pinta
... 25% of not treated are negat. in the 3rd st.., appropriate for therapy control Treponemal tests less influenced by therapy, specificity 98% Positive in newbornes of inficated mothers ? Congenital syphilis or passive transfer of maternal antibodies ...
... 25% of not treated are negat. in the 3rd st.., appropriate for therapy control Treponemal tests less influenced by therapy, specificity 98% Positive in newbornes of inficated mothers ? Congenital syphilis or passive transfer of maternal antibodies ...
Infectious Diseases
... Most Common Infectious Diseases http://science.discovery.com/top-ten/2009/infectious-diseases/infectiousdiseases.html ...
... Most Common Infectious Diseases http://science.discovery.com/top-ten/2009/infectious-diseases/infectiousdiseases.html ...
Diseases and Disease Related Organisms
... Symptoms – evidence of disease as noted by the patient Signs – objective manifestations the doctor or other health care professionals can observe. Syndrome – a characteristic group of symptoms and signs accompanying a given disease Prognosis – a prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based ...
... Symptoms – evidence of disease as noted by the patient Signs – objective manifestations the doctor or other health care professionals can observe. Syndrome – a characteristic group of symptoms and signs accompanying a given disease Prognosis – a prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based ...
Glandular Fever letter 6th class Dec 16
... affects adolescents and young adults; infection in younger children is often mild, so mild sometimes that no-one recognises the child to be ill. Incubation is usually between 4 and 8 weeks. It may last for six weeks or more with swollen glands, fever and feeling generally unwell. Sometimes there is ...
... affects adolescents and young adults; infection in younger children is often mild, so mild sometimes that no-one recognises the child to be ill. Incubation is usually between 4 and 8 weeks. It may last for six weeks or more with swollen glands, fever and feeling generally unwell. Sometimes there is ...
Chapter 7: Principle of Diseases
... TB is one of the oldest known diseases and affects one-third of the world’s population. The infection starts at a site in a lung and can move throughout the lung, possibly via host defense cells. Most people resolve the infection after the onset of the adaptive immune response. ...
... TB is one of the oldest known diseases and affects one-third of the world’s population. The infection starts at a site in a lung and can move throughout the lung, possibly via host defense cells. Most people resolve the infection after the onset of the adaptive immune response. ...
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
... Slight fever with mild cold symptoms Enlarged lymph nodes behind ears and back of neck Faint rash (macules) Symptoms last only a few days ...
... Slight fever with mild cold symptoms Enlarged lymph nodes behind ears and back of neck Faint rash (macules) Symptoms last only a few days ...
Causes, Symptoms, Prevention and Treatment of Common Ailments
... of Common Ailments of the Respiratory System Ailment ...
... of Common Ailments of the Respiratory System Ailment ...
Most Common STIs - AIDS Support Group
... mucous membranes are the source of infection and the bacteria are transmitted by direct contact, usually sexual or during passage of a newborn through the birth canal. Causes, Incidence, and Risk Factors This infection occurs in people who have been infected with gonorrhea. It affects women more fre ...
... mucous membranes are the source of infection and the bacteria are transmitted by direct contact, usually sexual or during passage of a newborn through the birth canal. Causes, Incidence, and Risk Factors This infection occurs in people who have been infected with gonorrhea. It affects women more fre ...
Disease factsheet: Rift Valley Fever
... History and spread of the disease First discovered in Kenya in 1931, it is characterised by a short incubation period, fever, hepatitis, high morbidity in lambs less than one week of age, and high abortion rates. The disease is caused by the Rift Valley Fever (RVF) virus, a member of the genus Phleb ...
... History and spread of the disease First discovered in Kenya in 1931, it is characterised by a short incubation period, fever, hepatitis, high morbidity in lambs less than one week of age, and high abortion rates. The disease is caused by the Rift Valley Fever (RVF) virus, a member of the genus Phleb ...
The Fungi of Medical Importance
... n Histoplasma capsulatum n Coccidioides immitis n Blastomyces dermatitidis n Paracoccidioidomycosis brasiliensis ...
... n Histoplasma capsulatum n Coccidioides immitis n Blastomyces dermatitidis n Paracoccidioidomycosis brasiliensis ...
Typhoid and Paratyphoid fever ICD-10 A01.0: Typhoid Fever ICD
... typhi or S. paratyphi through positive culture of blood, stool, urine or bone marrow (laboratory investigation: culture of blood early in the disease; stool and urine after the first week; or bone marrow culture which provide the best bacteriologic confirmation (90%-95% recovery) even in patients wh ...
... typhi or S. paratyphi through positive culture of blood, stool, urine or bone marrow (laboratory investigation: culture of blood early in the disease; stool and urine after the first week; or bone marrow culture which provide the best bacteriologic confirmation (90%-95% recovery) even in patients wh ...
7-17_MICROBES_AND_DISEASE
... AIDS – disease of the human immune system caused by the HIV virus Chicken Pox & Shingles – diseases caused by the varicella zoster virus (VZV) Common Cold –infection of the upper respiratory tract – nose and throat Dengue Fever –infection from bite of an infected mosquito – usually in the tropics Eb ...
... AIDS – disease of the human immune system caused by the HIV virus Chicken Pox & Shingles – diseases caused by the varicella zoster virus (VZV) Common Cold –infection of the upper respiratory tract – nose and throat Dengue Fever –infection from bite of an infected mosquito – usually in the tropics Eb ...
2017 MICROBES AND DISEASE Normal flora – Many microbes
... AIDS – disease of the human immune system caused by the HIV virus Chicken Pox & Shingles – diseases caused by the varicella zoster virus (VZV) Common Cold –infection of the upper respiratory tract – nose and throat Dengue Fever –infection from bite of an infected mosquito – usually in the tropics Eb ...
... AIDS – disease of the human immune system caused by the HIV virus Chicken Pox & Shingles – diseases caused by the varicella zoster virus (VZV) Common Cold –infection of the upper respiratory tract – nose and throat Dengue Fever –infection from bite of an infected mosquito – usually in the tropics Eb ...
Non-infectious Diseases
... Genetic disease – an example is Bovine Leukocyte Adhesion Deficiency (BLAD) which affects Holstein calves causing stunted growth, pneumonia, delayed wound healing and early death. The mutation affects the ability of the calves to fight infection by interfering with the normal function of neutrophils ...
... Genetic disease – an example is Bovine Leukocyte Adhesion Deficiency (BLAD) which affects Holstein calves causing stunted growth, pneumonia, delayed wound healing and early death. The mutation affects the ability of the calves to fight infection by interfering with the normal function of neutrophils ...
Slapped cheek syndrome - NHS Ayrshire and Arran.
... The rash typically spreads to the body and limbs, and may last up to three weeks. It often fades, but returns when exposed to sunlight or heat. Before the rash develops, the following symptoms may occur: • mild fever or flu-like symptoms; ...
... The rash typically spreads to the body and limbs, and may last up to three weeks. It often fades, but returns when exposed to sunlight or heat. Before the rash develops, the following symptoms may occur: • mild fever or flu-like symptoms; ...
tsukamurella
... accommodate a group of chemically unique organisms characterized by a series of very long chain (68– 76 carbons), highly unsaturated mycolic acids, meso-diaminopimelic acid and arabinogalactan, common to the genus Corynebacterium. The type species is T. paurometabola, and the following additional sp ...
... accommodate a group of chemically unique organisms characterized by a series of very long chain (68– 76 carbons), highly unsaturated mycolic acids, meso-diaminopimelic acid and arabinogalactan, common to the genus Corynebacterium. The type species is T. paurometabola, and the following additional sp ...
Disease Information - Glory Cubed Productions
... all three sputum are negative: no respiratory isolation. Chest X-rays to diagnose and to see how it’s responding to treatment., After diagnosis, theses tests are done to establish a baseline: Liver function test, I&H and ryfanmin (turns your urine orange), Ethambutol, (monitor vision for color chang ...
... all three sputum are negative: no respiratory isolation. Chest X-rays to diagnose and to see how it’s responding to treatment., After diagnosis, theses tests are done to establish a baseline: Liver function test, I&H and ryfanmin (turns your urine orange), Ethambutol, (monitor vision for color chang ...
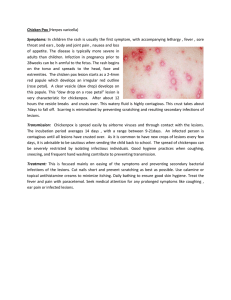
Chicken Pox (Herpes varicella) Symptoms: In children the rash is
... Transmission: Chickenpox is spread easily by airborne viruses and through contact with the lesions. The incubation period averages 14 days , with a range between 9-21days. An infected person is contagious until all lesions have crusted over. As it is common to have new crops of lesions every few day ...
... Transmission: Chickenpox is spread easily by airborne viruses and through contact with the lesions. The incubation period averages 14 days , with a range between 9-21days. An infected person is contagious until all lesions have crusted over. As it is common to have new crops of lesions every few day ...
File
... Syphilis is transmitted through contact with a syphilis sore Mirrors symptoms of common medical problems The first symptom is a painless sore (Pimple) The second stage is a body rash Also fever, swollen lymph nodes, sore throat, loss of hair, headaches, weight loss, muscle aches, and tiredness. If r ...
... Syphilis is transmitted through contact with a syphilis sore Mirrors symptoms of common medical problems The first symptom is a painless sore (Pimple) The second stage is a body rash Also fever, swollen lymph nodes, sore throat, loss of hair, headaches, weight loss, muscle aches, and tiredness. If r ...
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD) Fact Sheet
... available information is limited, currently there is no clear evidence that maternal enteroviral infection causes adverse outcomes of pregnancy such as abortion, stillbirth, or congenital defects. However, mothers infected shortly before delivery may pass the virus to the newborn. Babies born to mot ...
... available information is limited, currently there is no clear evidence that maternal enteroviral infection causes adverse outcomes of pregnancy such as abortion, stillbirth, or congenital defects. However, mothers infected shortly before delivery may pass the virus to the newborn. Babies born to mot ...
ImmunIsatIon Is for lIfe
... people, especially small children, may not show any symptoms even though they may have the virus and can pass it onto others. yyWhile most people recover fully, it sometimes leads to death from overwhelming infection of the liver. ...
... people, especially small children, may not show any symptoms even though they may have the virus and can pass it onto others. yyWhile most people recover fully, it sometimes leads to death from overwhelming infection of the liver. ...
Slayt 1
... •Enteroviruses enter via the oropharynx, intestinal mucosa, or upper respiratory tract and infect the underlying lymphatic tissue; rhinoviruses are restricted to the Body_ID: B056003 upper respiratory tract •In the absence of serum antibody, enterovirus spreads by viremia to cells of a receptor-bear ...
... •Enteroviruses enter via the oropharynx, intestinal mucosa, or upper respiratory tract and infect the underlying lymphatic tissue; rhinoviruses are restricted to the Body_ID: B056003 upper respiratory tract •In the absence of serum antibody, enterovirus spreads by viremia to cells of a receptor-bear ...
Coccidioidomycosis

Coccidioidomycosis (/kɒkˌsɪdiɔɪdoʊmaɪˈkoʊsɪs/, kok-sid-ee-oy-doh-my-KOH-sis), commonly known as cocci, ""valley fever"", as well as ""California fever"", ""desert rheumatism"", and ""San Joaquin Valley fever"", is a mammalian fungal disease caused by Coccidioides immitis or Coccidioides posadasii. It is endemic in certain parts of Arizona, California, Nevada, New Mexico, Texas, Utah, and northern Mexico.C. immitis is a dimorphic saprophytic fungus that grows as a mycelium in the soil and produces a spherule form in the host organism. It resides in the soil in certain parts of the southwestern United States, most notably in California and Arizona. It is also commonly found in northern Mexico, and parts of Central and South America. C. immitis is dormant during long dry spells, then develops as a mold with long filaments that break off into airborne spores when it rains. The spores, known as arthroconidia, are swept into the air by disruption of the soil, such as during construction, farming, or an earthquake.Coccidioidomycosis is a common cause of community acquired pneumonia in the endemic areas of the United States. Infections usually occur due to inhalation of the arthroconidial spores after soil disruption. The disease is not contagious. In some cases the infection may recur or be permanent.