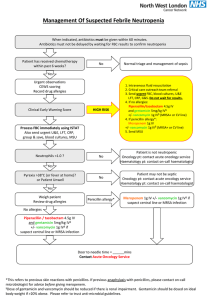
Infection Control: IV Drug Administration
... culture. • Send blood cultures & swab from site. • Monitor vital signs. • Remove the line - send tip to microbiology for culture. ...
... culture. • Send blood cultures & swab from site. • Monitor vital signs. • Remove the line - send tip to microbiology for culture. ...
Administration of IV Therapy
... culture. • Send blood cultures & swab from site. • Monitor vital signs. • Remove the line - send tip to microbiology for culture. ...
... culture. • Send blood cultures & swab from site. • Monitor vital signs. • Remove the line - send tip to microbiology for culture. ...
To Draw or Not to Draw: Drawing Blood Cultures From a Potentially
... superficial exudate can be aspirated and cultured from the port pocket, this should be done in an attempt to identify the organism and tailor antibiotic therapy appropriately (Wickham, Purl, & Welker, 1992). The catheter tunnel also should be inspected and palpated, as a tunnel infection may be pres ...
... superficial exudate can be aspirated and cultured from the port pocket, this should be done in an attempt to identify the organism and tailor antibiotic therapy appropriately (Wickham, Purl, & Welker, 1992). The catheter tunnel also should be inspected and palpated, as a tunnel infection may be pres ...
22 Staphylococci
... produce a serious septic condition. They are more commonly the cause of puerperal sepsis than other bacteria. ...
... produce a serious septic condition. They are more commonly the cause of puerperal sepsis than other bacteria. ...
CNS Infections - Columbia University
... Greater incidence of sepsis - immature immune function Greater incidence of meningitis - “Sepsis” work-up includes LP - difficult to distinguish viral from bacterial disease Clinical clues – high or low WBC irritability – non specific sx’s ...
... Greater incidence of sepsis - immature immune function Greater incidence of meningitis - “Sepsis” work-up includes LP - difficult to distinguish viral from bacterial disease Clinical clues – high or low WBC irritability – non specific sx’s ...
Post operative complications Classification
... abdomen these bands of tissue may form between or over loops of small bowel in particular. may lead to “kinking” or compression of small bowel loops, causing obstruction and even infarction of the blood ...
... abdomen these bands of tissue may form between or over loops of small bowel in particular. may lead to “kinking” or compression of small bowel loops, causing obstruction and even infarction of the blood ...
Infectious disseases in hospitals
... Animals: scrapie - sheep, bovine spongiform encephalopathy [BSE or Mad Cow Disease] Humans: Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease [CJD] Prions found in blood, tonsil and appendix tissue ...
... Animals: scrapie - sheep, bovine spongiform encephalopathy [BSE or Mad Cow Disease] Humans: Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease [CJD] Prions found in blood, tonsil and appendix tissue ...
Post-op Pain Control, Fever and Wound Care
... – to pull : No air leak x24 hours, usu < 100cc/24, d/c suction, full insp, rapid pull, CXR. Note pneumo resorbs at 1% thoracic volume / day ...
... – to pull : No air leak x24 hours, usu < 100cc/24, d/c suction, full insp, rapid pull, CXR. Note pneumo resorbs at 1% thoracic volume / day ...
Impact of macrolide therapy on mortality for patients with severe sepsis
... the ninth leading cause of death in the USA and is associated with a high fatality rate, significant morbidity and great financial cost [2]. Respiratory infections, whether community- or hospital-acquired, account for the largest number of sepsis cases [1–3]. Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) is on ...
... the ninth leading cause of death in the USA and is associated with a high fatality rate, significant morbidity and great financial cost [2]. Respiratory infections, whether community- or hospital-acquired, account for the largest number of sepsis cases [1–3]. Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) is on ...
EN: Procalcitonin (PCT) Reference Ranges
... laboratory findings and clinical signs, and interpret the concrete values in the context of the patient’s clinical situation. 1) Increased PCT levels may not always be related to systemic bacterial infection. There are a few situations described where PCT can be elevated by non-bacterial causes. The ...
... laboratory findings and clinical signs, and interpret the concrete values in the context of the patient’s clinical situation. 1) Increased PCT levels may not always be related to systemic bacterial infection. There are a few situations described where PCT can be elevated by non-bacterial causes. The ...
Sepsis-induced Innate and Adaptive Immune
... The Department of Pediatrics, Section of Critical Care Medicine, The Ohio State University College of Medicine; Nationwide Children’s Hospital; 3The Research Institute at Nationwide Children’s Hospital Abstract: The inflammatory response to sepsis has classically been characterized by an overactive ...
... The Department of Pediatrics, Section of Critical Care Medicine, The Ohio State University College of Medicine; Nationwide Children’s Hospital; 3The Research Institute at Nationwide Children’s Hospital Abstract: The inflammatory response to sepsis has classically been characterized by an overactive ...
Pathogenesis of Bacterial Disease
... can cause sepsis syndrome with shock and multiorgan failure strep may produce severe necrosis of muscles and fascia - "flesh eating" ...
... can cause sepsis syndrome with shock and multiorgan failure strep may produce severe necrosis of muscles and fascia - "flesh eating" ...
Host–pathogen interactions in sepsis
... toxic properties by itself.13 The toxicity of lipopolysaccharide is related to the host response to this microbial mediator. Similar pathogen-associated molecular pattern mediators exist in Gram-positive bacteria and fungi that induce a potentially harmful host response during severe sepsis. Superan ...
... toxic properties by itself.13 The toxicity of lipopolysaccharide is related to the host response to this microbial mediator. Similar pathogen-associated molecular pattern mediators exist in Gram-positive bacteria and fungi that induce a potentially harmful host response during severe sepsis. Superan ...
Clinical Syndromes – General - Assets
... Because the appropriateness of any therapy is based on a correct diagnosis, the main focus of the proper approach to the FUO patient is diagnostic rather than therapeutic. The diagnostic workup of the FUO patient should take into account the frequency of distribution of disorders, noninfectious as w ...
... Because the appropriateness of any therapy is based on a correct diagnosis, the main focus of the proper approach to the FUO patient is diagnostic rather than therapeutic. The diagnostic workup of the FUO patient should take into account the frequency of distribution of disorders, noninfectious as w ...
Prevalence of Metallo Beta Lactamase Production among
... factors (Home delivery, Meconium stained amniotic fluid) were present as risk factors (76-85%). Schuchat et al., (2000) found an obstetric risk factor-preterm delivery, intrapartum fever, or membrane rupture >/ =18 hours in 49% of GBS. Tallur et al., (2000) reported association of PROM > 24 hours in ...
... factors (Home delivery, Meconium stained amniotic fluid) were present as risk factors (76-85%). Schuchat et al., (2000) found an obstetric risk factor-preterm delivery, intrapartum fever, or membrane rupture >/ =18 hours in 49% of GBS. Tallur et al., (2000) reported association of PROM > 24 hours in ...
Clinical Manifestation
... Fail to capture causative organisms in bacteremia Unnecessary to diagnose sepsis ...
... Fail to capture causative organisms in bacteremia Unnecessary to diagnose sepsis ...
Diapositive 1 - UJF) Grenoble
... - Time consuming (days of incubation for lymphocyte proliferation), - Home-made protocols => difficult to standardize => Not suitable for routine monitoring - They remain essential to gain insights in the understanding of pathophysiology and to assess the validity of surrogate markers ...
... - Time consuming (days of incubation for lymphocyte proliferation), - Home-made protocols => difficult to standardize => Not suitable for routine monitoring - They remain essential to gain insights in the understanding of pathophysiology and to assess the validity of surrogate markers ...
Bacterial Gastrointestinal Infection
... acetylcholine release .. Flaccid paralysis, Respiratory or Cardiac failure.. Death.. Early Specific Antitoxin Treatment may help.. No Antibiotics ...
... acetylcholine release .. Flaccid paralysis, Respiratory or Cardiac failure.. Death.. Early Specific Antitoxin Treatment may help.. No Antibiotics ...
policy: infection control
... Rationale: Every reasonable attempt will be made to prevent the spread of infection at 3 Sisters Hacienda. A variety of infection control measures outlined below are used for decreasing the risk of transmission of organisms. All body and blood fluids will be considered infectious regardless of the p ...
... Rationale: Every reasonable attempt will be made to prevent the spread of infection at 3 Sisters Hacienda. A variety of infection control measures outlined below are used for decreasing the risk of transmission of organisms. All body and blood fluids will be considered infectious regardless of the p ...
Lecture 19 – Abnormalities of puerperium
... morbidity and mortality Definition of puerperal fever and puerperal sepsis Various puerperal abnormalities Causes of puerperal fever Aseptic and antiseptic measures to be adopted for the ...
... morbidity and mortality Definition of puerperal fever and puerperal sepsis Various puerperal abnormalities Causes of puerperal fever Aseptic and antiseptic measures to be adopted for the ...
National Estimates of Emergency Department Visits
... (defined by the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision codes), we identified children <18 years old presenting with both infection (triage fever or ICD9 infection) and organ dysfunction (triage hypotension or ICD-9 organ dysfunction). Results. Of 28.2 million pediatric patients pre ...
... (defined by the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision codes), we identified children <18 years old presenting with both infection (triage fever or ICD9 infection) and organ dysfunction (triage hypotension or ICD-9 organ dysfunction). Results. Of 28.2 million pediatric patients pre ...
Gas Gangrene
... Gangrene is necrosis and subsequent decay of body tissues caused by infection or thrombosis or lack of blood flow. It is usually the result of critically insufficient blood supply sometimes caused by injury and subsequent contamination with bacteria. This condition is most common in the extremities. ...
... Gangrene is necrosis and subsequent decay of body tissues caused by infection or thrombosis or lack of blood flow. It is usually the result of critically insufficient blood supply sometimes caused by injury and subsequent contamination with bacteria. This condition is most common in the extremities. ...
Bacteraemia diagnosis: blood cultures
... - bacteraemia is identified in only about 30% of patients with sepsis, depending on previous antibiotic treatment - early clinical sings of sepsis (fever, tachycardia and leucocytosis) are non-specific and overlap with sings of systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) of non-infectious origin ...
... - bacteraemia is identified in only about 30% of patients with sepsis, depending on previous antibiotic treatment - early clinical sings of sepsis (fever, tachycardia and leucocytosis) are non-specific and overlap with sings of systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) of non-infectious origin ...
Sepsis
Sepsis (/ˈsɛpsɨs/) is a whole-body inflammatory response to an infection. Common signs and symptoms include fever, increased heart rate, increased breathing rate, and confusion. There may also be symptoms related to a specific infection, such as a cough with pneumonia, or painful urination with a kidney infection. In the very young, old, and people with a weakened immune system, there may be no symptoms of a specific infection and the body temperature may be low or normal rather than high. Severe sepsis is sepsis causing poor organ function or insufficient blood flow. Insufficient blood flow may be evident by low blood pressure, high blood lactate, or low urine output. Septic shock is low blood pressure due to sepsis that does not improve after reasonable amounts of intravenous fluids are given.Sepsis is caused by an immune response triggered by an infection. The infection is most commonly by bacteria, but can also be by fungi, viruses, or parasites. Common locations for the primary infection include: lungs, brain, urinary tract, skin, and abdominal organs. Risk factors include young or old age, a weakened immune system from conditions such as cancer or diabetes, and major trauma or burns. Diagnosis is based on meeting at least two systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) criteria due to a presumed infection. Blood cultures are recommended preferably before antibiotics are started; however, infection of the blood is not required for the diagnosis. Medical imaging should be done looking for the possible location of infection. Other potential causes of similar signs and symptoms include: anaphylaxis, adrenal insufficiency, low blood volume, heart failure, and pulmonary embolism among others.Sepsis is usually treated with intravenous fluids and antibiotics. This is often done in an intensive care unit. If fluid replacement is not enough to maintain blood pressure, medications that raise blood pressure can be used. Mechanical ventilation and dialysis may be needed to support the function of the lungs and kidneys, respectively. To guide treatment, a central venous catheter and an arterial catheter may be placed. Other measurements such as cardiac output and superior vena cava oxygen saturation may also be used. People with sepsis need preventive measures for deep vein thrombosis, stress ulcers and pressure ulcers, unless other conditions prevent such interventions. Some might benefit from tight control of blood sugar levels with insulin. The use of corticosteroids is controversial. Activated drotrecogin alfa, originally marketed for severe sepsis, has not been found to be helpful, and was withdrawn from sale in 2011.Disease severity partly determines the outcome with the risk of death from sepsis being as high as 30%, severe sepsis as high as 50%, and septic shock as high as 80%. The total number of cases worldwide is unknown as there is little data from the developing world. Estimates suggest sepsis affects millions of people a year. In the developed world about 0.2 to 3 per 1000 people gets sepsis yearly or about a million cases per year in the United States. Rates of disease have been increasing. Sepsis is more common among males than females. The terms septicemia and blood poisoning referred to the microorganisms or their toxins in the blood and are no longer commonly used. The condition has been described at least since the time of Hippocrates.