Streptococcus group A pneumonia P.H.M. D
... 43 IVDMs. Of the seven cases of S. pyogenes infection six were drug users, all of whom had signs of pulmonary infection. Since the documented large epidemics of the 1960's, streptococcal pneumonia has been seen only in sporadic cases, often with an underlying problem [4]. In streptococcal septicaemi ...
... 43 IVDMs. Of the seven cases of S. pyogenes infection six were drug users, all of whom had signs of pulmonary infection. Since the documented large epidemics of the 1960's, streptococcal pneumonia has been seen only in sporadic cases, often with an underlying problem [4]. In streptococcal septicaemi ...
Neonatal Infections
... - 50-85% meningitis cases have + blood culture - Yield reportedly low if respiratory distress is the only major sign of infection - Specific signs & symptoms occur in less than 50% of infants with meningitis - Using “selective criteria” for obtaining CSF may result in missed or delayed diagnosis in ...
... - 50-85% meningitis cases have + blood culture - Yield reportedly low if respiratory distress is the only major sign of infection - Specific signs & symptoms occur in less than 50% of infants with meningitis - Using “selective criteria” for obtaining CSF may result in missed or delayed diagnosis in ...
Bacterial Sepsis following Pregnancy
... Any woman with suspected bacterial sepsis should be carefully examined for skin and soft-tissue infection, particularly looking at intravenous cannulae or injection sites and caesarean or episiotomy wounds. Swabs should be taken of any discharge. If drains, vascular access devices or other indwellin ...
... Any woman with suspected bacterial sepsis should be carefully examined for skin and soft-tissue infection, particularly looking at intravenous cannulae or injection sites and caesarean or episiotomy wounds. Swabs should be taken of any discharge. If drains, vascular access devices or other indwellin ...
Coding Clinic clarifies SIRS query questions
... [in the Definitions document] is specific for sepsis. A high cardiac output is commonly observed following major surgical procedures or multiple traumas. Arterial hypotension can be caused by many conditions other than sepsis, such as acute left ventricular failure secondary to acute myocardial infa ...
... [in the Definitions document] is specific for sepsis. A high cardiac output is commonly observed following major surgical procedures or multiple traumas. Arterial hypotension can be caused by many conditions other than sepsis, such as acute left ventricular failure secondary to acute myocardial infa ...
Laboratory Animal Models to Mimic Human Sepsis: A Review
... represented by bacteria, although viruses [29] and even archaea [30] are also reported. The microbial profiling studies have revealed that the individual variation in terms of gut resident bacterial species is very high though common patterns have emerged at the phylum level. Gram negative Bacteroid ...
... represented by bacteria, although viruses [29] and even archaea [30] are also reported. The microbial profiling studies have revealed that the individual variation in terms of gut resident bacterial species is very high though common patterns have emerged at the phylum level. Gram negative Bacteroid ...
specimen collection - University of Glasgow
... Sterile venepuncture from peripheral sites “No touch technique” Decontaminate the bottle tops with 70% alcohol only. Draw 20ml of blood (for adults and older children), inoculate aerobic and anaerobic bottle with 10ml each. Change needles after venepuncture and between bottles. For infants draw 0.5- ...
... Sterile venepuncture from peripheral sites “No touch technique” Decontaminate the bottle tops with 70% alcohol only. Draw 20ml of blood (for adults and older children), inoculate aerobic and anaerobic bottle with 10ml each. Change needles after venepuncture and between bottles. For infants draw 0.5- ...
Stem Cell Therapy for Critical Illness involving
... are found in multicellular organisms, but are most commonly isolated from mammals. There are two broad types of mammalian stem cells: embryonic stem cells, which are isolated from embryos at early developmental stages, and adult stem cells, which are found in various adult tissues. In terms of clini ...
... are found in multicellular organisms, but are most commonly isolated from mammals. There are two broad types of mammalian stem cells: embryonic stem cells, which are isolated from embryos at early developmental stages, and adult stem cells, which are found in various adult tissues. In terms of clini ...
Infectious diseases/ Haematology/ Rheumatology/ Dermatology
... o Early consultation and multi-disciplinary approach o If >10% factor VIII activity – desmopressin may be tried, especially if past h/o response o Follow specialized treatment plans usually available with patient o Factor VII infusions – 3500IU bolus then 1750 IU 12hrly in severe bleeds, titrate sma ...
... o Early consultation and multi-disciplinary approach o If >10% factor VIII activity – desmopressin may be tried, especially if past h/o response o Follow specialized treatment plans usually available with patient o Factor VII infusions – 3500IU bolus then 1750 IU 12hrly in severe bleeds, titrate sma ...
FEVER: SYNOPSIS
... Ex: use ceftazidime or piperacillin-tazobactam Consider double coverage for possible resistant Pseudomonas Ex: add amikacin or tobramycin Consider gram-positive coverage (central line, skin infections) Ex: add vancomycin Consider anaerobic coverage (mucositis, typhlitis) Ex: use pipera ...
... Ex: use ceftazidime or piperacillin-tazobactam Consider double coverage for possible resistant Pseudomonas Ex: add amikacin or tobramycin Consider gram-positive coverage (central line, skin infections) Ex: add vancomycin Consider anaerobic coverage (mucositis, typhlitis) Ex: use pipera ...
SIRS - MODS
... Sepsis describes an infectious process that causes a systemic inflammatory response (SIRS) evidenced by fever, tachypnea, tachycardia and leukocytosis (Table 1). Mortality from sepsis occurs as a result of acquired, progressive abnormalities in organ function, a process known as multiple organ dysfu ...
... Sepsis describes an infectious process that causes a systemic inflammatory response (SIRS) evidenced by fever, tachypnea, tachycardia and leukocytosis (Table 1). Mortality from sepsis occurs as a result of acquired, progressive abnormalities in organ function, a process known as multiple organ dysfu ...
Neonatal Sepsis Powerpoint
... - 50-85% meningitis cases have + blood culture - Yield reportedly low if respiratory distress is the only major sign of infection - Specific signs & symptoms occur in less than 50% of infants with meningitis ...
... - 50-85% meningitis cases have + blood culture - Yield reportedly low if respiratory distress is the only major sign of infection - Specific signs & symptoms occur in less than 50% of infants with meningitis ...
G ICU
... Marked decline in renal function Decrease in renal blood flow, atrophy of the afferent and efferent arterioles, decrease in renal tubular cells Decrease ability to conserve sodium and water and excrete H Decrease in GFR about 45% by age 85 Serum creatinine remains unchanged due to decrease in lean b ...
... Marked decline in renal function Decrease in renal blood flow, atrophy of the afferent and efferent arterioles, decrease in renal tubular cells Decrease ability to conserve sodium and water and excrete H Decrease in GFR about 45% by age 85 Serum creatinine remains unchanged due to decrease in lean b ...
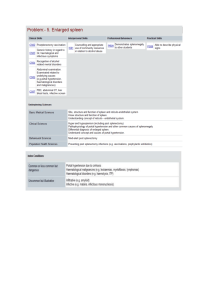
Problem 05- Enlarged Spleen
... vein, which then branches into smaller vessels and travels through the liver. If the vessels in the liver are blocked, it is hard for the blood to flow causing high pressure in the portal system. The most common cause of portal hypertension is cirrhosis of the liver. Cirrhosis results from scarring ...
... vein, which then branches into smaller vessels and travels through the liver. If the vessels in the liver are blocked, it is hard for the blood to flow causing high pressure in the portal system. The most common cause of portal hypertension is cirrhosis of the liver. Cirrhosis results from scarring ...
isolation and identification of bacteria associated
... wounds which may be produced in road accidents, by factory machinery. This type of wound is frequently contaminated and it supplies an excellent ...
... wounds which may be produced in road accidents, by factory machinery. This type of wound is frequently contaminated and it supplies an excellent ...
Hemobartonellosis in Cats
... pending. The infection is susceptible to tetracycline-type antibiotics (such as doxycycline), with clinical improvement noted within just a few days. The parasite is never completely eliminated from the blood, however, so cats may become chronic carriers. Relapse of infection is uncommon but can occ ...
... pending. The infection is susceptible to tetracycline-type antibiotics (such as doxycycline), with clinical improvement noted within just a few days. The parasite is never completely eliminated from the blood, however, so cats may become chronic carriers. Relapse of infection is uncommon but can occ ...
Empiric Treatment of Neonatal Sepsis in
... signs (not feeding well, convulsions, drowsiness or unconsciousness, movement only when stimulated or no movement at all, fast breathing ≥60 breaths/min, grunting, severe chest in-drawing, raised temperature >38°C, hypothermia <35.5°C or central cyanosis) and priority signs (severe jaundice, severe ...
... signs (not feeding well, convulsions, drowsiness or unconsciousness, movement only when stimulated or no movement at all, fast breathing ≥60 breaths/min, grunting, severe chest in-drawing, raised temperature >38°C, hypothermia <35.5°C or central cyanosis) and priority signs (severe jaundice, severe ...
to the printable PDF
... launched. Dental practitioners began advertising to their patients that they were “100-percenters,” which meant that the dentist would remove 100% of the patient’s teeth to prevent systemic disease. Medicine also embraced the concept of “focal infection” and tooth extraction was widely used in medic ...
... launched. Dental practitioners began advertising to their patients that they were “100-percenters,” which meant that the dentist would remove 100% of the patient’s teeth to prevent systemic disease. Medicine also embraced the concept of “focal infection” and tooth extraction was widely used in medic ...
Slide 1
... – A patient with a known defect in the immune system. – proposed definition – A patient who does not survive on infectious episode. ...
... – A patient with a known defect in the immune system. – proposed definition – A patient who does not survive on infectious episode. ...
Characteristics of Bacteria Virulence
... Brushing your teeth causes bacteremia with few effects. However, bacteremia can progress to sepsis. ...
... Brushing your teeth causes bacteremia with few effects. However, bacteremia can progress to sepsis. ...
Line associated infections and bacteraemia
... • Site of catheter – int. jugular > subclavian • Number of catheter days • Frequency of catheter manipulation • Setting of catheter placement i.e. emergency/elective ...
... • Site of catheter – int. jugular > subclavian • Number of catheter days • Frequency of catheter manipulation • Setting of catheter placement i.e. emergency/elective ...
O A Immunophenotyping of Lymphocyte Subpopulations and pre-inflammatory mediators in neonatal sepsis
... designed to elucidate the changes in the lymphocyte subsets and in the pre-inflammatory mediators; IL-6 and IL-1b in full-term neonates with sepsis Patients and methods: A prospective study was carried out at the neonatology intensive care unit of Cairo University in the period from June 2007 to Jun ...
... designed to elucidate the changes in the lymphocyte subsets and in the pre-inflammatory mediators; IL-6 and IL-1b in full-term neonates with sepsis Patients and methods: A prospective study was carried out at the neonatology intensive care unit of Cairo University in the period from June 2007 to Jun ...
Reservoir
... Infected cells swell (cyto-, mega-) Latent in white blood cells May be asymptomatic or mild Transmitted across the placenta; may cause mental ...
... Infected cells swell (cyto-, mega-) Latent in white blood cells May be asymptomatic or mild Transmitted across the placenta; may cause mental ...
Understand How ICD-10 Expands Sepsis Coding
... ICD-10-CM: A41.0, Z16, R65.21, J96.0 Acute respiratory failure As you can see, the changes in ICD-10-CM coding eliminate ICD-9-CM’s current code redundancy of coding sepsis due to infectious conditions. The ICD-10-CM coding system more accurately reflects the clinical significance and increased comp ...
... ICD-10-CM: A41.0, Z16, R65.21, J96.0 Acute respiratory failure As you can see, the changes in ICD-10-CM coding eliminate ICD-9-CM’s current code redundancy of coding sepsis due to infectious conditions. The ICD-10-CM coding system more accurately reflects the clinical significance and increased comp ...
SPONTANEOUS INFECTION OF A CEPHALOHEMATOMA
... Echerichia coli infection of a parietal cephalohematoma, that had never been incised for blood aspiration. This is a rare and dangerous event, following prolonged spontaneous labour, that can happen even without the use of surgical instruments. Although rare, cases of infected cephalohematomas are d ...
... Echerichia coli infection of a parietal cephalohematoma, that had never been incised for blood aspiration. This is a rare and dangerous event, following prolonged spontaneous labour, that can happen even without the use of surgical instruments. Although rare, cases of infected cephalohematomas are d ...
Sepsis
Sepsis (/ˈsɛpsɨs/) is a whole-body inflammatory response to an infection. Common signs and symptoms include fever, increased heart rate, increased breathing rate, and confusion. There may also be symptoms related to a specific infection, such as a cough with pneumonia, or painful urination with a kidney infection. In the very young, old, and people with a weakened immune system, there may be no symptoms of a specific infection and the body temperature may be low or normal rather than high. Severe sepsis is sepsis causing poor organ function or insufficient blood flow. Insufficient blood flow may be evident by low blood pressure, high blood lactate, or low urine output. Septic shock is low blood pressure due to sepsis that does not improve after reasonable amounts of intravenous fluids are given.Sepsis is caused by an immune response triggered by an infection. The infection is most commonly by bacteria, but can also be by fungi, viruses, or parasites. Common locations for the primary infection include: lungs, brain, urinary tract, skin, and abdominal organs. Risk factors include young or old age, a weakened immune system from conditions such as cancer or diabetes, and major trauma or burns. Diagnosis is based on meeting at least two systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) criteria due to a presumed infection. Blood cultures are recommended preferably before antibiotics are started; however, infection of the blood is not required for the diagnosis. Medical imaging should be done looking for the possible location of infection. Other potential causes of similar signs and symptoms include: anaphylaxis, adrenal insufficiency, low blood volume, heart failure, and pulmonary embolism among others.Sepsis is usually treated with intravenous fluids and antibiotics. This is often done in an intensive care unit. If fluid replacement is not enough to maintain blood pressure, medications that raise blood pressure can be used. Mechanical ventilation and dialysis may be needed to support the function of the lungs and kidneys, respectively. To guide treatment, a central venous catheter and an arterial catheter may be placed. Other measurements such as cardiac output and superior vena cava oxygen saturation may also be used. People with sepsis need preventive measures for deep vein thrombosis, stress ulcers and pressure ulcers, unless other conditions prevent such interventions. Some might benefit from tight control of blood sugar levels with insulin. The use of corticosteroids is controversial. Activated drotrecogin alfa, originally marketed for severe sepsis, has not been found to be helpful, and was withdrawn from sale in 2011.Disease severity partly determines the outcome with the risk of death from sepsis being as high as 30%, severe sepsis as high as 50%, and septic shock as high as 80%. The total number of cases worldwide is unknown as there is little data from the developing world. Estimates suggest sepsis affects millions of people a year. In the developed world about 0.2 to 3 per 1000 people gets sepsis yearly or about a million cases per year in the United States. Rates of disease have been increasing. Sepsis is more common among males than females. The terms septicemia and blood poisoning referred to the microorganisms or their toxins in the blood and are no longer commonly used. The condition has been described at least since the time of Hippocrates.