Molecular Biology Unit Notes
... mRNA binding site P-site holds the tRNA carrying the growing polypeptide chain A-site holds tRNA to be added to the chain with a amino acid E-site is where the discharged tRNAs leave the ribosome 2. tRNA (transfer) reads Codons (made up of three consecutive nucleotides) a. tRNA transfers amio acids ...
... mRNA binding site P-site holds the tRNA carrying the growing polypeptide chain A-site holds tRNA to be added to the chain with a amino acid E-site is where the discharged tRNAs leave the ribosome 2. tRNA (transfer) reads Codons (made up of three consecutive nucleotides) a. tRNA transfers amio acids ...
Bill Nye: Genes
... 7. How does Bill define a Gene? A specific piece of DNA 8. Why is the white blood cell dark on the computer screen? Because it has chromosomes in it. 9. What can you do with DNA after you take it out of an organism? a. Cut it into smaller pieces b. Place into another organism 10. What 2 organisms we ...
... 7. How does Bill define a Gene? A specific piece of DNA 8. Why is the white blood cell dark on the computer screen? Because it has chromosomes in it. 9. What can you do with DNA after you take it out of an organism? a. Cut it into smaller pieces b. Place into another organism 10. What 2 organisms we ...
Prenatal.Chp. 9ppt - Columbian High School
... Fetal alcohol syndrome affects baby both physically and mentally - short in stature, small head, flat nose, wide spaced eyes Radiation - can cause mutations( change in gene structure) avoid x-rays. ...
... Fetal alcohol syndrome affects baby both physically and mentally - short in stature, small head, flat nose, wide spaced eyes Radiation - can cause mutations( change in gene structure) avoid x-rays. ...
This would be given at the end of the unit
... b. DNA analysis is believed to allow investigators to distinguish body cells of different individuals, who are unlikely to have the same DNA. c. bacterial DNA on the hands of criminals may provide a clue as to where that person was when the crime was committed. d . DNA found on murder weapons is eas ...
... b. DNA analysis is believed to allow investigators to distinguish body cells of different individuals, who are unlikely to have the same DNA. c. bacterial DNA on the hands of criminals may provide a clue as to where that person was when the crime was committed. d . DNA found on murder weapons is eas ...
Structural analysis of the protein complex involved in the
... Structural analysis of the protein complex involved in the maintenance of plasmid DNA Researchers at the Cellular Physiology Laboratory (Chief Scientist: Dr. Fumio Hanaoka; Senior Research Scientist: Dr. Katsuhiko Kamada) have determined the structure of the protein complex involved in the maintenan ...
... Structural analysis of the protein complex involved in the maintenance of plasmid DNA Researchers at the Cellular Physiology Laboratory (Chief Scientist: Dr. Fumio Hanaoka; Senior Research Scientist: Dr. Katsuhiko Kamada) have determined the structure of the protein complex involved in the maintenan ...
Gene Section YPEL5 (yippee-like 5 (Drosophila)) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Hosono K, Noda S, Shimizu A, Nakanishi N, Ohtsubo M, Shimizu N, Minoshima S.. YPEL5 protein of the YPEL gene family is involved in the cell cycle progression by interacting with two distinct proteins RanBPM and RanBP10. Genomics. 2010 Aug;96(2):102-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2010.05.003. Epub 2010 May ...
... Hosono K, Noda S, Shimizu A, Nakanishi N, Ohtsubo M, Shimizu N, Minoshima S.. YPEL5 protein of the YPEL gene family is involved in the cell cycle progression by interacting with two distinct proteins RanBPM and RanBP10. Genomics. 2010 Aug;96(2):102-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2010.05.003. Epub 2010 May ...
Review for exam 1
... (parental) strand and a new (daughter) strand. • As each strand acts as a template, process is called ...
... (parental) strand and a new (daughter) strand. • As each strand acts as a template, process is called ...
Complex patterns of inheritance
... Temperature – sea turtles produce more females in warm years and more males in cold years Identical twins – nutrition, healthcare & physical activity influence appearance ...
... Temperature – sea turtles produce more females in warm years and more males in cold years Identical twins – nutrition, healthcare & physical activity influence appearance ...
Final Take-Home Exam
... 5. (10 points) A genetic counselor has the following DNA testing results. For each case study, describe how the test might be performed. determine what advice the counselor can offer in the way of disease risk or possible treatment for the given outcome. a. A DNA test for APOE (Apolipoprotein E) ...
... 5. (10 points) A genetic counselor has the following DNA testing results. For each case study, describe how the test might be performed. determine what advice the counselor can offer in the way of disease risk or possible treatment for the given outcome. a. A DNA test for APOE (Apolipoprotein E) ...
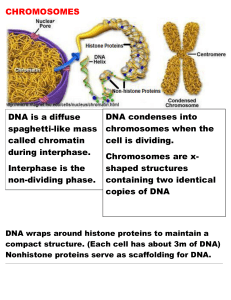
Chromosomes Notes
... chromosomes that have the same genes. However, they will be different versions of the gene (alleles) You get one chromosome of the pair from each parent. ...
... chromosomes that have the same genes. However, they will be different versions of the gene (alleles) You get one chromosome of the pair from each parent. ...
3.3.1: How is DNA Passed Through the Generations?
... o Both cells split into two, with the resulting cells each containing a single chromosome set. (Half the chromosomes of the parent cell. This is how each egg cell and sperm cell contains half the chromosomes of body cells. Therefore, when the sperm and egg combine, they contain the correct number of ...
... o Both cells split into two, with the resulting cells each containing a single chromosome set. (Half the chromosomes of the parent cell. This is how each egg cell and sperm cell contains half the chromosomes of body cells. Therefore, when the sperm and egg combine, they contain the correct number of ...
Spring Semester Exam Study Guide- Biology 2016 Complete this
... 26. In a simple oceanic food chain, phytoplankton, which obtain their energy by photosynthesis of light from the Sun, are eaten by small shrimp, which are then eaten by whales. However, the amount of energy that the phytoplankton have obtained from the Sun is far greater than the amount of energy av ...
... 26. In a simple oceanic food chain, phytoplankton, which obtain their energy by photosynthesis of light from the Sun, are eaten by small shrimp, which are then eaten by whales. However, the amount of energy that the phytoplankton have obtained from the Sun is far greater than the amount of energy av ...
Chapter 2- Genetics
... These diseases are genetic; the mutation is present in every cell of the offspring. In most cases a parent is a carrier and the mutated gene is ______________ to the healthy gene of the other parent. ___ chance of having disease, ½ of carrier and ¼ healthy. d) Genetic Diseases Each disease o ...
... These diseases are genetic; the mutation is present in every cell of the offspring. In most cases a parent is a carrier and the mutated gene is ______________ to the healthy gene of the other parent. ___ chance of having disease, ½ of carrier and ¼ healthy. d) Genetic Diseases Each disease o ...
The University of Chicago Genetic Services Laboratories KIAA1279
... Mowat-Wilson syndrome (OMIM # 235730), has phenotypic overlap with GOSHS but is a genetically distinct disorder caused by mutations in the ZEB2 gene (5). Distinctive features of Mowat-Wilson syndrome include epilepsy, cortical malformations and agenesis of the corpus callosum which have not been wel ...
... Mowat-Wilson syndrome (OMIM # 235730), has phenotypic overlap with GOSHS but is a genetically distinct disorder caused by mutations in the ZEB2 gene (5). Distinctive features of Mowat-Wilson syndrome include epilepsy, cortical malformations and agenesis of the corpus callosum which have not been wel ...
11.1 Intro Evo and Mutations
... Why would a cuckoo bird lay her eggs in another birds’ nest? Why did white moths become less common and gray moths become more common near a factory? ...
... Why would a cuckoo bird lay her eggs in another birds’ nest? Why did white moths become less common and gray moths become more common near a factory? ...
prenatal & Birth
... (1) during gestation across the placenta; (2) during delivery through contact with blood or fluids; (3) post-partum through breast-feeding. ...
... (1) during gestation across the placenta; (2) during delivery through contact with blood or fluids; (3) post-partum through breast-feeding. ...
Chapter 20~ DNA Technology & Genomics
... human genome CGACTAGCATGATCGATCAGCTACATGCTAGCACACYC GTACATCGATCCTGACATCGACCTGCTCGTACATGCTA ...
... human genome CGACTAGCATGATCGATCAGCTACATGCTAGCACACYC GTACATCGATCCTGACATCGACCTGCTCGTACATGCTA ...
Thanksgiving Extra Credit Assignment
... 56. What do promoters mark the beginning of on prokaryotic DNA? 57. When a promoter binds to DNA, What happens to the double helix? 58. Are both strands of DNA copied during transcription? 59. As RNA polymerase moves along the DNA template strand, what is being added? 60. What bases pair with each ...
... 56. What do promoters mark the beginning of on prokaryotic DNA? 57. When a promoter binds to DNA, What happens to the double helix? 58. Are both strands of DNA copied during transcription? 59. As RNA polymerase moves along the DNA template strand, what is being added? 60. What bases pair with each ...
Name: Date: Period:___ Midterm Review: Study Guide # 4 TOPICS
... I am able to list the characteristics of the following genetic disorders: Cystic fibrosis – fluid build up in the lungs; 2 recessive genes Tay Sachs – fat build up in the brain; 2 recessive genes Sickle Cell – RBC can’t carry oxygen properly; seen partially when heterozygous Hemophilia - i ...
... I am able to list the characteristics of the following genetic disorders: Cystic fibrosis – fluid build up in the lungs; 2 recessive genes Tay Sachs – fat build up in the brain; 2 recessive genes Sickle Cell – RBC can’t carry oxygen properly; seen partially when heterozygous Hemophilia - i ...