2914 preventing the spread of contagious illness
... • Keep in mind that just about all types of flu viruses, seasonal, avian, swine and others, can live outside the human body for hours and can infect anyone coming in contact with them during that span. ...
... • Keep in mind that just about all types of flu viruses, seasonal, avian, swine and others, can live outside the human body for hours and can infect anyone coming in contact with them during that span. ...
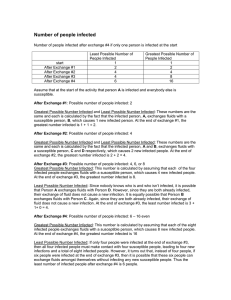
Number of people infected
... same and each is calculated by the fact that the infected person, A, exchanges fluids with a susceptible person, B, which causes 1 new infected person. At the end of exchange #1, the greatest number infected is 1 + 1 = 2. After Exchange #2: Possible number of people infected: 4 Greatest Possible Num ...
... same and each is calculated by the fact that the infected person, A, exchanges fluids with a susceptible person, B, which causes 1 new infected person. At the end of exchange #1, the greatest number infected is 1 + 1 = 2. After Exchange #2: Possible number of people infected: 4 Greatest Possible Num ...
Virus chart1
... HA and NA brought to surface of host cell and stick out, M proteins accumulate, packaged RNA is incorporated and virion buds off Disease: 1. Influenza - fever above 101˚F; myalgia, chills or malaise; cough or respiratory discharge abrupt onset, lasts for 2-4 days but some symptoms can persist for 2 ...
... HA and NA brought to surface of host cell and stick out, M proteins accumulate, packaged RNA is incorporated and virion buds off Disease: 1. Influenza - fever above 101˚F; myalgia, chills or malaise; cough or respiratory discharge abrupt onset, lasts for 2-4 days but some symptoms can persist for 2 ...
NORWALK-LIKE VIRUSES - okyanusbilgiambari.com
... symptoms. The duration of illness is usually between 24-60 hours. Excretion of the virus in stools occurs from onset for up to 1-2 weeks following infection. High levels of virus may also be discharged in vomit. The disease is generally mild and selflimiting. Hospitalisation is not generally require ...
... symptoms. The duration of illness is usually between 24-60 hours. Excretion of the virus in stools occurs from onset for up to 1-2 weeks following infection. High levels of virus may also be discharged in vomit. The disease is generally mild and selflimiting. Hospitalisation is not generally require ...
Introduction to Bacteria and Viruses
... All bacteria and viruses are microbes but not all microbes are bacteria and viruses. All germs are bacteria or viruses but not all bacteria are germs. All viruses are germs. Viruses are not considered organisms because they are not considered alive. Bacteria are unicellular microbes that do not have ...
... All bacteria and viruses are microbes but not all microbes are bacteria and viruses. All germs are bacteria or viruses but not all bacteria are germs. All viruses are germs. Viruses are not considered organisms because they are not considered alive. Bacteria are unicellular microbes that do not have ...
Follow up of Indeterminate QFT-G An indeterminate QFT
... infection in persons with symptoms or signs suggestive of TB disease The performance of QFT-G has not been determined in persons who, because of impaired immune function (e.g., HIV infection), are at increased risk for M. tuberculosis infection progressing to TB disease As with a negative TST result ...
... infection in persons with symptoms or signs suggestive of TB disease The performance of QFT-G has not been determined in persons who, because of impaired immune function (e.g., HIV infection), are at increased risk for M. tuberculosis infection progressing to TB disease As with a negative TST result ...
Potomac Horse Fever
... Research has shown that once an equid develops an infection with N. risticii, the equid can develop an immunity to that particular strain for as long as 20 months. In contrast, vaccination has been associated with a poor immune response. Research has shown that only 50 percent of the vaccines are pr ...
... Research has shown that once an equid develops an infection with N. risticii, the equid can develop an immunity to that particular strain for as long as 20 months. In contrast, vaccination has been associated with a poor immune response. Research has shown that only 50 percent of the vaccines are pr ...
deadinburgh
... conditions of our stomach, enabling the bugs to thrive. By changing the make-up of intestinal cells, Salmonella bacteria are able to cross the gut wall and infect vital organs such as the kidneys and the liver. When exposed to the highly acidic conditions of our stomach Campylobacter change their be ...
... conditions of our stomach, enabling the bugs to thrive. By changing the make-up of intestinal cells, Salmonella bacteria are able to cross the gut wall and infect vital organs such as the kidneys and the liver. When exposed to the highly acidic conditions of our stomach Campylobacter change their be ...
12. Management of the infected vascular access
... more difficult in silent catheter endoluminal contamination or low grade infection. In these cases, only specific blood and catheter clot culture will help to make the diagnosis [5]. Recently, it was shown that catheter clot culture after endoluminal brushing was more sensitive than blood culture to ...
... more difficult in silent catheter endoluminal contamination or low grade infection. In these cases, only specific blood and catheter clot culture will help to make the diagnosis [5]. Recently, it was shown that catheter clot culture after endoluminal brushing was more sensitive than blood culture to ...
NEW YORK MEDICAL COLLEGE Environmental Health and Safety
... sleeping sickness, leptospirosis, relapsing fever (Borrelia), and viral hemorrhagic fevers (including Ebola) ...
... sleeping sickness, leptospirosis, relapsing fever (Borrelia), and viral hemorrhagic fevers (including Ebola) ...
If you have a positive IGRA test
... mean that you are ill. It is believed that approximately 1/3 of the world’s population are IGRA positive without suffering from tuberculosis, meaning they have what is called latent tuberculosis infection. Is latent tuberculosis infection dangerous? A person with a latent tuberculosis infection ...
... mean that you are ill. It is believed that approximately 1/3 of the world’s population are IGRA positive without suffering from tuberculosis, meaning they have what is called latent tuberculosis infection. Is latent tuberculosis infection dangerous? A person with a latent tuberculosis infection ...
Lecture 22
... – Smallpox (Variola) virus causes two types of skin infections: variola major and variola minor. – Very high infectious nature; 10-100 virus particles needed. – Smallpox is transmitted by the respiratory route, and the virus is moved to the skin via the bloodstream. – The only host for smallpox is h ...
... – Smallpox (Variola) virus causes two types of skin infections: variola major and variola minor. – Very high infectious nature; 10-100 virus particles needed. – Smallpox is transmitted by the respiratory route, and the virus is moved to the skin via the bloodstream. – The only host for smallpox is h ...
LECTURE 1 - UCLA School of Public Health
... Laundering personal items such as towels and supporters after each use Cleaning or laundering shared athletic equipment such as pads or helmets at least once a week but ideally after each use ...
... Laundering personal items such as towels and supporters after each use Cleaning or laundering shared athletic equipment such as pads or helmets at least once a week but ideally after each use ...
Diseases of Beef Cattle
... Idaho Code requires that all intact female cattle in the state used for breeding, grazing or dairying purposes be officially vaccinated against brucellosis. ISDA requires the vaccination of all imported intact female cattle and domestic bison 4 months (120 days) and older prior to entering the state ...
... Idaho Code requires that all intact female cattle in the state used for breeding, grazing or dairying purposes be officially vaccinated against brucellosis. ISDA requires the vaccination of all imported intact female cattle and domestic bison 4 months (120 days) and older prior to entering the state ...
Why is home hygiene important? - International Scientific Forum on
... The incidence of non-food-borne infections in the UK is estimated at over 4 million cases per year, the largest proportion of which are norovirus infections, which are transmitted easily from person-to-person within community groups. Norovirus, which is mainly spread from person-to-person, is no ...
... The incidence of non-food-borne infections in the UK is estimated at over 4 million cases per year, the largest proportion of which are norovirus infections, which are transmitted easily from person-to-person within community groups. Norovirus, which is mainly spread from person-to-person, is no ...
Occupational Hazards of Health Care Personnel-I
... • is caused by a virus called the human immunodeficiency virus, or HIV. – is very fragile and will not survive very long outside of the human body – It is primarily of concern to employees providing first aid or medical care in situations involving fresh blood or other potentially infectious materia ...
... • is caused by a virus called the human immunodeficiency virus, or HIV. – is very fragile and will not survive very long outside of the human body – It is primarily of concern to employees providing first aid or medical care in situations involving fresh blood or other potentially infectious materia ...
Trichinosis

Trichinosis, trichinellosis or trichiniasis is a parasitic disease caused by roundworms of the genus Trichinella. Several subspecies cause human disease, but T. spiralis is the most known. Infection may occur without symptoms, while intestinal invasion can cause diarrhea, abdominal pain or vomiting. Larval migration into muscle tissue (one week after being infected) can cause edema of the face or around the eyes, conjunctivitis, fever, muscle pains, splinter hemorrhages, rashes, and peripheral eosinophilia. Life-threatening cases can result in myocarditis, central nervous system involvement, and pneumonitis. Larval encystment in the muscles causes pain and weakness, followed by slow progression of symptoms.Trichinosis is mainly caused by eating undercooked meat containing encysted larval Trichinella. In the stomach the larvae are exposed to stomach acid and pepsin which releases them from their cysts. They then start invading wall of the small intestine, where they develop into adult worms. Females are 2.2 mm in length; males 1.2 mm. The life span in the small intestine is about four weeks. After 1 week, the females release more larvae that migrate to voluntarily controlled muscles where they encyst. Diagnosis is usually made based on symptoms, and is confirmed by serology or by finding encysted or non-encysted larvae in biopsy or autopsy samples.The best way to prevent trichinellosis is to cook meat to safe temperatures. Using food thermometers can make sure the temperature inside the meat is high enough to kill the parasites. The meat should not be tasted until it is completely cooked. Once infection has been verified treatment with antiparasitic drugs such as albendazole or mebendazole should be started at once. A fast response may help kill adult worms and thereby stop further release of larvae. Once the larvae have established in muscle cells, usually by 3 to 4 weeks after infection, treatment may not completely get rid of the infection or symptoms. Both drugs are considered safe but have been associated with side effects such as bone marrow suppression. Patients on longer courses should be monitored though regular blood counts to detect adverse effects quickly and then discontinue treatment. Both medicines should be treated with caution during pregnancy or children under the age of 2 years, but the WHO weighs the benefits of treatment higher than the risks. In addition to antiparasitic medication, treatment with steroids is sometimes required in severe cases.Trichinosis can be acquired by eating both domestic and wild animals, but is not soil-transmitted.