Frog Dissection Guide
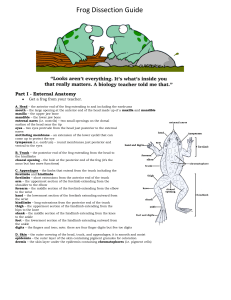
... Look for the opening to the frog’s cloaca, located between the hind legs. Use forceps to lift the skin and use scissors to cut along the center of the body from the cloaca to the lip. Turn back the skin, cut toward the side at each leg, and pin the skin flat. The diagram above shows how to make thes ...
... Look for the opening to the frog’s cloaca, located between the hind legs. Use forceps to lift the skin and use scissors to cut along the center of the body from the cloaca to the lip. Turn back the skin, cut toward the side at each leg, and pin the skin flat. The diagram above shows how to make thes ...
Ophiacodontidae - Dr. Stuart Sumida
... and Varanosaurus specimens, the interparietal is divided in two by a longitudinal fissure ...
... and Varanosaurus specimens, the interparietal is divided in two by a longitudinal fissure ...
CD_files/15. Set Posterior Teeth Ling & Monopl
... • Can be unstable if condylar guidance is steep (posterior teeth separate, leaving only the anteriors in contact) ...
... • Can be unstable if condylar guidance is steep (posterior teeth separate, leaving only the anteriors in contact) ...
Charlier, Cindy_Simple_tooth_STYLED
... The skull can be divided into the fused bones of the calvarium, the upper jaw, and the lower jaw. The cranial portion of the calvarium consists of the paired frontal bones, which articulate cranially with the nasal bones and maxillae, and caudally with the parietal bones. The nasal cavity contains a ...
... The skull can be divided into the fused bones of the calvarium, the upper jaw, and the lower jaw. The cranial portion of the calvarium consists of the paired frontal bones, which articulate cranially with the nasal bones and maxillae, and caudally with the parietal bones. The nasal cavity contains a ...
Factors of Mandibular Movements related to occlusal Morphology
... sizes or eruption patterns, the teeth occlude in a way that maxillary buccal cusps contact in the central fossa of mandibular teeth. This is referred to as cross-bite. ...
... sizes or eruption patterns, the teeth occlude in a way that maxillary buccal cusps contact in the central fossa of mandibular teeth. This is referred to as cross-bite. ...
Common diseases and conditions of pet rabbits
... True diarrhoea is a serious problem requiring urgent veterinary attention as the rabbit will be very ill. Young rabbits around the weaning period are much more prone to diarrhoea than adults. Diarrhoea can be caused by bacterial or viral infections, or toxins produced by Clostridial bacteria in the ...
... True diarrhoea is a serious problem requiring urgent veterinary attention as the rabbit will be very ill. Young rabbits around the weaning period are much more prone to diarrhoea than adults. Diarrhoea can be caused by bacterial or viral infections, or toxins produced by Clostridial bacteria in the ...
pdf file - Duke People
... and the pharynx. The dentition of mammals is heterodontic, which means that the teeth do not all look alike as they do in fish, reptiles and most other vertebrates. Instead, mammals have incisors, canines, premolars and molars in both the upper and the lower jaw. These tooth types are structurally di ...
... and the pharynx. The dentition of mammals is heterodontic, which means that the teeth do not all look alike as they do in fish, reptiles and most other vertebrates. Instead, mammals have incisors, canines, premolars and molars in both the upper and the lower jaw. These tooth types are structurally di ...
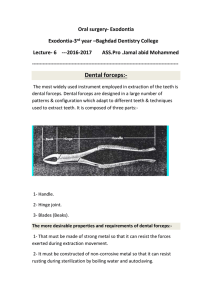
2-The upper premolar forceps
... junction of the crown and root & to adapt to the root surface and not to the crown. Also beaks designed for single rooted, two rooted, and three rooted teeth so that the tips of the blades will adapt closely to various root formation decreasing the chance for the root fracture. Other variation is th ...
... junction of the crown and root & to adapt to the root surface and not to the crown. Also beaks designed for single rooted, two rooted, and three rooted teeth so that the tips of the blades will adapt closely to various root formation decreasing the chance for the root fracture. Other variation is th ...
Projection of central ray.
... Occlusal Radiography: used to examine large areas of maxilla or mandible on one film size 4( intraoral film) ,the film is named because the patient occlude or bites on the entire film . Uses of Occlusal Radiography: 1-To locate retained roots of extracted teeth. 2- To locate supernumerary,unerupted ...
... Occlusal Radiography: used to examine large areas of maxilla or mandible on one film size 4( intraoral film) ,the film is named because the patient occlude or bites on the entire film . Uses of Occlusal Radiography: 1-To locate retained roots of extracted teeth. 2- To locate supernumerary,unerupted ...
General assessment for Oral Surgery
... • To present a comprehensive description of the basic oral surgery procedures that the general practitioner performs in his/her practice. • To provide information on advanced and complex surgical management of patients provided by specialists in oral and maxillofacial surgery. ...
... • To present a comprehensive description of the basic oral surgery procedures that the general practitioner performs in his/her practice. • To provide information on advanced and complex surgical management of patients provided by specialists in oral and maxillofacial surgery. ...
3/7/17 Digestive System
... A. Mouth 5. Teeth -____ two _____ sets _____during form ____________ development deciduous ______ teeth _____ form and -________ primary (__________) ______ erupt through the _____, gums or _______, gingiva between the ______ ages of __ 6 ________ months and __ 4 ______ years ...
... A. Mouth 5. Teeth -____ two _____ sets _____during form ____________ development deciduous ______ teeth _____ form and -________ primary (__________) ______ erupt through the _____, gums or _______, gingiva between the ______ ages of __ 6 ________ months and __ 4 ______ years ...
Biology 3B Laboratory The Chordates Objectives • Learn and
... The subphylum Vertebrata represents only one of the three subphyla within the phylum Chordata. The other two are the Urochordata and Cephalochordata. Examination of the representative specimens of each of these subphyla available in the laboratory will provide a better understanding of the phylogene ...
... The subphylum Vertebrata represents only one of the three subphyla within the phylum Chordata. The other two are the Urochordata and Cephalochordata. Examination of the representative specimens of each of these subphyla available in the laboratory will provide a better understanding of the phylogene ...
15a – Histo of Nose, Teeth, Throat I – McWho
... o Basal stem cells – divide and give rise to two other types o Base of each bud rests on basal lamina and is entered by afferent sensory axons that form synapses on the gustatory cells o Microvilli project through and opening called taste pore o Molecules (tastants) dissolved in saliva contact micro ...
... o Basal stem cells – divide and give rise to two other types o Base of each bud rests on basal lamina and is entered by afferent sensory axons that form synapses on the gustatory cells o Microvilli project through and opening called taste pore o Molecules (tastants) dissolved in saliva contact micro ...
Parts
... Tongue. isthmus of fauces * contents: teeth, tongue. * palate: hard palate soft palate palatine velum palatoglossal arch palatopharyngeal arch palatine tonsil * isthmus of fauces: uvula free margin of palatine velum palatoglossal arch root of tongue. ...
... Tongue. isthmus of fauces * contents: teeth, tongue. * palate: hard palate soft palate palatine velum palatoglossal arch palatopharyngeal arch palatine tonsil * isthmus of fauces: uvula free margin of palatine velum palatoglossal arch root of tongue. ...
ORAL CAVITY - University of Kansas Medical Center
... Superior salivatory nucleus via CN VII. To: ...
... Superior salivatory nucleus via CN VII. To: ...
Mouth and Tongue
... Lymphatics from the medial part of the lower lip extend to submental nodes. II. ...
... Lymphatics from the medial part of the lower lip extend to submental nodes. II. ...
GENERAL SPLANCHNOLOGY
... An organ is a part of the human body and it serves as an instrument for adaptation of the organism to the environment. The organ has a definite, inherent only by it, shape, structure, function, development, and, position in the human body. The vital activity of an organ occurs under the direct effec ...
... An organ is a part of the human body and it serves as an instrument for adaptation of the organism to the environment. The organ has a definite, inherent only by it, shape, structure, function, development, and, position in the human body. The vital activity of an organ occurs under the direct effec ...
Diversity in Nutrition
... Ruminant herbivores such as cows have no incisors or canine teeth in the upper jaw. Instead they have a dental pad against which the bottom incisors and underdeveloped canines cut through blades of long grass. The dental pad helps tear off the long grass. The space between the incisors and molars is ...
... Ruminant herbivores such as cows have no incisors or canine teeth in the upper jaw. Instead they have a dental pad against which the bottom incisors and underdeveloped canines cut through blades of long grass. The dental pad helps tear off the long grass. The space between the incisors and molars is ...
KEY TERMS
... A malocclusion with the proper molar relationship and teeth that are crowded together, spaced apart, an overbite, an openbite, a posterior crossbite or an anterior crossbite ...
... A malocclusion with the proper molar relationship and teeth that are crowded together, spaced apart, an overbite, an openbite, a posterior crossbite or an anterior crossbite ...
VERTEBRATE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
... tongue that serves as a sensing organ. The oral cavity contains mucus secreting cells, and in some snakes & lizards, complex oral glands secrete venoms and digestive enzymes. Salivary glands are usually absent. The stomach tends to be tubular. The hindgut of most herbivores is longer and it includes ...
... tongue that serves as a sensing organ. The oral cavity contains mucus secreting cells, and in some snakes & lizards, complex oral glands secrete venoms and digestive enzymes. Salivary glands are usually absent. The stomach tends to be tubular. The hindgut of most herbivores is longer and it includes ...
What`s on the Menu?
... The upper and lower parts of a shark’s jaw are hinged in a way that makes it difficult for the lower part to move separately from the upper part, so they don’t chew their food the way people do. Sharks catch and hold prey in their strong jaws and use their sharp teeth to tear it into pieces small en ...
... The upper and lower parts of a shark’s jaw are hinged in a way that makes it difficult for the lower part to move separately from the upper part, so they don’t chew their food the way people do. Sharks catch and hold prey in their strong jaws and use their sharp teeth to tear it into pieces small en ...
Frog Dissection - Carbonado Historical School District
... mouth . Insert probe into opening and pushobserve where it comes out. • Two large Muscular Pads are in the roof of the mouth(eyes retract here when it blinks) • Locate Tongue.What unusual features do you notice? ...
... mouth . Insert probe into opening and pushobserve where it comes out. • Two large Muscular Pads are in the roof of the mouth(eyes retract here when it blinks) • Locate Tongue.What unusual features do you notice? ...
ORAL CAVITY The oral cavity (O.C) and its accessory organs
... The entrance of the oral cavity-(rima oris) is bounded by the edges of the upper and lower lips to unite on each side at the angle of the mouth. The lips of the domestic mammals exist for sucking, prehension of food and also acts as a tactile organ (sense organ). They differ in shape and motility fr ...
... The entrance of the oral cavity-(rima oris) is bounded by the edges of the upper and lower lips to unite on each side at the angle of the mouth. The lips of the domestic mammals exist for sucking, prehension of food and also acts as a tactile organ (sense organ). They differ in shape and motility fr ...
Oral Cavity
... branches of the maxillary nerve [V2]. • The lower parts, including the teeth and oral part of the tongue, are innervated by branches of the ...
... branches of the maxillary nerve [V2]. • The lower parts, including the teeth and oral part of the tongue, are innervated by branches of the ...
Equine masticatory organ Part III
... Department of Histology and Embryology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Agriculture University of Wrocław, Kożuchowska 5, 51-631 Wrocław, Poland The masticatory system, which is also referred to as the stomatognathic system, consists of the temporomandibular joints, dentoalveolar apparatus, dentoden ...
... Department of Histology and Embryology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Agriculture University of Wrocław, Kożuchowska 5, 51-631 Wrocław, Poland The masticatory system, which is also referred to as the stomatognathic system, consists of the temporomandibular joints, dentoalveolar apparatus, dentoden ...
Tooth

A tooth (plural teeth) is a small, calcified, whitish structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores, also use teeth for hunting or for defensive purposes. The roots of teeth are covered by gums. Teeth are not made of bone, but rather of multiple tissues of varying density and hardness. The cellular tissues that ultimately become teeth originate from the embryonic germ layer, the ectoderm.The general structure of teeth is similar across the vertebrates, although there is considerable variation in their form and position. The teeth of mammals have deep roots, and this pattern is also found in some fish, and in crocodilians. In most teleost fish, however, the teeth are attached to the outer surface of the bone, while in lizards they are attached to the inner surface of the jaw by one side. In cartilaginous fish, such as sharks, the teeth are attached by tough ligaments to the hoops of cartilage that form the jaw.Some animals develop only one set of teeth (monophyodont) while others develop many sets (polyphyodont). Sharks, for example, grow a new set of teeth every two weeks to replace worn teeth. Rodent incisors grow and wear away continually through gnawing, which helps maintain relatively constant length. The industry of the beaver is due in part to this qualification. Many rodents such as voles (but not mice) and guinea pigs, as well as leporidae like rabbits, have continuously growing molars in addition to incisors.Teeth are not always attached to the jaw, as they are in mammals. In many reptiles and fish, teeth are attached to the palate or to the floor of the mouth, forming additional rows inside those on the jaws proper. Some teleosts even have teeth in the pharynx. While not true teeth in the usual sense, the denticles of sharks are almost identical in structure, and are likely to have the same evolutionary origin. Indeed, teeth appear to have first evolved in sharks, and are not found in the more primitive jawless fish - while lampreys do have tooth-like structures on the tongue, these are in fact, composed of keratin, not of dentine or enamel, and bear no relationship to true teeth. Though ""modern"" teeth-like structures with dentine and enamel have been found in late conodonts, they are now supposed to have evolved independently of later vertebrates' teeth. Living amphibians typically have small teeth, or none at all, since they commonly feed only on soft foods. In reptiles, teeth are generally simple and conical in shape, although there is some variation between species, most notably the venom-injecting fangs of snakes. The pattern of incisors, canines, premolars and molars is found only in mammals, and to varying extents, in their evolutionary ancestors. The numbers of these types of teeth varies greatly between species; zoologists use a standardised dental formula to describe the precise pattern in any given group.