2-1-2 Key Macroeconomic Concepts - Student
... 7. What exchange rate would you like with the US dollar if you were a Canadian traveller to the US? 8. What exchange rate would you like with the Canadian dollar if you were an American tourist travelling in Canada? 9. What are the two most common types of exchange rate systems? Explain each type of ...
... 7. What exchange rate would you like with the US dollar if you were a Canadian traveller to the US? 8. What exchange rate would you like with the Canadian dollar if you were an American tourist travelling in Canada? 9. What are the two most common types of exchange rate systems? Explain each type of ...
Emerging Market Economies: economies in an earlier stage of
... Stage1: Initiation of Financial Crisis Path1: Mismanagement of Financial Liberalization/Globalization 1) Eliminating restrictions Fixed Exchange Rate Interest Rate increases 2) Weak Supervision 3) Moral hazard problems and adverse selection 4) Deterioration in bank’s balance sheets Example: Mexico E ...
... Stage1: Initiation of Financial Crisis Path1: Mismanagement of Financial Liberalization/Globalization 1) Eliminating restrictions Fixed Exchange Rate Interest Rate increases 2) Weak Supervision 3) Moral hazard problems and adverse selection 4) Deterioration in bank’s balance sheets Example: Mexico E ...
Monetary Policy - ais
... increase the rate of growth of the economy and the money supply by increasing the velocity of circulation of money What is the current cash rate? ...
... increase the rate of growth of the economy and the money supply by increasing the velocity of circulation of money What is the current cash rate? ...
Macroeconomics: BSc Year One The Monetarist View of Interest
... the original interest rate and income level, but a higher price point. There has, however, been a period of lower interest rates, and the government seeks to repeat the process. This process, however, generates inflation, which may become expected as before, leading to no short-term benefits. Also, ...
... the original interest rate and income level, but a higher price point. There has, however, been a period of lower interest rates, and the government seeks to repeat the process. This process, however, generates inflation, which may become expected as before, leading to no short-term benefits. Also, ...
personal finance - De Smet Jesuit High School
... a. When inflation is low, there is more money out there to lend and interest rates are low. b. Interest rate: the price you pay to borrow money. c. Investments do better during low inflation because people are spending money on investing; thus driving stock prices up. d. To project inflation issues ...
... a. When inflation is low, there is more money out there to lend and interest rates are low. b. Interest rate: the price you pay to borrow money. c. Investments do better during low inflation because people are spending money on investing; thus driving stock prices up. d. To project inflation issues ...
Take-Home Quiz
... 13. (1 POINT) If the nominal interest rate on a loan is 14%, and inflation is expected to be 5%, what is the real interest rate? Who would benefit if inflation were actually 8%? (circle your answer) ...
... 13. (1 POINT) If the nominal interest rate on a loan is 14%, and inflation is expected to be 5%, what is the real interest rate? Who would benefit if inflation were actually 8%? (circle your answer) ...
Economics considerations for new and existing businesses
... Inflation makes the business appear that it has increased profitability. Firms with large loans benefit from inflation ...
... Inflation makes the business appear that it has increased profitability. Firms with large loans benefit from inflation ...
Objective of MP - qazieconometrics
... policy may be defined as “that branch of economic policy which is concerned with the regulation of the availability (or supply), the costs and the directions of credit”. It is effected by various techniques (methods) in the hands of the central bank. ...
... policy may be defined as “that branch of economic policy which is concerned with the regulation of the availability (or supply), the costs and the directions of credit”. It is effected by various techniques (methods) in the hands of the central bank. ...
CENTRAL BANKING
... government securities or other securities from the market in order to lower interest rates and increase the money supply. Quantitative easing increases the money supply by flooding financial institutions with capital in an effort to promote increased lending and liquidity. QE targets commercial bank ...
... government securities or other securities from the market in order to lower interest rates and increase the money supply. Quantitative easing increases the money supply by flooding financial institutions with capital in an effort to promote increased lending and liquidity. QE targets commercial bank ...
Worksheet #4 - The Digital Economist
... Calculate the rate of inflation between 1999 & 2000, derive the real rate of interest (return) for the year 2000 if nominal interest rates are 7%: Is this real rate of interest above or below the rate of economic growth for the same period of time?____________ Is this to the benefit of lenders or bo ...
... Calculate the rate of inflation between 1999 & 2000, derive the real rate of interest (return) for the year 2000 if nominal interest rates are 7%: Is this real rate of interest above or below the rate of economic growth for the same period of time?____________ Is this to the benefit of lenders or bo ...
New Keynesian Economics
... • The interest rate term might seem counter-intuitive; but, recall that the real rate is assumed to be constant so a rise in i means an increase in expected inflation, which, in turn, reduces the desirability of holding home’s currency • Also, for a country that is not inflating, rising rates of GDP ...
... • The interest rate term might seem counter-intuitive; but, recall that the real rate is assumed to be constant so a rise in i means an increase in expected inflation, which, in turn, reduces the desirability of holding home’s currency • Also, for a country that is not inflating, rising rates of GDP ...
Brazil`s 1998-1999 BOP Crisis
... 1999- Brazil devaluates Real by 8% Real’s value continues to loose value down to 40%. Recession occurs due to the government’s attempt to correct the fall of the currency. ...
... 1999- Brazil devaluates Real by 8% Real’s value continues to loose value down to 40%. Recession occurs due to the government’s attempt to correct the fall of the currency. ...
Simple Rules for Open Economies John B. Taylor Stanford University
... – standard error of .06. – Plot of the actual and fitted values from this regression: ...
... – standard error of .06. – Plot of the actual and fitted values from this regression: ...
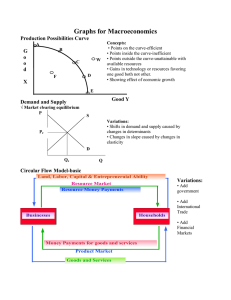
Graphs for Macroeconomics Production Possibilities Curve G o
... • As new demand and supply factors impact this market, changes in interest rate causes changes in investment and interest rate-driven consumption, which affects AD, ASsr, ASlr PL and Real GDP. • When government financing deficit spending, the impact of borrowing increases the demand curve and raises ...
... • As new demand and supply factors impact this market, changes in interest rate causes changes in investment and interest rate-driven consumption, which affects AD, ASsr, ASlr PL and Real GDP. • When government financing deficit spending, the impact of borrowing increases the demand curve and raises ...
Interest Rates & Inflation
... – There are short term & long term interest rates • Low interest rates are critical for a healthy economy (GDP) – As interest rates ↑ => cost of borrowing money ↑ => Investment (I) ↓ ...
... – There are short term & long term interest rates • Low interest rates are critical for a healthy economy (GDP) – As interest rates ↑ => cost of borrowing money ↑ => Investment (I) ↓ ...
Slide 1
... there were signs of improving business confidence. There had also been signs that the second-quarter decline in consumption would be smaller than the Committee had previously anticipated. ...
... there were signs of improving business confidence. There had also been signs that the second-quarter decline in consumption would be smaller than the Committee had previously anticipated. ...
Interest rate
An interest rate is the rate at which interest is paid by borrowers (debtors) for the use of money that they borrow from lenders (creditors). Specifically, the interest rate is a percentage of principal paid a certain number of times per period for all periods during the total term of the loan or credit. Interest rates are normally expressed as a percentage of the principal for a period of one year, sometimes they are expressed for different periods such as a month or a day. Different interest rates exist parallelly for the same or comparable time periods, depending on the default probability of the borrower, the residual term, the payback currency, and many more determinants of a loan or credit. For example, a company borrows capital from a bank to buy new assets for its business, and in return the lender receives rights on the new assets as collateral and interest at a predetermined interest rate for deferring the use of funds and instead lending it to the borrower.Interest-rate targets are a vital tool of monetary policy and are taken into account when dealing with variables like investment, inflation, and unemployment. The central banks of countries generally tend to reduce interest rates when they wish to increase investment and consumption in the country's economy. However, a low interest rate as a macro-economic policy can be risky and may lead to the creation of an economic bubble, in which large amounts of investments are poured into the real-estate market and stock market. In developed economies, interest-rate adjustments are thus made to keep inflation within a target range for the health of economic activities or cap the interest rate concurrently with economic growth to safeguard economic momentum.