FedViews
... 2009-31, “Disagreement about the Inflation Outlook.”) Expectations of inflation over the next five years have been falling, while longer-term expectations have edged up. (Recent measures of inflation expectations from financial markets are similarly ambiguous. See FRBSF Working Paper 2008-34, “Infla ...
... 2009-31, “Disagreement about the Inflation Outlook.”) Expectations of inflation over the next five years have been falling, while longer-term expectations have edged up. (Recent measures of inflation expectations from financial markets are similarly ambiguous. See FRBSF Working Paper 2008-34, “Infla ...
Homework 1
... 5. On January 1, 2011, you open up the newspaper and see the 1 year interest rate on US dollar lending is .1264% ( i = .001264). On the same day, you find 1 year interest rates on Japanese Yen, Australian dollars and the Euro. You also see the current spot exchange rate with the US dollar for those ...
... 5. On January 1, 2011, you open up the newspaper and see the 1 year interest rate on US dollar lending is .1264% ( i = .001264). On the same day, you find 1 year interest rates on Japanese Yen, Australian dollars and the Euro. You also see the current spot exchange rate with the US dollar for those ...
Economic and monetary developments 2007 was the third
... Inflation was relatively low, standing below the inflation target for most of 2007. A surge in inflation in 2007 Q4 and January 2008 was due mainly to a sharp rise in world prices of food, changes to indirect taxes and a further pick-up in regulated prices. These components of inflation will keep it ...
... Inflation was relatively low, standing below the inflation target for most of 2007. A surge in inflation in 2007 Q4 and January 2008 was due mainly to a sharp rise in world prices of food, changes to indirect taxes and a further pick-up in regulated prices. These components of inflation will keep it ...
Lecture25(Ch21[1]
... Gross investment during this year ($1.5 trillion) Net investment ($.5 trillion) Depreciation ($1 trillion) ...
... Gross investment during this year ($1.5 trillion) Net investment ($.5 trillion) Depreciation ($1 trillion) ...
INTEREST RATE RISK: A WINDING ROAD
... the lesson of the last recovery that inflation is capable of rising even if the level of economic activity has not returned to its pre-recession trend.” Jeffrey M. Lacker, President, FRB Richmond, April, 2011 ...
... the lesson of the last recovery that inflation is capable of rising even if the level of economic activity has not returned to its pre-recession trend.” Jeffrey M. Lacker, President, FRB Richmond, April, 2011 ...
FRBSF E L CONOMIC ETTER
... est rate premium is enough to offset the increased demand for foreign funds, implying consumers borrow less during economic downturns than during upturns. Contagion and external factors Currency and banking crises in emerging market economies have tended to be bunched together over the last decade. ...
... est rate premium is enough to offset the increased demand for foreign funds, implying consumers borrow less during economic downturns than during upturns. Contagion and external factors Currency and banking crises in emerging market economies have tended to be bunched together over the last decade. ...
Canada`s Money Supply
... Interest rates influence money supply Commercial banks and other financial institutions provide most of the assets used as money through loans made to individuals and businesses. In that sense, financial institutions create, or can create money. The Bank of Canada manages the rate of money growth in ...
... Interest rates influence money supply Commercial banks and other financial institutions provide most of the assets used as money through loans made to individuals and businesses. In that sense, financial institutions create, or can create money. The Bank of Canada manages the rate of money growth in ...
Untitled
... • Growth of the money supply – quantity theory – inflation states that too much money in the economy causes inflation • changes in aggregate demand – (amount of goods and services in the economy that will be purchases at all possible price levels) can be affected by inflation • changes in aggregate ...
... • Growth of the money supply – quantity theory – inflation states that too much money in the economy causes inflation • changes in aggregate demand – (amount of goods and services in the economy that will be purchases at all possible price levels) can be affected by inflation • changes in aggregate ...
Sections 5 & 6 - Vocab Review
... on the economy in the long run and only result in a proportional change in the price level. _____the total value of financial assets in the economy that are considered money. _____an asset that individuals acquire for the purpose of trading for goods and services rather than for their own consumptio ...
... on the economy in the long run and only result in a proportional change in the price level. _____the total value of financial assets in the economy that are considered money. _____an asset that individuals acquire for the purpose of trading for goods and services rather than for their own consumptio ...
Martin NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES OF MONETARY FLICY
... changes the effective tax rate on investits as well as the real net—of—tax interest rate. More specifically, historic cost depreciation and inventory accounting rules reduce substantially the real after—tax return on corporate investments (see Feldstein and Sununers, 1979). An easy—money policy rais ...
... changes the effective tax rate on investits as well as the real net—of—tax interest rate. More specifically, historic cost depreciation and inventory accounting rules reduce substantially the real after—tax return on corporate investments (see Feldstein and Sununers, 1979). An easy—money policy rais ...
Handout #10
... Again, if we know the value of these multipliers, then we do not need to solve the entire model. ...
... Again, if we know the value of these multipliers, then we do not need to solve the entire model. ...
1 Economics 259 Midterm I – Spring 2014 Name: You have 50
... countries where money supply grows faster experience __________ rate of inflation, while if one looks at the relationship between money inflation and money growth in the US across time, periods with relatively higher money growth rate are also periods of relatively _________ inflation. a. lower; hig ...
... countries where money supply grows faster experience __________ rate of inflation, while if one looks at the relationship between money inflation and money growth in the US across time, periods with relatively higher money growth rate are also periods of relatively _________ inflation. a. lower; hig ...
Business cycles
... – Domestic and global economic analysis – Industry analysis – Company analysis ...
... – Domestic and global economic analysis – Industry analysis – Company analysis ...
The IS-MP-model and the difference between neoclassical and
... the surplus money away. In order to avoid inflation, the central bank has to set its real rate of interest at a level which equates supply of and demand for (assets denominated in) its currency. This argument is reflected in graph 5 in the left hand diagram of the asset market. As the relevant rate ...
... the surplus money away. In order to avoid inflation, the central bank has to set its real rate of interest at a level which equates supply of and demand for (assets denominated in) its currency. This argument is reflected in graph 5 in the left hand diagram of the asset market. As the relevant rate ...
Economics 202
... This course uses market analysis (supply and demand at the national level) to develop an understanding of the working of the macroeconomy. The macroeconomic system is analyzed by studying five aggregated markets: the output market, the labor market, the financial (credit) market, the foreign exchang ...
... This course uses market analysis (supply and demand at the national level) to develop an understanding of the working of the macroeconomy. The macroeconomic system is analyzed by studying five aggregated markets: the output market, the labor market, the financial (credit) market, the foreign exchang ...
Policy Instrument - Porterville College Home
... A Change in Supply In 2009, an outbreak of swine flu in Mexico reduced tourist travel, shifting the supply curve of dollars to the left The result was a depreciation of the peso (appreciation of the dollar), that is, an equilibrium exchange rate with more pesos ...
... A Change in Supply In 2009, an outbreak of swine flu in Mexico reduced tourist travel, shifting the supply curve of dollars to the left The result was a depreciation of the peso (appreciation of the dollar), that is, an equilibrium exchange rate with more pesos ...
Macroeconomics
... increased prices (inflation) Real GDP is adjusted for changing prices Increase in GDP=good economic performance Decrease in GDP=poor economic performance Economic Growth=% change in real GDP from one year to the next ...
... increased prices (inflation) Real GDP is adjusted for changing prices Increase in GDP=good economic performance Decrease in GDP=poor economic performance Economic Growth=% change in real GDP from one year to the next ...
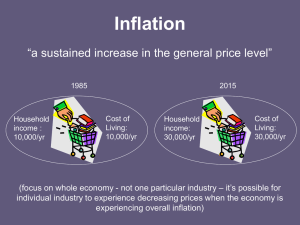
Inflation
... Measuring Inflation 1. Family Expenditure Survey – find out what households spend their money on (average basket of goods – approx. 600) 2. Weights Determined – goods that we spend a higher proportion of income on get more importance in the basket 3. Prices Checked – from stores across the UK 4. We ...
... Measuring Inflation 1. Family Expenditure Survey – find out what households spend their money on (average basket of goods – approx. 600) 2. Weights Determined – goods that we spend a higher proportion of income on get more importance in the basket 3. Prices Checked – from stores across the UK 4. We ...
Interest rate
An interest rate is the rate at which interest is paid by borrowers (debtors) for the use of money that they borrow from lenders (creditors). Specifically, the interest rate is a percentage of principal paid a certain number of times per period for all periods during the total term of the loan or credit. Interest rates are normally expressed as a percentage of the principal for a period of one year, sometimes they are expressed for different periods such as a month or a day. Different interest rates exist parallelly for the same or comparable time periods, depending on the default probability of the borrower, the residual term, the payback currency, and many more determinants of a loan or credit. For example, a company borrows capital from a bank to buy new assets for its business, and in return the lender receives rights on the new assets as collateral and interest at a predetermined interest rate for deferring the use of funds and instead lending it to the borrower.Interest-rate targets are a vital tool of monetary policy and are taken into account when dealing with variables like investment, inflation, and unemployment. The central banks of countries generally tend to reduce interest rates when they wish to increase investment and consumption in the country's economy. However, a low interest rate as a macro-economic policy can be risky and may lead to the creation of an economic bubble, in which large amounts of investments are poured into the real-estate market and stock market. In developed economies, interest-rate adjustments are thus made to keep inflation within a target range for the health of economic activities or cap the interest rate concurrently with economic growth to safeguard economic momentum.




![Lecture25(Ch21[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008219352_1-9f95e5a074002ea83218cbb8cead45d4-300x300.png)