EOC Review 2 - Wayne County Public Schools
... Skin color, eye color, height are determined by many genes and are called _________ traits. The phenotype that shows up more frequently are blended. • polygenic ...
... Skin color, eye color, height are determined by many genes and are called _________ traits. The phenotype that shows up more frequently are blended. • polygenic ...
Control of Gene Expression
... culture and give rise to differentiated cells But they are harder to culture than embryonic stem cells. They generally give rise to only a limited range of cell types, in contrast with embryonic stem cells. ...
... culture and give rise to differentiated cells But they are harder to culture than embryonic stem cells. They generally give rise to only a limited range of cell types, in contrast with embryonic stem cells. ...
Biology 30 Unit C 1 Mr. R. Peebles Biology 30
... • the simplest forms of life all contain DNA • it is the only molecule that we know can replicate itself • DNA makes up the genes (100 000) found on the chromosomes • it provides continuity of life from generation to generation • it is responsible for cells ability to repair itself and reproduce • i ...
... • the simplest forms of life all contain DNA • it is the only molecule that we know can replicate itself • DNA makes up the genes (100 000) found on the chromosomes • it provides continuity of life from generation to generation • it is responsible for cells ability to repair itself and reproduce • i ...
Academic Biology
... Describe some sex-linked disorders and explain why they are more common in males than in females o o o Male only receives sex-linked alleles from his_________________ o Male needs _____ copy of the sex-linked allele to exhibit the recessive trait o Female must inherit _________recessive alleles – on ...
... Describe some sex-linked disorders and explain why they are more common in males than in females o o o Male only receives sex-linked alleles from his_________________ o Male needs _____ copy of the sex-linked allele to exhibit the recessive trait o Female must inherit _________recessive alleles – on ...
Transposition and transposable elements
... • cut themselves out of original site, producing double strand break • cut target site and ligate to element ends, thereby inserting at new site • original site break repaired usually with sister chromosome, restoring transposon at original site sometimes end healed without transposon, can also be a ...
... • cut themselves out of original site, producing double strand break • cut target site and ligate to element ends, thereby inserting at new site • original site break repaired usually with sister chromosome, restoring transposon at original site sometimes end healed without transposon, can also be a ...
Week 5 EOC Review DNA, Mitosis, Meiosis, and Genetics
... will also need to know that the basic processes of DNA are universal in organisms. o Similarities in the genetic codes of organisms are due to common ancestry and the process of inheritance. • The differences and similarities in the processes of mitosis and meiosis and relate these to the processes ...
... will also need to know that the basic processes of DNA are universal in organisms. o Similarities in the genetic codes of organisms are due to common ancestry and the process of inheritance. • The differences and similarities in the processes of mitosis and meiosis and relate these to the processes ...
From DNA To Protein
... • Bases in DNA and bases in mRNA strands are same in all organisms • Only sequence of bases differs • Each codon of mRNA “codes” for a particular amino acid or a stop codon • Genetic code can be translated to determine amino acid sequence for proteins from any section of DNA • Since all organisms us ...
... • Bases in DNA and bases in mRNA strands are same in all organisms • Only sequence of bases differs • Each codon of mRNA “codes” for a particular amino acid or a stop codon • Genetic code can be translated to determine amino acid sequence for proteins from any section of DNA • Since all organisms us ...
mutation PP
... to be made, while at other times it can be “turned off” (inhibited or repressed) to save energy - like a light bulb • Genes also change over time, like people do. A mutation is a change in a DNA sequence. ...
... to be made, while at other times it can be “turned off” (inhibited or repressed) to save energy - like a light bulb • Genes also change over time, like people do. A mutation is a change in a DNA sequence. ...
Revised Higher Human Biology Unit 1 Revision Summary STEM
... membrane of the mitochondrion. The movement of H+ ions from a HC to a LC across the membrane rotate ATP synthase molecule, producing ATP from ADP and P. In glycolysis, glucose (a 6C compound) is broken down into pyruvate. Glycolysis is a series of enzyme controlled steps, and occurs in two main stag ...
... membrane of the mitochondrion. The movement of H+ ions from a HC to a LC across the membrane rotate ATP synthase molecule, producing ATP from ADP and P. In glycolysis, glucose (a 6C compound) is broken down into pyruvate. Glycolysis is a series of enzyme controlled steps, and occurs in two main stag ...
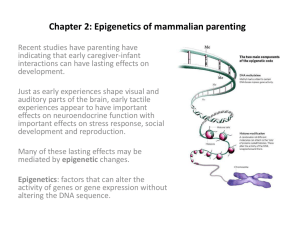
Chapter 2: Epigenetics of mammalian parenting
... • Decrease hippocampal plasticity – reduced learning and memory capacity • All these effects are traceable to changes in neurotransmitter receptor and activity levels in the brain. ...
... • Decrease hippocampal plasticity – reduced learning and memory capacity • All these effects are traceable to changes in neurotransmitter receptor and activity levels in the brain. ...
Slide 1
... • Discovered the method by which “crossing over” of chromosomes or genetic recombination occurs. • She did this despite facing considerable sexism, in a field where women were almost universally excluded. ...
... • Discovered the method by which “crossing over” of chromosomes or genetic recombination occurs. • She did this despite facing considerable sexism, in a field where women were almost universally excluded. ...
How is coordinated DNA damage repair and control of mitotic
... Candidates are welcome for a Postdoctoral position at Gustave Roussy Cancer Campus, Villejuif, France. Applications for funding will be submitted to European or French agencies (EMBO fellowships…). During proliferation, all somatic cells reproducibly execute an intermediate G2 phase, of up to severa ...
... Candidates are welcome for a Postdoctoral position at Gustave Roussy Cancer Campus, Villejuif, France. Applications for funding will be submitted to European or French agencies (EMBO fellowships…). During proliferation, all somatic cells reproducibly execute an intermediate G2 phase, of up to severa ...
Exam3-1406_Spring'06.doc
... 35) The anticodon for AUC is A) TAG. B) AUC. C) GAU. D) CUA. E) UAG. 36) The process of converting the "message" of mRNA into a sequence of amino acids is called A) translation. B) transcription. C) activation. D) replication. E) repression. 37) The site of protein synthesis is the A) smooth endopla ...
... 35) The anticodon for AUC is A) TAG. B) AUC. C) GAU. D) CUA. E) UAG. 36) The process of converting the "message" of mRNA into a sequence of amino acids is called A) translation. B) transcription. C) activation. D) replication. E) repression. 37) The site of protein synthesis is the A) smooth endopla ...
DNA CODES…
... TRANSLATED one codon at a time by tRNA molecules that each carries a particular amino acid. The tRNA has a portion called an anticodon that matches up to the codon found on the mRNA molecule. The codon and the anticodon are groups of three nitrogen bases. As the tRNA molecules line up along the mRNA ...
... TRANSLATED one codon at a time by tRNA molecules that each carries a particular amino acid. The tRNA has a portion called an anticodon that matches up to the codon found on the mRNA molecule. The codon and the anticodon are groups of three nitrogen bases. As the tRNA molecules line up along the mRNA ...
DNA RNA Proteins
... 3.inversion: if a fragment reattaches to the original chromosome but in the reverse direction. Less likely than deletions or duplications to produce harmful effects, because all genes are still present in normal number 4. translocation: moves a segment from one chromosome to another nonhomolog ...
... 3.inversion: if a fragment reattaches to the original chromosome but in the reverse direction. Less likely than deletions or duplications to produce harmful effects, because all genes are still present in normal number 4. translocation: moves a segment from one chromosome to another nonhomolog ...
Code Breaker - Georgia Tech ISyE
... by targeting thousands of variations within human genes, acquired this new area of discovery called histone methylation. Histones are through inherited mutations or through changes resulting from proteins that are part of the complex packaging of DNA within the environmental influences or disease. n ...
... by targeting thousands of variations within human genes, acquired this new area of discovery called histone methylation. Histones are through inherited mutations or through changes resulting from proteins that are part of the complex packaging of DNA within the environmental influences or disease. n ...
Carrots and Genomics
... • A plant consists of many different cells, each with identical DNA content • DNA consists of two complementary strands • During duplication, each strand acts as a template to produce two identical copies • Duplication of DNA occurs prior to: – Cell division → two identical diploïd cells – Gamete pr ...
... • A plant consists of many different cells, each with identical DNA content • DNA consists of two complementary strands • During duplication, each strand acts as a template to produce two identical copies • Duplication of DNA occurs prior to: – Cell division → two identical diploïd cells – Gamete pr ...
The chemical components in DNA
... (2) Nucleotides are linked by phosphodiester bridges from 3’ to 5’; (3) Polymers of ribonucleotides are ribonucleic acids, or RNA; (4) Polymers of deoxyribonucleotides are deoxyribonucleic acids, or DNA; (1) DNA are found in different cells and viruses. They code for genetic information; (2) DNA nea ...
... (2) Nucleotides are linked by phosphodiester bridges from 3’ to 5’; (3) Polymers of ribonucleotides are ribonucleic acids, or RNA; (4) Polymers of deoxyribonucleotides are deoxyribonucleic acids, or DNA; (1) DNA are found in different cells and viruses. They code for genetic information; (2) DNA nea ...
this lesson
... • Applied direct current to separate molecules based on charge and size • The higher the voltage, the faster separation will be achieved • Can be done in liquid or gel medium, slab or capillary ...
... • Applied direct current to separate molecules based on charge and size • The higher the voltage, the faster separation will be achieved • Can be done in liquid or gel medium, slab or capillary ...
How to isolate DNA from yeast
... least 30 sec. This operation is repeated as many times as necessary (5-15 in our experience) until more than 90% of the cells have been broken (determined by measuring the ratio of intact cells to cell ghosts by phase contrast microscopy; quality of liberated nuclei may be assessed by fluorescence m ...
... least 30 sec. This operation is repeated as many times as necessary (5-15 in our experience) until more than 90% of the cells have been broken (determined by measuring the ratio of intact cells to cell ghosts by phase contrast microscopy; quality of liberated nuclei may be assessed by fluorescence m ...
Genetic engineering
... - are special enzymes used to cut the DNA at specific places. - different enzymes cut DNA at specific base sequences known as a recognition site. For example i) One restriction enzyme will always cut DNA at the base sequence: GAATTC. ii) Another restriction enzyme only cuts at the sequence: GATC. - ...
... - are special enzymes used to cut the DNA at specific places. - different enzymes cut DNA at specific base sequences known as a recognition site. For example i) One restriction enzyme will always cut DNA at the base sequence: GAATTC. ii) Another restriction enzyme only cuts at the sequence: GATC. - ...
MBLG1001 Lecture 9 The Flow of Genetic Information Replication
... • In the first generation after medium change the DNA would be composed of solely H:L • In the next generation you would expect H:L and L:L in a ratio of 1:1. • In the following generation the H:L and L:L would have a ratio of 1:3. In the next generation it would be 1:7. ...
... • In the first generation after medium change the DNA would be composed of solely H:L • In the next generation you would expect H:L and L:L in a ratio of 1:1. • In the following generation the H:L and L:L would have a ratio of 1:3. In the next generation it would be 1:7. ...
DNA supercoil

DNA supercoiling refers to the over- or under-winding of a DNA strand, and is an expression of the strain on that strand. Supercoiling is important in a number of biological processes, such as compacting DNA. Additionally, certain enzymes such as topoisomerases are able to change DNA topology to facilitate functions such as DNA replication or transcription. Mathematical expressions are used to describe supercoiling by comparing different coiled states to relaxed B-form DNA.As a general rule, the DNA of most organisms is negatively supercoiled.