Agricultural Economics 430 - Department of Agricultural Economics
... Occurs in the classical range of the aggregate supply curve, or where it becomes perfectly inelastic. ...
... Occurs in the classical range of the aggregate supply curve, or where it becomes perfectly inelastic. ...
... of San Francisco or of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System.This publication is edited by Judith Goff, with the assistance of Anita Todd. Permission to reprint portions of articles or whole articles must be obtained in writing. Permission to photocopy is unrestricted. Please send edi ...
Honduras_en.pdf
... September 2012. ECLAC forecasts slightly higher growth in 2014 (3.0%), since the international economy is expected to recover to some extent. Year-on-year inflation stood at 4.6% in October, lower than the rate recorded in the same month in 2012 (5.7%). ECLAC expects this rate to increase towards th ...
... September 2012. ECLAC forecasts slightly higher growth in 2014 (3.0%), since the international economy is expected to recover to some extent. Year-on-year inflation stood at 4.6% in October, lower than the rate recorded in the same month in 2012 (5.7%). ECLAC expects this rate to increase towards th ...
How Long Can the Business Expansion Continue?
... – Continuing innovation, albeit less revolutionary than late 1990s ...
... – Continuing innovation, albeit less revolutionary than late 1990s ...
Peru_en.pdf
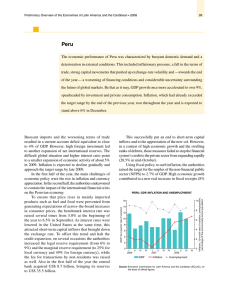
... end of the year. Meanwhile, rising domestic demand boosted imports, which expanded by over 20% in real terms. Higher prices for imported food and fuel contributed to a steeper rise in the consumer price index (CPI), which in November stood at 6.75% (clearly exceeding the inflation target ceiling of ...
... end of the year. Meanwhile, rising domestic demand boosted imports, which expanded by over 20% in real terms. Higher prices for imported food and fuel contributed to a steeper rise in the consumer price index (CPI), which in November stood at 6.75% (clearly exceeding the inflation target ceiling of ...
Objective 1.02
... goods and services purchased by consumers. The sales are an indicator of general consumer spending patterns. ...
... goods and services purchased by consumers. The sales are an indicator of general consumer spending patterns. ...
Peru_en.pdf
... total financial system credit increased by 17.5%. The dollarization ratio of the financial system maintained its downward trend to stand at 44% in October 2010 (down from 46% in December 2009). Between December 2009 and October 2010, the new sol appreciated by 3.8% in nominal terms against the dolla ...
... total financial system credit increased by 17.5%. The dollarization ratio of the financial system maintained its downward trend to stand at 44% in October 2010 (down from 46% in December 2009). Between December 2009 and October 2010, the new sol appreciated by 3.8% in nominal terms against the dolla ...
Problem Set 1
... 2. For the consumer price index values shown, calculate the rate of inflation in each year from 1930 to 1933. What is unusual about this period, relative to recent experience? Year: 1929 1930 1931 CPI : 51.3 50.0 45.6 ...
... 2. For the consumer price index values shown, calculate the rate of inflation in each year from 1930 to 1933. What is unusual about this period, relative to recent experience? Year: 1929 1930 1931 CPI : 51.3 50.0 45.6 ...
Chapter 16 Government and the Economy
... – The setting of interest on loans to member banks • Open market operations – The buying and selling of government securities • Reserve requirements – The amount of liquid assets and ready cash that banks are required to hold to meet depositors’ demands ...
... – The setting of interest on loans to member banks • Open market operations – The buying and selling of government securities • Reserve requirements – The amount of liquid assets and ready cash that banks are required to hold to meet depositors’ demands ...
Bolivia_en.pdf
... 2011, nominal tax revenues rose by 29.7% compared with the same period the previous year, on the back of an increase in hydrocarbon tax receipts, which went up by 14.3% during the period. Current expenditure expanded by 16% in nominal terms in the year to September 2011 compared with the same period ...
... 2011, nominal tax revenues rose by 29.7% compared with the same period the previous year, on the back of an increase in hydrocarbon tax receipts, which went up by 14.3% during the period. Current expenditure expanded by 16% in nominal terms in the year to September 2011 compared with the same period ...
Ch. 15 / 16 StudyGuide Multiple Choice ____ 1. You are President
... ____ 11. An example of expansionary fiscal policy would be A. cutting taxes. C. cutting production of consumer goods. B. cutting government spending. D. cutting prices of consumer goods. ____ 12. All of the following are features of classical economics EXCEPT A. a free market economy. B. the law of ...
... ____ 11. An example of expansionary fiscal policy would be A. cutting taxes. C. cutting production of consumer goods. B. cutting government spending. D. cutting prices of consumer goods. ____ 12. All of the following are features of classical economics EXCEPT A. a free market economy. B. the law of ...
What effect does a rise in government spending have on an ISLM
... (2) If the speculative demand for money is perfectly interest elastic, the LM curve is horizontal. Monetary policy will not be effective in changing national income. This is because the rise in the money supply does not cause a fall in the interest rate. (3) If investment is perfectly interest elast ...
... (2) If the speculative demand for money is perfectly interest elastic, the LM curve is horizontal. Monetary policy will not be effective in changing national income. This is because the rise in the money supply does not cause a fall in the interest rate. (3) If investment is perfectly interest elast ...
This at the conference “Finance and Macroeconomics” held
... entire yield curve to just two factors—the general level of interest rates and the slope or tilt of the yield curve—and then model these two factors along with real GDP growth. Hördahl,Tristani, and Vestin examine a similar structure with a more detailed accounting for macroeconomic dynamics that re ...
... entire yield curve to just two factors—the general level of interest rates and the slope or tilt of the yield curve—and then model these two factors along with real GDP growth. Hördahl,Tristani, and Vestin examine a similar structure with a more detailed accounting for macroeconomic dynamics that re ...
The Philippines: In Brief
... The Philippines: In Brief Land Area: 299,764 sq. km. Location: The Philippines is located at the heart of Southeast Asia. It is surrounded by the Pacific Ocean on the east, the Celebes (sulawesi) Sea on the south, and the South China Sea on the West and North. Geography: Three main island groups: Lu ...
... The Philippines: In Brief Land Area: 299,764 sq. km. Location: The Philippines is located at the heart of Southeast Asia. It is surrounded by the Pacific Ocean on the east, the Celebes (sulawesi) Sea on the south, and the South China Sea on the West and North. Geography: Three main island groups: Lu ...
WAY THE FINANCIAL CRISIS OF 2007
... domestic investors increased their buying of long-term overseas securities. This was creating problems in financing the current account deficit reaching roughly $800 billion per year. The USA must attract about $70 billion per month of foreign investment, but the sentiments of foreign investors begi ...
... domestic investors increased their buying of long-term overseas securities. This was creating problems in financing the current account deficit reaching roughly $800 billion per year. The USA must attract about $70 billion per month of foreign investment, but the sentiments of foreign investors begi ...
How far we`ve come, how little we`ve changed
... how far we have yet to go. Twelve months ago, we were in the midst of a financial panic (which is beginning to be referred to as the Great Recession) where the worst fears were that the global financial system would collapse. Global economic activity was falling faster than in the 1930s. As a result ...
... how far we have yet to go. Twelve months ago, we were in the midst of a financial panic (which is beginning to be referred to as the Great Recession) where the worst fears were that the global financial system would collapse. Global economic activity was falling faster than in the 1930s. As a result ...
Flexible labor markets
... inequality has increased in most countries, but growth has actually slowed down significantly. ...
... inequality has increased in most countries, but growth has actually slowed down significantly. ...
... In the first half of the year, the balance-of-payments current account yielded a deficit of US$ 5.8 billion (2% of GDP), an increase on the same period in 2014 (1.3% of GDP). This widening was due to a 15.1% fall in goods and services exports —largely a result of the drop in demand from Brazil and t ...
... have shrunk overall, although half of the decline in exports was attributable to falls in both prices and volumes of agricultural exports (basically soybeans). On the import side, 40% of the reduction is explained by a drop in oil imports. On the services account, all categories showed downturns on ...
Defense for Ease
... underpricing risk, and bidding up prices of assets from corporate bonds to houses and in the process driving down returns on those assets, such as long-term interest rates. ...
... underpricing risk, and bidding up prices of assets from corporate bonds to houses and in the process driving down returns on those assets, such as long-term interest rates. ...
Interest rate
An interest rate is the rate at which interest is paid by borrowers (debtors) for the use of money that they borrow from lenders (creditors). Specifically, the interest rate is a percentage of principal paid a certain number of times per period for all periods during the total term of the loan or credit. Interest rates are normally expressed as a percentage of the principal for a period of one year, sometimes they are expressed for different periods such as a month or a day. Different interest rates exist parallelly for the same or comparable time periods, depending on the default probability of the borrower, the residual term, the payback currency, and many more determinants of a loan or credit. For example, a company borrows capital from a bank to buy new assets for its business, and in return the lender receives rights on the new assets as collateral and interest at a predetermined interest rate for deferring the use of funds and instead lending it to the borrower.Interest-rate targets are a vital tool of monetary policy and are taken into account when dealing with variables like investment, inflation, and unemployment. The central banks of countries generally tend to reduce interest rates when they wish to increase investment and consumption in the country's economy. However, a low interest rate as a macro-economic policy can be risky and may lead to the creation of an economic bubble, in which large amounts of investments are poured into the real-estate market and stock market. In developed economies, interest-rate adjustments are thus made to keep inflation within a target range for the health of economic activities or cap the interest rate concurrently with economic growth to safeguard economic momentum.