DNA-RNA-Protein Synthesis
... 1. Compare and contrast DNA and RNA. You may use a ven diagram, chart, table, or drawing. ...
... 1. Compare and contrast DNA and RNA. You may use a ven diagram, chart, table, or drawing. ...
DNA Technology and its Applications
... to change the information it contains. By changing this information, genetic engineering changes the type or amount of proteins an organism is capable of producing, thus enabling it to make new substances or perform new functions. ...
... to change the information it contains. By changing this information, genetic engineering changes the type or amount of proteins an organism is capable of producing, thus enabling it to make new substances or perform new functions. ...
TOPIC 4: GENETICS - Doctor Golub`s Living Environment
... The flounder is a species of fish that can live in very cold water. The fish produces an “antifreeze” protein that prevents ice crystals from forming in its blood. The DNA for this protein has been identified. An enzyme is used to cut and remove this section of flounder DNA that is then spliced into ...
... The flounder is a species of fish that can live in very cold water. The fish produces an “antifreeze” protein that prevents ice crystals from forming in its blood. The DNA for this protein has been identified. An enzyme is used to cut and remove this section of flounder DNA that is then spliced into ...
TruSight One Sequencing Panel Workflow
... Streamline your laboratory’s workflow. Illumina can take you from DNA sample to sequence to report in just four days*—increasing productivity, reducing handling errors and lowering costs. And this is just the beginning. Planned enhancements will further shorten workflow time from sample to report, w ...
... Streamline your laboratory’s workflow. Illumina can take you from DNA sample to sequence to report in just four days*—increasing productivity, reducing handling errors and lowering costs. And this is just the beginning. Planned enhancements will further shorten workflow time from sample to report, w ...
CHAPTER 10
... – DNA replication follows a semiconservative model – The two DNA strands separate – Each strand is used as a pattern to produce a complementary strand, using specific base pairing – Each new DNA helix has one old strand with one new strand – A binds T – C binds G ...
... – DNA replication follows a semiconservative model – The two DNA strands separate – Each strand is used as a pattern to produce a complementary strand, using specific base pairing – Each new DNA helix has one old strand with one new strand – A binds T – C binds G ...
DNA profiling - Our eclass community
... Biotechnology is using living things to create products or to do tasks for human beings. It is the practice of using plants, animals and micro-organisms and ...
... Biotechnology is using living things to create products or to do tasks for human beings. It is the practice of using plants, animals and micro-organisms and ...
1.PtI.SNPs and TAS2R38 Bitter Taste Receptor Gene.v3
... What Are Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs)? •! Polymorphism - refers to the presence of more than one allele of a gene in a population –! The frequency of this allele is greater than 1% of the population –! It is stable. –! The above distinguish it from a mutation. •! A SNP is a specific type ...
... What Are Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs)? •! Polymorphism - refers to the presence of more than one allele of a gene in a population –! The frequency of this allele is greater than 1% of the population –! It is stable. –! The above distinguish it from a mutation. •! A SNP is a specific type ...
Prokaryotes, Viruses, and Protistans
... Single-celled organisms that are too small to be seen without a microscope Bacteria are the smallest living organisms ...
... Single-celled organisms that are too small to be seen without a microscope Bacteria are the smallest living organisms ...
Ch 20 GR
... 3. What is the other name for restriction enzymes and what do these enzymes do for bacteria in “Nature”? 4. Define the following terms a. Restriction site b. Restriction fragments c. Sticky end 5. Label the following diagram. ...
... 3. What is the other name for restriction enzymes and what do these enzymes do for bacteria in “Nature”? 4. Define the following terms a. Restriction site b. Restriction fragments c. Sticky end 5. Label the following diagram. ...
Manipulating DNA - tools and techniques 2012
... Enzymes cleave DNA at specific sites These enzymes are significant in two ways 1. Allow a form of physical mapping that was previously impossible 2. Allow the creation of recombinant DNA molecules (from two different sources) ...
... Enzymes cleave DNA at specific sites These enzymes are significant in two ways 1. Allow a form of physical mapping that was previously impossible 2. Allow the creation of recombinant DNA molecules (from two different sources) ...
DNA - Paxon Biology
... - Both strands of each new helix contain both a mixture of old and new DNA. ...
... - Both strands of each new helix contain both a mixture of old and new DNA. ...
Cells
... 2 divisions result in 4 daughter cells. Each daughter cell contains 23 chromosomes. Resulting gamete may unite with another gamete to create a zygote. The zygote inherits the DNA, half from each parent, to develop and function normally. ...
... 2 divisions result in 4 daughter cells. Each daughter cell contains 23 chromosomes. Resulting gamete may unite with another gamete to create a zygote. The zygote inherits the DNA, half from each parent, to develop and function normally. ...
Topic Definition 3` Refers to the third carbon of the nucleic acid
... that gene. Exons are found only in eukaryotic genomes, and are separated by introns. Although the introns are transcribed with the exons, the latter are spliced out and discarded during RNA processing. A frame is a single series of adjacent nucleotide triplets in DNA or RNA: one frame would have bas ...
... that gene. Exons are found only in eukaryotic genomes, and are separated by introns. Although the introns are transcribed with the exons, the latter are spliced out and discarded during RNA processing. A frame is a single series of adjacent nucleotide triplets in DNA or RNA: one frame would have bas ...
2054, Chap. 13, page 1 I. Microbial Recombination and Plasmids
... A. recombination = process of combining genetic material from 2 organisms to produce a genotype different from either parent (exchange of DNA between different genes) 1. occurs during meiosis as crossing over between homologous chromosomes 2. genetic recombination (homologous recombination) is the m ...
... A. recombination = process of combining genetic material from 2 organisms to produce a genotype different from either parent (exchange of DNA between different genes) 1. occurs during meiosis as crossing over between homologous chromosomes 2. genetic recombination (homologous recombination) is the m ...
Topic Definition 3` Refers to the third carbon of the nucleic acid
... that gene. Exons are found only in eukaryotic genomes, and are separated by introns. Although the introns are transcribed with the exons, the latter are spliced out and discarded during RNA processing. A frame is a single series of adjacent nucleotide triplets in DNA or RNA: one frame would have bas ...
... that gene. Exons are found only in eukaryotic genomes, and are separated by introns. Although the introns are transcribed with the exons, the latter are spliced out and discarded during RNA processing. A frame is a single series of adjacent nucleotide triplets in DNA or RNA: one frame would have bas ...
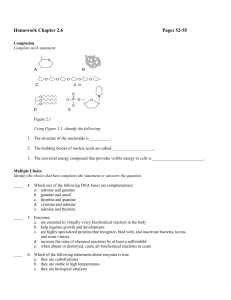
Homework Chapter 2.6 Pages 52-55 Completion Complete each
... c. are highly specialized proteins that recognize, bind with, and inactivate bacteria, toxins, and some viruses d. increase the rates of chemical reactions by at least a millionfold e. when absent or destroyed, cause all biochemical reactions to cease ...
... c. are highly specialized proteins that recognize, bind with, and inactivate bacteria, toxins, and some viruses d. increase the rates of chemical reactions by at least a millionfold e. when absent or destroyed, cause all biochemical reactions to cease ...
Chapter 12 Learning Objectives
... 14. Explain the differences between the three types of RNA and explain their roles 15. Explain that changing the activity of proteins within cells and/or by changing whether and how often particular genes are expressed (i.e. “regulating genes”) can change how cells function 16. Explain how most euka ...
... 14. Explain the differences between the three types of RNA and explain their roles 15. Explain that changing the activity of proteins within cells and/or by changing whether and how often particular genes are expressed (i.e. “regulating genes”) can change how cells function 16. Explain how most euka ...
Genetics BOE approved April 15, 2010 Learner Objective: Cells go
... Learner Objective: Chromosomal patterns have an effect on the phenotype of an organism. A. A chromosome includes DNA and the proteins that allow DNA to be replicated. B. The 24 chromosomes in a human cell are distinguished by size, shape, staining pattern and DNA sequence. C. Extra sets of chromosom ...
... Learner Objective: Chromosomal patterns have an effect on the phenotype of an organism. A. A chromosome includes DNA and the proteins that allow DNA to be replicated. B. The 24 chromosomes in a human cell are distinguished by size, shape, staining pattern and DNA sequence. C. Extra sets of chromosom ...
11. Use the following mRNA codon key as needed to... GCC Alanine AAU
... A mutation has been found in the DNA sequence below, indicated with the box. Comparing this sequence to the normal sequence, what effect will this mutation have on the protein ultimately produced from this gene, and why? Normal: 5ʼGGGTATAAT3ʼ template 3ʼCCCATATTA5ʼ coding Mutation: 5ʼ GGGTAGGAT 3ʼ t ...
... A mutation has been found in the DNA sequence below, indicated with the box. Comparing this sequence to the normal sequence, what effect will this mutation have on the protein ultimately produced from this gene, and why? Normal: 5ʼGGGTATAAT3ʼ template 3ʼCCCATATTA5ʼ coding Mutation: 5ʼ GGGTAGGAT 3ʼ t ...
Ingenious Genes Curriculum Links for AQA GCSE Biology (8461
... • the cell divides twice to form four gametes, each with a single set of chromosomes • all gametes are genetically different from each other. Gametes join at fertilisation to restore the normal number of chromosomes. The new cell divides by mitosis. The number of cells increases. As the embryo devel ...
... • the cell divides twice to form four gametes, each with a single set of chromosomes • all gametes are genetically different from each other. Gametes join at fertilisation to restore the normal number of chromosomes. The new cell divides by mitosis. The number of cells increases. As the embryo devel ...
DNA consists of two strands, each of which is a linear arrangement
... two strands are involved, it is known as a double helix. The length of a short segment of DNA is usually measured in terms of the number of base pairs (bp). Longer segments are measured in terms of kilobases (1 kb = 1000 bases) or even megabases (1 Mb = 1000 kb). The most important aspect of DNA str ...
... two strands are involved, it is known as a double helix. The length of a short segment of DNA is usually measured in terms of the number of base pairs (bp). Longer segments are measured in terms of kilobases (1 kb = 1000 bases) or even megabases (1 Mb = 1000 kb). The most important aspect of DNA str ...
Lab Business - Memorial University
... interest, because (1) the method is “well understood, widely used, and fairly uniform” and hence not a strong candidate for protection, (2) the necessary information to make a cDNA is typically in the public domain, for example BRCA sequences are in GenBank, and (3) cDNAs are generally of commercial ...
... interest, because (1) the method is “well understood, widely used, and fairly uniform” and hence not a strong candidate for protection, (2) the necessary information to make a cDNA is typically in the public domain, for example BRCA sequences are in GenBank, and (3) cDNAs are generally of commercial ...
DNA supercoil

DNA supercoiling refers to the over- or under-winding of a DNA strand, and is an expression of the strain on that strand. Supercoiling is important in a number of biological processes, such as compacting DNA. Additionally, certain enzymes such as topoisomerases are able to change DNA topology to facilitate functions such as DNA replication or transcription. Mathematical expressions are used to describe supercoiling by comparing different coiled states to relaxed B-form DNA.As a general rule, the DNA of most organisms is negatively supercoiled.