learn the basic concepts of social cognition. One of these is attribution, the ways in which individuals form judgments about other individuals’ behavior and about their own. Attributions of behavior are a blend of situational and dispositional factors. The influence of stereotypes on ...
Chapter 15 Lecture Outline Interpersonal Attraction (important
... Common mistakes or biases that we tend to make when we engage in the process of making attributions: 1. Actor-Observer Bias (there are two sides to this, depending on whether you=re making an attribution about yourself, or someone else). - We have a tendency to see other people's behavior as influen ...
... Common mistakes or biases that we tend to make when we engage in the process of making attributions: 1. Actor-Observer Bias (there are two sides to this, depending on whether you=re making an attribution about yourself, or someone else). - We have a tendency to see other people's behavior as influen ...
Social Perception
... “Well, no, I can’t tell Harriet!...First thing she’s gonna ask me is what I was doin’ checkin’ out a decoy!” ...
... “Well, no, I can’t tell Harriet!...First thing she’s gonna ask me is what I was doin’ checkin’ out a decoy!” ...
Social Psychology
... social comparison- compare ourselves to others to determine if our view of reality is correct ...
... social comparison- compare ourselves to others to determine if our view of reality is correct ...
Introduction to Psychology - Parkway C-2
... Heider (1958) suggested that we have a tendency to say others’ behavior is caused by internal and external attributions. ...
... Heider (1958) suggested that we have a tendency to say others’ behavior is caused by internal and external attributions. ...
Chapter 18 Social Psychology
... • Fundamental attribution error: the tendency as an observer to overestimate dispositional influences (internal causes) and underestimate situational influences (external causes) upon others’ behavior • Just world hypothesis: the assumption that the world is just and that people get what they deserv ...
... • Fundamental attribution error: the tendency as an observer to overestimate dispositional influences (internal causes) and underestimate situational influences (external causes) upon others’ behavior • Just world hypothesis: the assumption that the world is just and that people get what they deserv ...
Chapter 3
... organize perceptions is the script. A script is a guide to action. Scripts consist of sequences of activities that are expected of us and others in particular situations. They are based on our experiences and observations of interaction in various contexts. Many of our daily activities are governed ...
... organize perceptions is the script. A script is a guide to action. Scripts consist of sequences of activities that are expected of us and others in particular situations. They are based on our experiences and observations of interaction in various contexts. Many of our daily activities are governed ...
Unit 3, Key Area 4: What you should know
... a behaviour pattern when it is no longer reinforced. 16. Most people belong to one or more social __________________ of different types and size. 17. In general, individuals are found to perform familiar tasks better in _______________________ situations then on their own. This process is called soc ...
... a behaviour pattern when it is no longer reinforced. 16. Most people belong to one or more social __________________ of different types and size. 17. In general, individuals are found to perform familiar tasks better in _______________________ situations then on their own. This process is called soc ...
Ch. 13,14 組織行為( Organizational Behavior)
... factors and to overestimate the influence of internal or personal factors. e.g. 銷售經理易將部屬業績的滑落,歸咎於他不努力 ...
... factors and to overestimate the influence of internal or personal factors. e.g. 銷售經理易將部屬業績的滑落,歸咎於他不努力 ...
Social Psychology
... – We have the need to belong (Maslow) for feelings of identity, solidarity and safety – Those who are outside our group are threatening – We reserve greatest hatred for those most like us (Yankees ...
... – We have the need to belong (Maslow) for feelings of identity, solidarity and safety – Those who are outside our group are threatening – We reserve greatest hatred for those most like us (Yankees ...
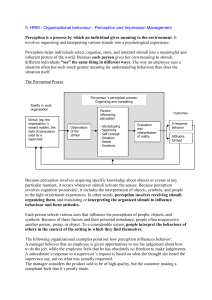
Perception and impression management
... involves cognition /poznávání/, it includes the interpretation of objects, symbols, and people in the light of pertinent experiences. In other words, perception involves receiving stimuli, organizing them, and translating or interpreting the organized stimuli to influence behaviour and form attitude ...
... involves cognition /poznávání/, it includes the interpretation of objects, symbols, and people in the light of pertinent experiences. In other words, perception involves receiving stimuli, organizing them, and translating or interpreting the organized stimuli to influence behaviour and form attitude ...
Ch14 Social Psychology
... • effects of social variables & cognitions – individual behavior & social interactions • social cognition• social influence- ...
... • effects of social variables & cognitions – individual behavior & social interactions • social cognition• social influence- ...
SOCIAL INTERACTION
... 2. Roles – refer to expected behavior, obligations, and privileges. - people learn how to play their roles by observing and interacting with other people who are more experienced than themselves. This is known as SOCIALIZATION. ...
... 2. Roles – refer to expected behavior, obligations, and privileges. - people learn how to play their roles by observing and interacting with other people who are more experienced than themselves. This is known as SOCIALIZATION. ...
Chapter 14 Notes
... • Group Cohesiveness: Degree of attraction among group members or their commitment to remain in the group • In Group: • Out Group: • What kinds of groups work the best together? •Status: Level of social power and importance •Norm: Accepted but usually unspoken standard for appropriate behavior ...
... • Group Cohesiveness: Degree of attraction among group members or their commitment to remain in the group • In Group: • Out Group: • What kinds of groups work the best together? •Status: Level of social power and importance •Norm: Accepted but usually unspoken standard for appropriate behavior ...
Interacting with patients:
... – dissonance exists when related cognitions contradict each other. • Conformity and obedience • Group influences on behaviour – polarization – groupthink ...
... – dissonance exists when related cognitions contradict each other. • Conformity and obedience • Group influences on behaviour – polarization – groupthink ...