The Endocrine System Negative Feedback Mechanism
... sexual function, and development). • Compared to the nervous system, the endocrine system is more closely associated with growth and development, and its responses tend to be long-lasting, whereas nervous system responses tend to be rapid and discrete. • What’s the benefit of the endocrine system’s ...
... sexual function, and development). • Compared to the nervous system, the endocrine system is more closely associated with growth and development, and its responses tend to be long-lasting, whereas nervous system responses tend to be rapid and discrete. • What’s the benefit of the endocrine system’s ...
Lecture 1A PowerPoint
... (Body temperature lowers) increased body temp. (Heart rate slows) increase heart rate (Decreased blood sugar levels) increase BS levels (Increase in blood glucose levels) decrease BS levels (High blood pressure) lowers BP (Dehydration) increased hydration ...
... (Body temperature lowers) increased body temp. (Heart rate slows) increase heart rate (Decreased blood sugar levels) increase BS levels (Increase in blood glucose levels) decrease BS levels (High blood pressure) lowers BP (Dehydration) increased hydration ...
Endocrine System
... The hormone FSH stimulates growth of the graafian follicle to grow in the: Ovaries The function of the thyroid hormones is to: ...
... The hormone FSH stimulates growth of the graafian follicle to grow in the: Ovaries The function of the thyroid hormones is to: ...
Endocrine System
... The hormone FSH stimulates growth of the graafian follicle to grow in the: Ovaries The function of the thyroid hormones is to: ...
... The hormone FSH stimulates growth of the graafian follicle to grow in the: Ovaries The function of the thyroid hormones is to: ...
17. Pituitary and Adrenal Glands
... FSH – a) in females: stimulates growth and development of ovarian follicles, and promotes estrogen secretion. b) in males: it is required for sperm production. LH – a) in females: responsible for ovulation and for luteinization. Regulates estrogen and progesterone. b) in males: stimulates inter ...
... FSH – a) in females: stimulates growth and development of ovarian follicles, and promotes estrogen secretion. b) in males: it is required for sperm production. LH – a) in females: responsible for ovulation and for luteinization. Regulates estrogen and progesterone. b) in males: stimulates inter ...
File - Ms. Poole`s Biology
... was removal of the testes to eliminate testosterone production. The two rats (normal and castrate) of each group were treated alike in all other ways (food, water, etc). All rats, except for those in the control group were injected with a hormone (ACTH, cortisol, LH, TRH, testosterone or TSH) on a d ...
... was removal of the testes to eliminate testosterone production. The two rats (normal and castrate) of each group were treated alike in all other ways (food, water, etc). All rats, except for those in the control group were injected with a hormone (ACTH, cortisol, LH, TRH, testosterone or TSH) on a d ...
13 Physiologicoanatomical peculiarities of endocrine system in
... acromegaly. GH-secreting tumors are typically recognized in the 5th decade of life. It is extremely rare for such a tumor to occur in childhood, but when it does the excessive GH can cause excessive growth, traditionally referred to as pituitary gigantism. ...
... acromegaly. GH-secreting tumors are typically recognized in the 5th decade of life. It is extremely rare for such a tumor to occur in childhood, but when it does the excessive GH can cause excessive growth, traditionally referred to as pituitary gigantism. ...
12Adrenal_Androgens2013-02
... Adrenal Androgens The adrenal cortex produces both androgens i.e. “male sex hormones” and estrogens or “female sex hormones. The adrenal cortex in both sexes produces small amounts of sex hormone of the opposite sex. Additional small amounts of sex hormones come from nonadrenal sources. Some testos ...
... Adrenal Androgens The adrenal cortex produces both androgens i.e. “male sex hormones” and estrogens or “female sex hormones. The adrenal cortex in both sexes produces small amounts of sex hormone of the opposite sex. Additional small amounts of sex hormones come from nonadrenal sources. Some testos ...
The Endocrine System - Leaving Cert Biology
... in the menstrual cycle and in preparing the female body for a possible conception • Testes: secrete testosterone which stimulates the changes that occur in the male at puberty and also help to maintain these changes (called secondary sexual characteristics) ...
... in the menstrual cycle and in preparing the female body for a possible conception • Testes: secrete testosterone which stimulates the changes that occur in the male at puberty and also help to maintain these changes (called secondary sexual characteristics) ...
Endocrine SystemExam
... 9. This is the gland that regulates the levels of calcium in the bloodstream: a. A b. D c. C d. B 10. Testosterone is secreted by this gland: a. H b. G c. A d. F 11. The gland found in the brain that “connects” the nervous system and the endocrine system is called the: a. Parathyroid b. Thyroid c. ...
... 9. This is the gland that regulates the levels of calcium in the bloodstream: a. A b. D c. C d. B 10. Testosterone is secreted by this gland: a. H b. G c. A d. F 11. The gland found in the brain that “connects” the nervous system and the endocrine system is called the: a. Parathyroid b. Thyroid c. ...
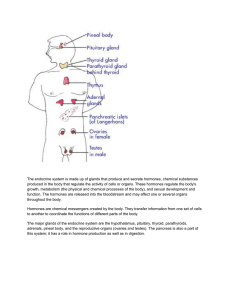
The endocrine system is founded on hormones and glands.
... when the adrenal glands don't produce enough corticosteroids. The symptoms of adrenal insufficiency may include weakness, fatigue, abdominal pain, nausea, dehydration, and skin changes. Growth hormone problems. Too much growth hormone in kids and teens who are still growing will make their bones and ...
... when the adrenal glands don't produce enough corticosteroids. The symptoms of adrenal insufficiency may include weakness, fatigue, abdominal pain, nausea, dehydration, and skin changes. Growth hormone problems. Too much growth hormone in kids and teens who are still growing will make their bones and ...
The Endocrine System
... • Produces a number of hormones, best known one is melatonin • Its function is not fully understood but it seems to play a role in biological rhythms e.g sleep ...
... • Produces a number of hormones, best known one is melatonin • Its function is not fully understood but it seems to play a role in biological rhythms e.g sleep ...
The Endocrine System - Immaculateheartacademy.org
... Target Tissue: Binds to receptors on the adrenal cortex gland and stimulates release of the Glucocorticoid hormones such as cortisol Target Tissue: Binds to melanocytes in the skin and increase skin pigmentaion ACTH is under the control of the ACTH releasing hormone secreted by the hypothalmus ...
... Target Tissue: Binds to receptors on the adrenal cortex gland and stimulates release of the Glucocorticoid hormones such as cortisol Target Tissue: Binds to melanocytes in the skin and increase skin pigmentaion ACTH is under the control of the ACTH releasing hormone secreted by the hypothalmus ...
Slide 1
... ↑ middle to late spermatogenesis = peak GSI (high # spermatocytes in testes) influence development of spermatogonia and repro. ducts routes of hormone transfer between testes and urogenital system: systemic circulation, binding sites in spermatozoa, enzymes in semen ...
... ↑ middle to late spermatogenesis = peak GSI (high # spermatocytes in testes) influence development of spermatogonia and repro. ducts routes of hormone transfer between testes and urogenital system: systemic circulation, binding sites in spermatozoa, enzymes in semen ...
Topic: The Endocrine System
... • Located behind the breastbone • Larger in infants, and shrinks as you get older • Secretes a hormone that is responsible for development and immunity ...
... • Located behind the breastbone • Larger in infants, and shrinks as you get older • Secretes a hormone that is responsible for development and immunity ...
Endocrine System
... • It has more sustained impulses • It is a “duct” less system. It gets secreted then heads directly to the blood stream. ...
... • It has more sustained impulses • It is a “duct” less system. It gets secreted then heads directly to the blood stream. ...
Chapter 14 Assignments, Study Guide, Word List, Pronunciation
... (also called testicle) the male gonads or reproductive glands, located in the scrotum (also called testis) either of the two male reproductive glands, enclosed within the scrotum, that produce spermatozoa and the hormone testosterone the sex hormone, secreted by the testes, that stimulates the d ...
... (also called testicle) the male gonads or reproductive glands, located in the scrotum (also called testis) either of the two male reproductive glands, enclosed within the scrotum, that produce spermatozoa and the hormone testosterone the sex hormone, secreted by the testes, that stimulates the d ...
Student Academic Learning Services The Endocrine System Quiz
... 6. Being lipid soluble, steroids can do all the following EXCEPT: A) B) C) D) ...
... 6. Being lipid soluble, steroids can do all the following EXCEPT: A) B) C) D) ...
Student Academic Learning Services The
... 6. Being lipid soluble, steroids can do all the following EXCEPT: A) B) C) D) ...
... 6. Being lipid soluble, steroids can do all the following EXCEPT: A) B) C) D) ...
Endocrine glands and their parts 1. Pituitary gland (hypophysis) 2
... Alpha cells of pancreatic islets (14) The cells of the islets of Langehans that secrete glucagon. Beta cells of pancreatic islets (15) The cells of the islets of Langehans that secrete insulin. Capsule of suprarenal gland (10) The tissue surrounding the adrenal glands. Corpus luteum (24) The rupture ...
... Alpha cells of pancreatic islets (14) The cells of the islets of Langehans that secrete glucagon. Beta cells of pancreatic islets (15) The cells of the islets of Langehans that secrete insulin. Capsule of suprarenal gland (10) The tissue surrounding the adrenal glands. Corpus luteum (24) The rupture ...
Endocrine System
... responsible for developing and maintaining female sexual traits, as well as maintaining a pregnancy. Along with the pituitary gonadotropins (luteinizing hormone or LH and follicle-stimulating hormone or FSH), they also control the menstrual cycle. The ovaries also produce inhibin, a protein that cur ...
... responsible for developing and maintaining female sexual traits, as well as maintaining a pregnancy. Along with the pituitary gonadotropins (luteinizing hormone or LH and follicle-stimulating hormone or FSH), they also control the menstrual cycle. The ovaries also produce inhibin, a protein that cur ...
Endocrine System
... metabolism, the immune system, and sexual development/function. • The inner part, or the Adrenal Medulla, makes hormones that increases blood pressure and heart rate when there is stress. ...
... metabolism, the immune system, and sexual development/function. • The inner part, or the Adrenal Medulla, makes hormones that increases blood pressure and heart rate when there is stress. ...
Definition Hormone - Home - KSU Faculty Member websites
... 1- protein hormones such as insulin . 2- Steroid hormones such as sex hormones . 3- Amino acid hormones such as thyroxine . ...
... 1- protein hormones such as insulin . 2- Steroid hormones such as sex hormones . 3- Amino acid hormones such as thyroxine . ...
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM: INTRODUCTION
... As a ductless gland, the pancreas produces two hormones. One of these is called insulin. Insulin is produced in clusters of cells scattered throughout the pancreas. These groups of cells are called the islets of Langerhans. Insulin controls the amount of sugar (glucose) in the blood. If the amount o ...
... As a ductless gland, the pancreas produces two hormones. One of these is called insulin. Insulin is produced in clusters of cells scattered throughout the pancreas. These groups of cells are called the islets of Langerhans. Insulin controls the amount of sugar (glucose) in the blood. If the amount o ...
Cryptorchidism

Cryptorchidism (derived from the Greek κρυπτός, kryptos, meaning hidden ὄρχις, orchis, meaning testicle) is the absence of one or both testes from the scrotum. It is the most common birth defect of the male genitalia. In unique cases, cryptorchidism can develop later in life, often as late as young adulthood. About 3% of full-term and 30% of premature infant boys are born with at least one undescended testis. However, about 80% of cryptorchid testes descend by the first year of life (the majority within three months), making the true incidence of cryptorchidism around 1% overall. Cryptorchidism is distinct from monorchism, the condition of having only one testicle.A testis absent from the normal scrotal position can be found:along the ""path of descent"" from high in the posterior (retroperitoneal) abdomen, just below the kidney, to the inguinal ring;in the inguinal canal;ectopically, that is, to have ""wandered"" from that path, usually outside the inguinal canal and sometimes even under the skin of the thigh, the perineum, the opposite scrotum, or the femoral canal;undeveloped (hypoplastic) or severely abnormal (dysgenetic);to have vanished (also see anorchia).About two thirds of cases without other abnormalities are unilateral; one third involve both testes. In 90% of cases an undescended testis can be felt in the inguinal canal; in a minority the testis or testes are in the abdomen or nonexistent (truly ""hidden"").Undescended testes are associated with reduced fertility, increased risk of testicular germ cell tumors and psychological problems when the boy is grown. Undescended testes are also more susceptible to testicular torsion (and subsequent infarction) and inguinal hernias. Without intervention, an undescended testicle will usually descend during the first year of life, but to reduce these risks, undescended testes can be brought into the scrotum in infancy by a surgical procedure called an orchiopexy.Although cryptorchidism nearly always refers to congenital absence or maldescent, a testis observed in the scrotum in early infancy can occasionally ""reascend"" (move back up) into the inguinal canal. A testis which can readily move or be moved between the scrotum and canal is referred to as retractile.