Course Outline Template Word Document - Physics for All
... semiconductors and nuclear physics. We will present a concise and comprehensive picture of quantum theory with emphasis on concept building. The concepts will be organized around the idea of wave particle duality and its consequences. Numerous applications to real world phenomena will be discussed t ...
... semiconductors and nuclear physics. We will present a concise and comprehensive picture of quantum theory with emphasis on concept building. The concepts will be organized around the idea of wave particle duality and its consequences. Numerous applications to real world phenomena will be discussed t ...
Chapter 6 Quantum Mechanics in One Dimension. Home
... (a) What value do you expect for < px > for the quantum oscillator? Support your answer with a symmetry argument rather than a calculation. (b) Energy principles for the quantum oscillator can be used to relate < p2x > to < x2 >. Use this relation, along with the value of < x2 > from Problem 32, to ...
... (a) What value do you expect for < px > for the quantum oscillator? Support your answer with a symmetry argument rather than a calculation. (b) Energy principles for the quantum oscillator can be used to relate < p2x > to < x2 >. Use this relation, along with the value of < x2 > from Problem 32, to ...
Aug 29 - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... Conjugates quantities of a particle (ex: position & momentum) can not be known simultaneously within a certain accuracy limit 2) Quantization: The measurement of a physical quantity in a confined system results in quanta (the measured values are discrete) 3) Wave-particle duality: All particles can ...
... Conjugates quantities of a particle (ex: position & momentum) can not be known simultaneously within a certain accuracy limit 2) Quantization: The measurement of a physical quantity in a confined system results in quanta (the measured values are discrete) 3) Wave-particle duality: All particles can ...
BWilliamsPaper - FSU High Energy Physics
... earth, and the earth in orbit around the sun, and so on. He was able to write a mathematical expression which quantified the force, called gravity, relating the attractive force between two objects to the product of their masses divided by the square of the distance between them. Newton also develo ...
... earth, and the earth in orbit around the sun, and so on. He was able to write a mathematical expression which quantified the force, called gravity, relating the attractive force between two objects to the product of their masses divided by the square of the distance between them. Newton also develo ...
Ideas of Modern Physics
... e. cannot be measured 5. A photon is found to have 100 eV of energy. Which answer is closest to its wavelength? a. 12000 nm b. 1200 nm c. 120 nm d. 12 nm ...
... e. cannot be measured 5. A photon is found to have 100 eV of energy. Which answer is closest to its wavelength? a. 12000 nm b. 1200 nm c. 120 nm d. 12 nm ...
Intro to Quantum Mechanics
... worry whether the measurement itself has changed what they were measuring. After all, what would be the sense in determining that a table is 80 cm long if the very act of measuring it changed its length! At the atomic scale of quantum mechanics, however, measurement becomes a very delicate process. ...
... worry whether the measurement itself has changed what they were measuring. After all, what would be the sense in determining that a table is 80 cm long if the very act of measuring it changed its length! At the atomic scale of quantum mechanics, however, measurement becomes a very delicate process. ...
Chem20u2(5.2) - Mr. Searcy Chemistry 20
... Unit II: Atoms and Elements 5.2 Quantum Theory and the Atom Pgs. 127-134 I. The learning objectives for this section are: 1. Define and give an example of: ground state, quantum mechanical model of the atom, atomic orbital, principal energy level, energy sublevel. 2. Summarize the contributions made ...
... Unit II: Atoms and Elements 5.2 Quantum Theory and the Atom Pgs. 127-134 I. The learning objectives for this section are: 1. Define and give an example of: ground state, quantum mechanical model of the atom, atomic orbital, principal energy level, energy sublevel. 2. Summarize the contributions made ...
Relativity Problem Set 9
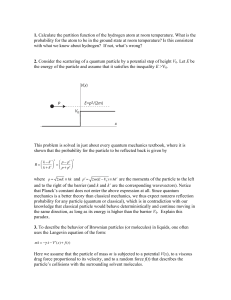
... We now consider the case where the total energy of each particle is smaller than the potential height, E < V0 . (a) Write down the wave function ψ(x) in the region x > 0. (b) Recall that for a beam of free particles, ψ ∗ (x)ψ(x) gives the number of particles per unit distance. Using this, discuss wh ...
... We now consider the case where the total energy of each particle is smaller than the potential height, E < V0 . (a) Write down the wave function ψ(x) in the region x > 0. (b) Recall that for a beam of free particles, ψ ∗ (x)ψ(x) gives the number of particles per unit distance. Using this, discuss wh ...
Chapter 8 - Fayetteville State University
... A. electrons in orbit around nuclei lose energy so slowly that the universe should exist for at least another five billion years. B. quantum theory is not applicable to the ultra-structure of an atom. C. electrons around a nucleus can have only certain particular energies and can only occupy certain ...
... A. electrons in orbit around nuclei lose energy so slowly that the universe should exist for at least another five billion years. B. quantum theory is not applicable to the ultra-structure of an atom. C. electrons around a nucleus can have only certain particular energies and can only occupy certain ...
Hw 20 - Cal Poly
... 3. Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle (HUP) says ΔxΔp ≥ ђ/2. Given the General Uncertainty Relation ΔAΔB ≥ |<[A, B]>|, prove HUP. Things to recall and/or note: - The right side of the inequality reads “the absolute value of the expectation value of the commutator of the operators A and B”. - The exp ...
... 3. Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle (HUP) says ΔxΔp ≥ ђ/2. Given the General Uncertainty Relation ΔAΔB ≥ |<[A, B]>|, prove HUP. Things to recall and/or note: - The right side of the inequality reads “the absolute value of the expectation value of the commutator of the operators A and B”. - The exp ...
1 ψ ω ω ω ψ ψ ψ
... to the square of the amplitude of the associated de Broglie wave. Amplitude of the associated wave is called the probability amplitude or the Wave function ...
... to the square of the amplitude of the associated de Broglie wave. Amplitude of the associated wave is called the probability amplitude or the Wave function ...
Quantum Disentanglement Eraser
... atomic cascade emission. • ‘Clicks’ at D3 or D4 provide which path information (No interference fringes!!) • ‘Clicks’ at D1 or D2 erase the which path information (Fringes!!) • absence or restoration of interference can be arranged via an appropriately contrived photon correlation experiment. ...
... atomic cascade emission. • ‘Clicks’ at D3 or D4 provide which path information (No interference fringes!!) • ‘Clicks’ at D1 or D2 erase the which path information (Fringes!!) • absence or restoration of interference can be arranged via an appropriately contrived photon correlation experiment. ...
Schrödinger`s `Cat-in-the-Box Experiment
... scientists to understand the behavior of particles in such environment. The two experiments are the double slit experiment and the Schrödinger cat paradox. I will introduce how those experiments were performed and a full analysis of its connection to the uncertainty principle. Probability wave funct ...
... scientists to understand the behavior of particles in such environment. The two experiments are the double slit experiment and the Schrödinger cat paradox. I will introduce how those experiments were performed and a full analysis of its connection to the uncertainty principle. Probability wave funct ...
Bohr–Einstein debates

The Bohr–Einstein debates were a series of public disputes about quantum mechanics between Albert Einstein and Niels Bohr. Their debates are remembered because of their importance to the philosophy of science. An account of the debates was written by Bohr in an article titled ""Discussions with Einsteinon Epistemological Problems in Atomic Physics"". Despite their differences of opinion regarding quantum mechanics, Bohr and Einstein had a mutual admiration that was to last the rest of their lives.The debates represent one of the highest points of scientific research in the first half of the twentieth century because it called attention to an element of quantum theory, quantum non-locality, which is absolutely central to our modern understanding of the physical world. The consensus view of professional physicists has been that Bohr proved victorious, and definitively established the fundamental probabilistic character of quantum measurement.