chap9-1
... A decline in bond prices results in a higher rate of return (interest rate) on bonds and other financial assets A higher interest rate results in a reduction in investment and consumption spending ...
... A decline in bond prices results in a higher rate of return (interest rate) on bonds and other financial assets A higher interest rate results in a reduction in investment and consumption spending ...
multiple choice
... b. the excess reserves of member banks are increased. c. a single commercial bank can no longer lend dollar-for-dollar with its excess reserves. d. the excess reserves of member banks are reduced. 30. The purpose of a tight money policy is to: a. b. c. d. ...
... b. the excess reserves of member banks are increased. c. a single commercial bank can no longer lend dollar-for-dollar with its excess reserves. d. the excess reserves of member banks are reduced. 30. The purpose of a tight money policy is to: a. b. c. d. ...
Principles of Macroeconomics Take
... 17. To be counted as part of the labor force, a person must [A] be working or actively looking for work. [B] be less than 65 years old. [C] be a discouraged worker. [D] have worked at some time in the past. [E] be under 16 years of age. 18. Frictional and structural unemployment are always present ...
... 17. To be counted as part of the labor force, a person must [A] be working or actively looking for work. [B] be less than 65 years old. [C] be a discouraged worker. [D] have worked at some time in the past. [E] be under 16 years of age. 18. Frictional and structural unemployment are always present ...
Zarnowitz, Victor. Business Cycles Observed and Assessed
... One of the earliest explanations of crises was the theory of “inflation”. The basis for this theory is that an increase in coin or paper money issued by the government causes an increase in prices, that later stimulates the business activity in the economy. This activity can cause extreme recklessne ...
... One of the earliest explanations of crises was the theory of “inflation”. The basis for this theory is that an increase in coin or paper money issued by the government causes an increase in prices, that later stimulates the business activity in the economy. This activity can cause extreme recklessne ...
ECON 102 Tutorial: Week 23
... Within Keynesian models the demand to hold money is called ‘liquidity preference’ (i.e., a preference to hold ‘money’ as the most liquid of wealth assets) as the alternative to holding bonds, This is written (and drawn below) as a demand curve for money: L = L(Y, r); with L1 > 0; L2 < 0. b) With an ...
... Within Keynesian models the demand to hold money is called ‘liquidity preference’ (i.e., a preference to hold ‘money’ as the most liquid of wealth assets) as the alternative to holding bonds, This is written (and drawn below) as a demand curve for money: L = L(Y, r); with L1 > 0; L2 < 0. b) With an ...
Part J: The Macroeconomic Environment
... that a reduction in real wage rates will lead to a corresponding increase in rates of profit)? That the proportion of profits that is spent is smaller than the proportion of wages that is spent. Thus a redistribution from wages to profits will reduce total expenditure. Do you personally gain or lose ...
... that a reduction in real wage rates will lead to a corresponding increase in rates of profit)? That the proportion of profits that is spent is smaller than the proportion of wages that is spent. Thus a redistribution from wages to profits will reduce total expenditure. Do you personally gain or lose ...
Money
... 1. Open market operations: CB purchases and sells government bonds. Increases / decreases M through change of B 2. Reserve requirements: CB sets minimum. Affects creation of money by banks (rr) 3. Discount rate: charged on loans by CB for banks (if do not have enough R, or want more loans ) Affects ...
... 1. Open market operations: CB purchases and sells government bonds. Increases / decreases M through change of B 2. Reserve requirements: CB sets minimum. Affects creation of money by banks (rr) 3. Discount rate: charged on loans by CB for banks (if do not have enough R, or want more loans ) Affects ...
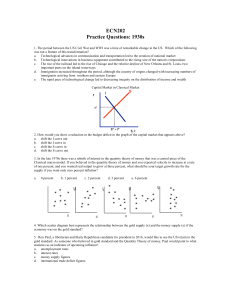
ECN202 Practice Questions: 1930s
... 9. After WWI England (UK) needed to make a decision regarding a return to the gold standard, and if they did return, they needed to set the price of the pound () in terms of gold. The basics of the problem can be seen in the table above. One of the problems was England had very high inflation rates ...
... 9. After WWI England (UK) needed to make a decision regarding a return to the gold standard, and if they did return, they needed to set the price of the pound () in terms of gold. The basics of the problem can be seen in the table above. One of the problems was England had very high inflation rates ...
Fiscal and Monetary Policy in the Growth Model Introduction A. Our
... Fiscal and Monetary Policy in the Growth Model Introduction A. Our focus will be on fiscal and monetary policies over a longtime horizon. (ex. 10 years) B. Ex. The federal budget deficit was much higher since 1980 (except for the late 1990s) than it was in the 1960s and 1970s. C. Ex. Money growth wa ...
... Fiscal and Monetary Policy in the Growth Model Introduction A. Our focus will be on fiscal and monetary policies over a longtime horizon. (ex. 10 years) B. Ex. The federal budget deficit was much higher since 1980 (except for the late 1990s) than it was in the 1960s and 1970s. C. Ex. Money growth wa ...
The IS–LM model
... This notation indicates that M d is a function, L, of the two arguments Y (GDP) and r , multiplied by the price level, P. The little plus and minus indicate, respectively, that Y has a positive effect on the demand for money while r has a negative effect. Let’s think about this. • Positive effect of ...
... This notation indicates that M d is a function, L, of the two arguments Y (GDP) and r , multiplied by the price level, P. The little plus and minus indicate, respectively, that Y has a positive effect on the demand for money while r has a negative effect. Let’s think about this. • Positive effect of ...
A rise in the price of oil imports has resulted in a decrease of short
... a. We have paper money backed by government held gold. b. We have coins made from valuable metals. c. We use the barter system in which people trade goods for goods. d. We have paper money based on the government's legal authority to create money. ...
... a. We have paper money backed by government held gold. b. We have coins made from valuable metals. c. We use the barter system in which people trade goods for goods. d. We have paper money based on the government's legal authority to create money. ...
What is deflation? A continual decline in the average price level of
... What theory says that wages and prices are sticky, private demand is inherently unstable thus requiring active government action, and persistent unemployment requires demand side policies? ...
... What theory says that wages and prices are sticky, private demand is inherently unstable thus requiring active government action, and persistent unemployment requires demand side policies? ...
Graphs - Mr. Thomas
... you understand how your AP exam is scored. You should also get into the habit of using graphs to help you answer questions even when a graph is not required. For example, drawing a supply and demand graph can often help you answer multiple-choice questions that involve the supply and demand model. A ...
... you understand how your AP exam is scored. You should also get into the habit of using graphs to help you answer questions even when a graph is not required. For example, drawing a supply and demand graph can often help you answer multiple-choice questions that involve the supply and demand model. A ...
Monetary Policy
... The newspapers usually get the rest correct, they define the “federal funds rate” as the interest rate that banks charge each other on overnight loans (When banks need quick money like this it’s usually keep their reserves sufficient). ...
... The newspapers usually get the rest correct, they define the “federal funds rate” as the interest rate that banks charge each other on overnight loans (When banks need quick money like this it’s usually keep their reserves sufficient). ...
The Great Depression
... Even if the authorities had cut interest rates, Keynesian economists would argue that this would result in a liquidity trap: a situation where interest rates are cut so low that the public believe that they can go no lower. They therefore expect interest rates to rise soon and bond prices to fall an ...
... Even if the authorities had cut interest rates, Keynesian economists would argue that this would result in a liquidity trap: a situation where interest rates are cut so low that the public believe that they can go no lower. They therefore expect interest rates to rise soon and bond prices to fall an ...