dental anatomy and physiology
... environment. It encloses the cytoplasm. The cell membrane also allows certain materials to pass through it as they enter or leave the cell. It is through the cell membrane that all materials essential to metabolism are received. All products of metabolism are disposed of through the cell membrane. T ...
... environment. It encloses the cytoplasm. The cell membrane also allows certain materials to pass through it as they enter or leave the cell. It is through the cell membrane that all materials essential to metabolism are received. All products of metabolism are disposed of through the cell membrane. T ...
The Primitive Cynodont Procynosuchus: Functional Anatomy of the
... The upper left dentition consists of five incisors within the premaxilla, an incisiform tooth whose alveolus is formed from the premaxilla internally and the maxilla externally, two incisiform teeth within the maxilla, a canine, and ten postcanine teeth. As the distinction between an incisor and a p ...
... The upper left dentition consists of five incisors within the premaxilla, an incisiform tooth whose alveolus is formed from the premaxilla internally and the maxilla externally, two incisiform teeth within the maxilla, a canine, and ten postcanine teeth. As the distinction between an incisor and a p ...
Sharks - The Institute for Marine Mammal Studies
... Rows of teeth are produced on a “conveyer belt” which sends new teeth forward to replace the ones that have are lost. It is estimated that some sharks can loose as many as 30,000 teeth in their lifetimes. This replacement is possible because the teeth are loosely embedded in tissue over the cartilag ...
... Rows of teeth are produced on a “conveyer belt” which sends new teeth forward to replace the ones that have are lost. It is estimated that some sharks can loose as many as 30,000 teeth in their lifetimes. This replacement is possible because the teeth are loosely embedded in tissue over the cartilag ...
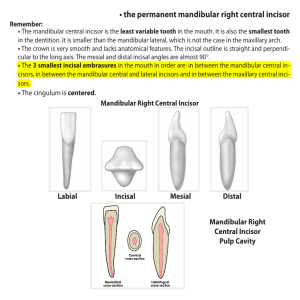
the permanent mandibular right central incisor
... • the permanent mandibular right central incisor Remember: • The mandibular central incisor is the least variable tooth in the mouth. It is also the smallest tooth in the dentition. It is smaller than the mandibular lateral, which is not the case in the maxillary arch. • The crown is very smooth and ...
... • the permanent mandibular right central incisor Remember: • The mandibular central incisor is the least variable tooth in the mouth. It is also the smallest tooth in the dentition. It is smaller than the mandibular lateral, which is not the case in the maxillary arch. • The crown is very smooth and ...
Development and growth of the mandible
... surrounding membrane bone and undergo absorption. III. The alveolar process It starts when the deciduous tooth germs reach the early bell stage. The bone of the mandible begins to grow on each side of the tooth germ. By this growth the tooth germs come to be in a trough or groove of bone, which also ...
... surrounding membrane bone and undergo absorption. III. The alveolar process It starts when the deciduous tooth germs reach the early bell stage. The bone of the mandible begins to grow on each side of the tooth germ. By this growth the tooth germs come to be in a trough or groove of bone, which also ...
LOCOREGIONAL ANESTHESIA OF THE HEAD PAIN
... Infraorbital Nerve Block Indications This block is used in procedures performed on any maxillary tooth or when major surgical procedures on the hard and soft tissues of the ipsilateral maxilla are performed. It needs to be noted that placement of the anesthetic agent outside the infraorbital foramen ...
... Infraorbital Nerve Block Indications This block is used in procedures performed on any maxillary tooth or when major surgical procedures on the hard and soft tissues of the ipsilateral maxilla are performed. It needs to be noted that placement of the anesthetic agent outside the infraorbital foramen ...
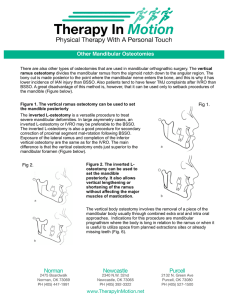
Other Mandibular Osteotomies
... Other Mandibular Osteotomies There are also other types of osteotomies that are used in mandibular orthognathic surgery. The vertical ramus osteotomy divides the mandibular ramus from the sigmoid notch down to the angular region. The bony cut is made posterior to the point where the mandibular nerve ...
... Other Mandibular Osteotomies There are also other types of osteotomies that are used in mandibular orthognathic surgery. The vertical ramus osteotomy divides the mandibular ramus from the sigmoid notch down to the angular region. The bony cut is made posterior to the point where the mandibular nerve ...
Kurzanov, S
... jaw. In principle, the same position is preserved in contemporary lizards and crocodiles, in contrast to Alioramus where the anterior and posterior branches articulate. The double wall of the labial openings of Alioramus is identified among other genera of the family. In North American types they a ...
... jaw. In principle, the same position is preserved in contemporary lizards and crocodiles, in contrast to Alioramus where the anterior and posterior branches articulate. The double wall of the labial openings of Alioramus is identified among other genera of the family. In North American types they a ...
Powerpoint, 6 MB
... fish can quickly boom and then crash when their own food supply runs out. • Yet despite their importance to the marine ecosystem, and by extension to commercial fisheries, surprisingly little is known about the life history, habits and numbers of the world’s sharks, and surprisingly few efforts have ...
... fish can quickly boom and then crash when their own food supply runs out. • Yet despite their importance to the marine ecosystem, and by extension to commercial fisheries, surprisingly little is known about the life history, habits and numbers of the world’s sharks, and surprisingly few efforts have ...
occlusion 12
... preferred sometimes and done in orthodontic treatment to some extent to induce certain movement of a certain tooth. ...
... preferred sometimes and done in orthodontic treatment to some extent to induce certain movement of a certain tooth. ...
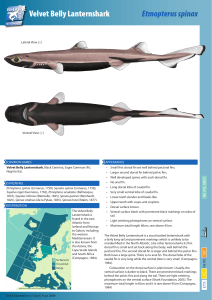
Velvet Belly Lanternshark
... The lower teeth are blade-like and unicuspidate. The upper teeth have cusps with three or fewer cusplets (Compagno, 1984). ...
... The lower teeth are blade-like and unicuspidate. The upper teeth have cusps with three or fewer cusplets (Compagno, 1984). ...
Oral embryology, histology and anatomy
... As the enamel organs grow and increase in size, the inner aspect becomes concave resembling skull caps. By the late cap stage, at 12 weeks of intrauterine life, cells on the inner aspect of the enamel organ change from cuboidal to columnar forming the inner enamel epithelium. The outer layer of cell ...
... As the enamel organs grow and increase in size, the inner aspect becomes concave resembling skull caps. By the late cap stage, at 12 weeks of intrauterine life, cells on the inner aspect of the enamel organ change from cuboidal to columnar forming the inner enamel epithelium. The outer layer of cell ...
The mandible osteology
... MANDIBLE The mandible or lower jaw is the largest and strongest bone of the face. it articulates with the skull at the temporo- mandibular joint. Horse shoe shaped body which lodges the teeth . A pair of rami which projects upward from the posterior ends . The body of the mandible meets the ramus o ...
... MANDIBLE The mandible or lower jaw is the largest and strongest bone of the face. it articulates with the skull at the temporo- mandibular joint. Horse shoe shaped body which lodges the teeth . A pair of rami which projects upward from the posterior ends . The body of the mandible meets the ramus o ...
FROG DISSECTION External Anatomy
... 20. Once inside the frog, you will see the peritoneum, a thin membrane covering the body cavity. Cut or peel away this membrane, which protects and suspends internal organs. 21. If your frog is a mature female, the body cavity may be filled with black-colored eggs covering the transparent ovaries. R ...
... 20. Once inside the frog, you will see the peritoneum, a thin membrane covering the body cavity. Cut or peel away this membrane, which protects and suspends internal organs. 21. If your frog is a mature female, the body cavity may be filled with black-colored eggs covering the transparent ovaries. R ...
Anatomy
... The teeth are different between children and adults. Children have deciduous teeth, also known as primary dentition. There are 20 deciduous teeth (4x central incisor, 4x lateral incisor, 4x cuspid or canine, 4x first molar, 4x second molar). These erupt from 6 months (central incisor) to 32 month ...
... The teeth are different between children and adults. Children have deciduous teeth, also known as primary dentition. There are 20 deciduous teeth (4x central incisor, 4x lateral incisor, 4x cuspid or canine, 4x first molar, 4x second molar). These erupt from 6 months (central incisor) to 32 month ...
zygomatic bone
... area dev from branchial arches). Occurs during first 6-8 weeks of pregnancy. • Inheritance: sporadic; reports of familial cases. May be auto dominant, auto recessive, or multifactorial. ...
... area dev from branchial arches). Occurs during first 6-8 weeks of pregnancy. • Inheritance: sporadic; reports of familial cases. May be auto dominant, auto recessive, or multifactorial. ...
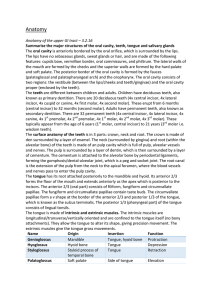
Figure 3-21. Maxillary Sinus. Figure 3
... Maxillary Sinus. The maxillary sinus (see figure 3-21) is a very prominent radiolucent structure. It sometimes appears as overlapping lobes or a single radiolucent area with a radiopaque border. The maxillary sinus is partially seen in all periapical radiographs of the bicuspid-molar area. It occupi ...
... Maxillary Sinus. The maxillary sinus (see figure 3-21) is a very prominent radiolucent structure. It sometimes appears as overlapping lobes or a single radiolucent area with a radiopaque border. The maxillary sinus is partially seen in all periapical radiographs of the bicuspid-molar area. It occupi ...
Basic Arabic for Qur`an Recitation Lesson 2
... The deepest part of the throat is the furthest away from the mouth and the closest to the chest ...
... The deepest part of the throat is the furthest away from the mouth and the closest to the chest ...
orthopedics appliances used in systemic odontology and pam
... treatment that aims at muscular relaxation.The touch of the teeth happens under the anterior AMP (PAM), stimulating the recuperation of the neuro-muscular balance of the Stomatognathic System. This apparatus is used for 60 to 90 days ( there can be an opening of the anterior bite when it is left in ...
... treatment that aims at muscular relaxation.The touch of the teeth happens under the anterior AMP (PAM), stimulating the recuperation of the neuro-muscular balance of the Stomatognathic System. This apparatus is used for 60 to 90 days ( there can be an opening of the anterior bite when it is left in ...
Soft Palate
... The Teeth Deciduous Teeth There are 20 deciduous teeth: four incisors, two canines, and four molars in each jaw. They begin to erupt about 6 months after birth and have all erupted by the end of 2 years. The teeth of the lower jaw usually appear before those of the upper jaw. Permanent Teeth There ...
... The Teeth Deciduous Teeth There are 20 deciduous teeth: four incisors, two canines, and four molars in each jaw. They begin to erupt about 6 months after birth and have all erupted by the end of 2 years. The teeth of the lower jaw usually appear before those of the upper jaw. Permanent Teeth There ...
A New Genus of Didymoconidae from the Paleocene
... Revised diagnosis: Skull is small with a posterolaterally expanded squamosal, posterior cranial platform is broadened, postorbital is small and bounded laterally by the squamosal, supratemporal fenestra is small, orbit is large, interorbital region is narrow, auditory canal is deep, anteromedial bra ...
... Revised diagnosis: Skull is small with a posterolaterally expanded squamosal, posterior cranial platform is broadened, postorbital is small and bounded laterally by the squamosal, supratemporal fenestra is small, orbit is large, interorbital region is narrow, auditory canal is deep, anteromedial bra ...
ORAL REGION ORAL CAVITY Mouth consists of ORAL VESTIBULE
... Soft palate can be elevated so that it is in contact with posterior wall of the pharynx—closes isthmus of the pharynx, so that you have to breathe through your mouth Soft palate can also be drawn inferiorly so that it is in contact with posterior part of tongue Closes isthmus of the fauces, so ...
... Soft palate can be elevated so that it is in contact with posterior wall of the pharynx—closes isthmus of the pharynx, so that you have to breathe through your mouth Soft palate can also be drawn inferiorly so that it is in contact with posterior part of tongue Closes isthmus of the fauces, so ...
Tooth

A tooth (plural teeth) is a small, calcified, whitish structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores, also use teeth for hunting or for defensive purposes. The roots of teeth are covered by gums. Teeth are not made of bone, but rather of multiple tissues of varying density and hardness. The cellular tissues that ultimately become teeth originate from the embryonic germ layer, the ectoderm.The general structure of teeth is similar across the vertebrates, although there is considerable variation in their form and position. The teeth of mammals have deep roots, and this pattern is also found in some fish, and in crocodilians. In most teleost fish, however, the teeth are attached to the outer surface of the bone, while in lizards they are attached to the inner surface of the jaw by one side. In cartilaginous fish, such as sharks, the teeth are attached by tough ligaments to the hoops of cartilage that form the jaw.Some animals develop only one set of teeth (monophyodont) while others develop many sets (polyphyodont). Sharks, for example, grow a new set of teeth every two weeks to replace worn teeth. Rodent incisors grow and wear away continually through gnawing, which helps maintain relatively constant length. The industry of the beaver is due in part to this qualification. Many rodents such as voles (but not mice) and guinea pigs, as well as leporidae like rabbits, have continuously growing molars in addition to incisors.Teeth are not always attached to the jaw, as they are in mammals. In many reptiles and fish, teeth are attached to the palate or to the floor of the mouth, forming additional rows inside those on the jaws proper. Some teleosts even have teeth in the pharynx. While not true teeth in the usual sense, the denticles of sharks are almost identical in structure, and are likely to have the same evolutionary origin. Indeed, teeth appear to have first evolved in sharks, and are not found in the more primitive jawless fish - while lampreys do have tooth-like structures on the tongue, these are in fact, composed of keratin, not of dentine or enamel, and bear no relationship to true teeth. Though ""modern"" teeth-like structures with dentine and enamel have been found in late conodonts, they are now supposed to have evolved independently of later vertebrates' teeth. Living amphibians typically have small teeth, or none at all, since they commonly feed only on soft foods. In reptiles, teeth are generally simple and conical in shape, although there is some variation between species, most notably the venom-injecting fangs of snakes. The pattern of incisors, canines, premolars and molars is found only in mammals, and to varying extents, in their evolutionary ancestors. The numbers of these types of teeth varies greatly between species; zoologists use a standardised dental formula to describe the precise pattern in any given group.