When do I need antibiotics
... understand about wanting to get well sooner. The choice of antibiotic is determined by the most likely bacterial cause for the specific infection. The dose is often weight based, sometimes age based. Using a “stronger” or broader spectrum antibiotic than is necessary can do more harm than good. Inap ...
... understand about wanting to get well sooner. The choice of antibiotic is determined by the most likely bacterial cause for the specific infection. The dose is often weight based, sometimes age based. Using a “stronger” or broader spectrum antibiotic than is necessary can do more harm than good. Inap ...
Evaluation of procalcitonin as a marker of infection in a... sample of febrile hospitalized patients
... The main epidemiologic and clinical characteristics of these patients are shown in Table 1. The most common infection sites were lower respiratory tract (31), urinary tract (23), and intraabdominal infection (14). Microbiologically documented infections corresponded to Gram-positive bacteria (17), G ...
... The main epidemiologic and clinical characteristics of these patients are shown in Table 1. The most common infection sites were lower respiratory tract (31), urinary tract (23), and intraabdominal infection (14). Microbiologically documented infections corresponded to Gram-positive bacteria (17), G ...
Infection control
... • Patients should be transported only when necessary, and should be dressed appropriately with PPE for transport • Use dedicated patient care equipment. If equipment needs to be shared clean and disinfect between patients. • Consult the Infection Control policy IC-14 located on RHINO regarding ...
... • Patients should be transported only when necessary, and should be dressed appropriately with PPE for transport • Use dedicated patient care equipment. If equipment needs to be shared clean and disinfect between patients. • Consult the Infection Control policy IC-14 located on RHINO regarding ...
The Spleen - Home - KSU Faculty Member websites
... The risk of sepsis is approximately 60 times greater than normal after splenectomy The risk is greatest in children younger than four years of age The risk of sepsis is higher among patients requiring splenectomy for inherited diseases The risk of sepsis after splenectomy is lowest after tra ...
... The risk of sepsis is approximately 60 times greater than normal after splenectomy The risk is greatest in children younger than four years of age The risk of sepsis is higher among patients requiring splenectomy for inherited diseases The risk of sepsis after splenectomy is lowest after tra ...
ExThera Medical Presents Results of Cytomegalovirus (CMV
... Seraph is the only device reported to remove both bacteria and viruses directly from whole blood without adding anything to the blood being treated. It therefore has the potential to treat so-called ‘polymicrobial’ infections seen in critically i l l and immuno-compromised patients. According to Dr. ...
... Seraph is the only device reported to remove both bacteria and viruses directly from whole blood without adding anything to the blood being treated. It therefore has the potential to treat so-called ‘polymicrobial’ infections seen in critically i l l and immuno-compromised patients. According to Dr. ...
IPOKRaTES Foundation
... January 22-24, 2015 Objectives IPOKRaTES seminars provide high quality postgraduate education, which enables professional to keep abreast of the most recent developments and offer participants the opportunity to discuss clinical problems or scientific issues personally with international experts. Th ...
... January 22-24, 2015 Objectives IPOKRaTES seminars provide high quality postgraduate education, which enables professional to keep abreast of the most recent developments and offer participants the opportunity to discuss clinical problems or scientific issues personally with international experts. Th ...
Bacteremia and Sepsis - University of Yeditepe Faculty of
... • False positive results of blood culture • Contamination is due to skin commensals: coagulasenegative staphylococci(CoNS) or other skin flora But: • Depending on the clinical situation these skin flora may not represent pseudobacteremia ...
... • False positive results of blood culture • Contamination is due to skin commensals: coagulasenegative staphylococci(CoNS) or other skin flora But: • Depending on the clinical situation these skin flora may not represent pseudobacteremia ...
Febrile Neutropenia
... Eg 2: Pseudomonas: 2 weeks of IV antibiotics. G- sepsis generally requires 2 weeks of antibiotics ...
... Eg 2: Pseudomonas: 2 weeks of IV antibiotics. G- sepsis generally requires 2 weeks of antibiotics ...
Methodic_students_3
... Inflammatory process - is an important way to protect human body from various infections. An important component in elimination of the pathogen are cells of phagocytic system - monocytes, macrophages, granulocytes. With different antigens in the human body are fighting certain factors and certain co ...
... Inflammatory process - is an important way to protect human body from various infections. An important component in elimination of the pathogen are cells of phagocytic system - monocytes, macrophages, granulocytes. With different antigens in the human body are fighting certain factors and certain co ...
Slides
... Objectives Discuss initial management of various complex infectiousdisease scenarios ...
... Objectives Discuss initial management of various complex infectiousdisease scenarios ...
Bleeding and Shock
... Venous Bleeding • Rupture of 1+ veins • Less severe than arterial • Steady blood flow • Bluish-red blood • Easier to control ...
... Venous Bleeding • Rupture of 1+ veins • Less severe than arterial • Steady blood flow • Bluish-red blood • Easier to control ...
DOC - HCPro
... Sepsis if pt. has SIRS (WBC>14k, “left shift”, temp>101, HR>90, AMS, due to that infection ...
... Sepsis if pt. has SIRS (WBC>14k, “left shift”, temp>101, HR>90, AMS, due to that infection ...
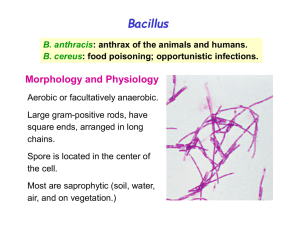
B. anthracis
... traumatic, penetrating injuries of the eye with a soilcontaminated object. intravenous catheter-related sepsis. Other infections: endocarditis, pneumonitis, sepsis, meningitis, etc. Symptomatic treatment is adequate for B. cereus gastroenteritis. The treatment of other Bacillus is complicated becaus ...
... traumatic, penetrating injuries of the eye with a soilcontaminated object. intravenous catheter-related sepsis. Other infections: endocarditis, pneumonitis, sepsis, meningitis, etc. Symptomatic treatment is adequate for B. cereus gastroenteritis. The treatment of other Bacillus is complicated becaus ...
Meningeal syndrome
... Overcoming of a protective barrier (meningococcaemia) Penetration of the agent through hematoencephalitic barrier, irritation of receptors of soft cerebral membrane of the brain and systems, forming cerebrospinal fluid Hypersecretion of cerebrospinal fluid Disorders of circulation of the blood in th ...
... Overcoming of a protective barrier (meningococcaemia) Penetration of the agent through hematoencephalitic barrier, irritation of receptors of soft cerebral membrane of the brain and systems, forming cerebrospinal fluid Hypersecretion of cerebrospinal fluid Disorders of circulation of the blood in th ...
Bleeding and Shock
... Venous Bleeding • Rupture of 1+ veins • Less severe than arterial • Steady blood flow • Bluish-red blood • Easier to control ...
... Venous Bleeding • Rupture of 1+ veins • Less severe than arterial • Steady blood flow • Bluish-red blood • Easier to control ...
Neonatal hypothermia
... scapula and in the mediastinum. when it used no replacement for it so it will finish when used and it is present till 6 month.it is mainly deposited during the 3rd trimester.so premature are with less brown fat. • Hypothermia leads to hypoglycemia, metabolic acidosis, loss of glycogen. ...
... scapula and in the mediastinum. when it used no replacement for it so it will finish when used and it is present till 6 month.it is mainly deposited during the 3rd trimester.so premature are with less brown fat. • Hypothermia leads to hypoglycemia, metabolic acidosis, loss of glycogen. ...
Streptoccocal Respiratory Infection
... Diagnosis & Treatment Lab Diagnosis: Culture.. Throat, Nose, Blood, Vagina, CSF. Definitive identification type of Hemolytic Strept. accomplished by using specific antistrepococcal sera by slide agglutination test. Detection Specific Antibodies: 2-4 weeks after throat or skin infection.. Antist ...
... Diagnosis & Treatment Lab Diagnosis: Culture.. Throat, Nose, Blood, Vagina, CSF. Definitive identification type of Hemolytic Strept. accomplished by using specific antistrepococcal sera by slide agglutination test. Detection Specific Antibodies: 2-4 weeks after throat or skin infection.. Antist ...
Health Care Associated Infections on the NICU (aka Nosocomial
... - Infants do not localize infections well - 50-85% meningitis cases have + blood culture - Specific signs & symptoms occur in less than 50% of infants with meningitis - Using “selective criteria” for obtaining CSF may result in missed or delayed diagnosis in up to 37% of infants with meningitis Wisw ...
... - Infants do not localize infections well - 50-85% meningitis cases have + blood culture - Specific signs & symptoms occur in less than 50% of infants with meningitis - Using “selective criteria” for obtaining CSF may result in missed or delayed diagnosis in up to 37% of infants with meningitis Wisw ...
Chapter 23 Powerpoint lecture
... • Clostridium perfringens, gram-positive, endospore-forming anaerobic rod, grows in necrotic tissue • Treatment includes surgical removal of necrotic tissue and/or ...
... • Clostridium perfringens, gram-positive, endospore-forming anaerobic rod, grows in necrotic tissue • Treatment includes surgical removal of necrotic tissue and/or ...
ICD-9-CM Implementations to Detect Severe Sepsis – Online
... o Pharmacologic immunosuppression (Prednisone >/= 20 mg for >/= 4 weeks, calcineurin inhibitor, methotrexate, tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitors, azathioprine, sulfasalazine, hydroxychloroquine, etc.) o Other (e.g. asplenia; please specify) 3. Were any of the following comorbidities present? o E ...
... o Pharmacologic immunosuppression (Prednisone >/= 20 mg for >/= 4 weeks, calcineurin inhibitor, methotrexate, tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitors, azathioprine, sulfasalazine, hydroxychloroquine, etc.) o Other (e.g. asplenia; please specify) 3. Were any of the following comorbidities present? o E ...
Sepsis
Sepsis (/ˈsɛpsɨs/) is a whole-body inflammatory response to an infection. Common signs and symptoms include fever, increased heart rate, increased breathing rate, and confusion. There may also be symptoms related to a specific infection, such as a cough with pneumonia, or painful urination with a kidney infection. In the very young, old, and people with a weakened immune system, there may be no symptoms of a specific infection and the body temperature may be low or normal rather than high. Severe sepsis is sepsis causing poor organ function or insufficient blood flow. Insufficient blood flow may be evident by low blood pressure, high blood lactate, or low urine output. Septic shock is low blood pressure due to sepsis that does not improve after reasonable amounts of intravenous fluids are given.Sepsis is caused by an immune response triggered by an infection. The infection is most commonly by bacteria, but can also be by fungi, viruses, or parasites. Common locations for the primary infection include: lungs, brain, urinary tract, skin, and abdominal organs. Risk factors include young or old age, a weakened immune system from conditions such as cancer or diabetes, and major trauma or burns. Diagnosis is based on meeting at least two systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) criteria due to a presumed infection. Blood cultures are recommended preferably before antibiotics are started; however, infection of the blood is not required for the diagnosis. Medical imaging should be done looking for the possible location of infection. Other potential causes of similar signs and symptoms include: anaphylaxis, adrenal insufficiency, low blood volume, heart failure, and pulmonary embolism among others.Sepsis is usually treated with intravenous fluids and antibiotics. This is often done in an intensive care unit. If fluid replacement is not enough to maintain blood pressure, medications that raise blood pressure can be used. Mechanical ventilation and dialysis may be needed to support the function of the lungs and kidneys, respectively. To guide treatment, a central venous catheter and an arterial catheter may be placed. Other measurements such as cardiac output and superior vena cava oxygen saturation may also be used. People with sepsis need preventive measures for deep vein thrombosis, stress ulcers and pressure ulcers, unless other conditions prevent such interventions. Some might benefit from tight control of blood sugar levels with insulin. The use of corticosteroids is controversial. Activated drotrecogin alfa, originally marketed for severe sepsis, has not been found to be helpful, and was withdrawn from sale in 2011.Disease severity partly determines the outcome with the risk of death from sepsis being as high as 30%, severe sepsis as high as 50%, and septic shock as high as 80%. The total number of cases worldwide is unknown as there is little data from the developing world. Estimates suggest sepsis affects millions of people a year. In the developed world about 0.2 to 3 per 1000 people gets sepsis yearly or about a million cases per year in the United States. Rates of disease have been increasing. Sepsis is more common among males than females. The terms septicemia and blood poisoning referred to the microorganisms or their toxins in the blood and are no longer commonly used. The condition has been described at least since the time of Hippocrates.