Macromolecular Sequence Analysis Biological sequences
... Due to the various properties of the amino acid side chains, certain residues are found more often in one or the other structural units. Some residues have been classified, for example, as α-helix breakers. Proline for example is a poor helix former due to the fact that its backbone N atom is alread ...
... Due to the various properties of the amino acid side chains, certain residues are found more often in one or the other structural units. Some residues have been classified, for example, as α-helix breakers. Proline for example is a poor helix former due to the fact that its backbone N atom is alread ...
Module B Keystone Exam Practice problems File
... 4. Hemophilia is an inheritable genetic disorder that prohibits the proper formation of blood clots. The recessive gene that causes hemophilia is located on the X-chromosome. Given this information, which of the following statements is true? a. In order for a male offspring to be a hemophiliac, his ...
... 4. Hemophilia is an inheritable genetic disorder that prohibits the proper formation of blood clots. The recessive gene that causes hemophilia is located on the X-chromosome. Given this information, which of the following statements is true? a. In order for a male offspring to be a hemophiliac, his ...
Chapter 7: Microbial Genetics 10/8/2015
... Prokaryotic DNA replication proceeds in both directions from the Origin until the 2 forks meet and the new copies are enzymatically separated from each other. • eukaryotic chromosomes are linear which requires special enzymes to complete replication of the ends, and they also have multiple origins o ...
... Prokaryotic DNA replication proceeds in both directions from the Origin until the 2 forks meet and the new copies are enzymatically separated from each other. • eukaryotic chromosomes are linear which requires special enzymes to complete replication of the ends, and they also have multiple origins o ...
Chapter 6A
... We previously have noted that gene evolution has involved exon shuffling between protein-coding genes in the genome. A large amount of shuffling has occurred due to the prevalence of interspersed repeats in the genome. Due to sequence conservation within these regions, crossover events can take plac ...
... We previously have noted that gene evolution has involved exon shuffling between protein-coding genes in the genome. A large amount of shuffling has occurred due to the prevalence of interspersed repeats in the genome. Due to sequence conservation within these regions, crossover events can take plac ...
Module 2 Keystone Review File - Dallastown Area School District
... i. the principle of independent assortment states that genes for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes 12. some alleles are neither dominant nor recessive, and many traits are controlled by multiple alleles or multiple genes a. incomplete dominance (RedXWhite = ...
... i. the principle of independent assortment states that genes for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes 12. some alleles are neither dominant nor recessive, and many traits are controlled by multiple alleles or multiple genes a. incomplete dominance (RedXWhite = ...
Presentation
... • 11.3 How Is DNA Replicated? • 11.4 How Are Errors in DNA Repaired? • 11.5 What Are Some Applications of Our Knowledge of DNA Structure and ...
... • 11.3 How Is DNA Replicated? • 11.4 How Are Errors in DNA Repaired? • 11.5 What Are Some Applications of Our Knowledge of DNA Structure and ...
Chapter 17 Presentation Transcription and Gene Expression
... completely separate from histone methylation, but may also be a way in which genes become inactivated. Evidence: Inactivated X chromosomes are heavily methylated. In many cells that have inactivated genes, the genes are more heavily methylated than in cells where the genes are active. ...
... completely separate from histone methylation, but may also be a way in which genes become inactivated. Evidence: Inactivated X chromosomes are heavily methylated. In many cells that have inactivated genes, the genes are more heavily methylated than in cells where the genes are active. ...
The Art and Science of PCR
... is typically about 50° C. Longer primers have a higher anneal temperature, and so tend to be more ...
... is typically about 50° C. Longer primers have a higher anneal temperature, and so tend to be more ...
Keystone Review Packet Selected Topics Winter 2015 #4 Keystone
... i. the principle of independent assortment states that genes for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes 12. some alleles are neither dominant nor recessive, and many traits are controlled by multiple alleles or multiple genes a. incomplete dominance (RedXWhite = ...
... i. the principle of independent assortment states that genes for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes 12. some alleles are neither dominant nor recessive, and many traits are controlled by multiple alleles or multiple genes a. incomplete dominance (RedXWhite = ...
Mutations booklet MutationsAND Consequences
... SWBAT use the relationship between sickle-cell disease and malaria to describe how mutations can increase genetic diversity of a group of organisms which can be important for the long-term survival of the population. ...
... SWBAT use the relationship between sickle-cell disease and malaria to describe how mutations can increase genetic diversity of a group of organisms which can be important for the long-term survival of the population. ...
Models for homologous recombination
... Homologous recombination has additional functions in eukaryotes Homologous recombination is required for chromosome segregation during meiosis Programmed generation of double –stranded DNA breaks occurs during meiosis MRX protein processes the cleaved DNA ends for assembly of the RecA-like strand –e ...
... Homologous recombination has additional functions in eukaryotes Homologous recombination is required for chromosome segregation during meiosis Programmed generation of double –stranded DNA breaks occurs during meiosis MRX protein processes the cleaved DNA ends for assembly of the RecA-like strand –e ...
- Horizon Discovery
... Deviation is higher at the lower allele frequencies, which reflects assay specific background (e.g. EGFR T790M) and increased variability when testing at these concentrations. EGFR Multiplex ...
... Deviation is higher at the lower allele frequencies, which reflects assay specific background (e.g. EGFR T790M) and increased variability when testing at these concentrations. EGFR Multiplex ...
OICR-1-Cancer Treatment Discovery-MichelleBrazas
... • 2 sequence reads have the same bases as the normal DNA sequence • + 2 reads have different bases compared to the normal DNA sequence ...
... • 2 sequence reads have the same bases as the normal DNA sequence • + 2 reads have different bases compared to the normal DNA sequence ...
Honors Biology – Chapter 11 and 14
... 15. Set up and complete Punnett squares for how one or two traits could be inherited and expressed, including traits that follow the principle of dominance as well as those show incomplete dominance and codominance 16. Explain the following terms: genotype, phenotype, trait, hybrid, gene, allele, se ...
... 15. Set up and complete Punnett squares for how one or two traits could be inherited and expressed, including traits that follow the principle of dominance as well as those show incomplete dominance and codominance 16. Explain the following terms: genotype, phenotype, trait, hybrid, gene, allele, se ...
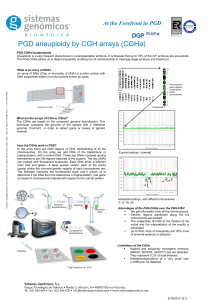
At the Forefront in PGD
... The CGHa are based on the compared genome hybridization. This technique compares the genome of the sample with a reference genome (“normal”), in order to detect gains or losses of genetic material. ...
... The CGHa are based on the compared genome hybridization. This technique compares the genome of the sample with a reference genome (“normal”), in order to detect gains or losses of genetic material. ...
Overview of DNA Purification for Nucleic Acid
... successfully applied in the analyses of cyanobacterial communities in water (20). A physical separation based on general binding properties or common affinities among whole groups of microorganisms also may be used (21). Such unspecific adsorption methods involve coating surfaces with lecithin, carb ...
... successfully applied in the analyses of cyanobacterial communities in water (20). A physical separation based on general binding properties or common affinities among whole groups of microorganisms also may be used (21). Such unspecific adsorption methods involve coating surfaces with lecithin, carb ...
DNA supercoil

DNA supercoiling refers to the over- or under-winding of a DNA strand, and is an expression of the strain on that strand. Supercoiling is important in a number of biological processes, such as compacting DNA. Additionally, certain enzymes such as topoisomerases are able to change DNA topology to facilitate functions such as DNA replication or transcription. Mathematical expressions are used to describe supercoiling by comparing different coiled states to relaxed B-form DNA.As a general rule, the DNA of most organisms is negatively supercoiled.