Notes Unit 4 Part 8
... transgenic = referring to organisms that contain __________ from a different organism within its genome If the plasmid is accepted, the foreign DNA will be replicated very fast as the bacteria multiply having lots of specific genes allows for those gene’s products to be _________________ as we ...
... transgenic = referring to organisms that contain __________ from a different organism within its genome If the plasmid is accepted, the foreign DNA will be replicated very fast as the bacteria multiply having lots of specific genes allows for those gene’s products to be _________________ as we ...
1 BIOL 213 Fourth Exam All atoms, chemical bonding and structures
... FAD yet is functional otherwise. The photosynthetic organism is still able to continue growth. Explain. ...
... FAD yet is functional otherwise. The photosynthetic organism is still able to continue growth. Explain. ...
Genetics Vocabulary
... DNA — (deoxyribonucleic acid) A specialized molecule that contains the genetic information that allows characteristics to be passed from parents to offspring. The information contained in the DNA molecule provides a “blueprint,” or a set of codes, for building other molecules used by the cell. ...
... DNA — (deoxyribonucleic acid) A specialized molecule that contains the genetic information that allows characteristics to be passed from parents to offspring. The information contained in the DNA molecule provides a “blueprint,” or a set of codes, for building other molecules used by the cell. ...
Genetics
... Sister chromatid: Crossing over: Draw a picture of metaphase in mitosis and metaphase 1 in meiosis (They are different!) ...
... Sister chromatid: Crossing over: Draw a picture of metaphase in mitosis and metaphase 1 in meiosis (They are different!) ...
Biotechnology and Recombinant DNA
... • Procedure where cells can take up plasmids (DNA) from the surrounding environment • The cell receiving the new DNA must be ...
... • Procedure where cells can take up plasmids (DNA) from the surrounding environment • The cell receiving the new DNA must be ...
BIOLOGY CONTENT STANDARDS REVIEW
... information from DNA into mRNA. Ribosomes synthesize proteins, using tRNAs to translate genetic information in mRNA. 18. Describe DNA replication. 19. Describe transcription and translation (include the terms nucleus, cytoplasm, DNA, mRNA, rRNA, tRNA, ribosome, codon, anticodon, and amino acids). Th ...
... information from DNA into mRNA. Ribosomes synthesize proteins, using tRNAs to translate genetic information in mRNA. 18. Describe DNA replication. 19. Describe transcription and translation (include the terms nucleus, cytoplasm, DNA, mRNA, rRNA, tRNA, ribosome, codon, anticodon, and amino acids). Th ...
Key Idea 2 - Valhalla High School
... How does selective breeding differ from genetic engineering? How long has each been around? In recent years new varieties of farm plants and animals have been engineered by _manipulating_____ their genetic instructions to produce new characteristics. What is recombinant DNA? Taking a piece of DNA fr ...
... How does selective breeding differ from genetic engineering? How long has each been around? In recent years new varieties of farm plants and animals have been engineered by _manipulating_____ their genetic instructions to produce new characteristics. What is recombinant DNA? Taking a piece of DNA fr ...
File
... genetic crosses. b. determine the actual outcomes of genetic crosses. c. determine which species should be used in genetic crosses. d. decide which organisms are best to use in genetic crosses. ...
... genetic crosses. b. determine the actual outcomes of genetic crosses. c. determine which species should be used in genetic crosses. d. decide which organisms are best to use in genetic crosses. ...
EOC Review Chapters6
... A. Each parent is carrying a recessive allele for the trait. B. Eye color is a sex linked trait and male children could have only the allele for blue eyes. ...
... A. Each parent is carrying a recessive allele for the trait. B. Eye color is a sex linked trait and male children could have only the allele for blue eyes. ...
Investigation 3 power point
... was that there was once a question of whether Tutankhamun was really the son of the previous Pharaoh. Through DNA testing, scientists were able to confirm that he really was the son of the previous Pharaoh in Egypt. ...
... was that there was once a question of whether Tutankhamun was really the son of the previous Pharaoh. Through DNA testing, scientists were able to confirm that he really was the son of the previous Pharaoh in Egypt. ...
Genetic Engineering
... Transforming Animal Cells • Can be transformed in some of the same ways as plant cells • Has applications in gene replacement therapy ...
... Transforming Animal Cells • Can be transformed in some of the same ways as plant cells • Has applications in gene replacement therapy ...
Chapter 13: Genetic Engineering
... electrical current pull DNA fragments through an agarose gel. DNA mixtures are placed in a well in agarose and electrical current is switched on. The small fragments travel faster, and the larger fragments cannot travel as far. DNA fingerprint produced by gel ...
... electrical current pull DNA fragments through an agarose gel. DNA mixtures are placed in a well in agarose and electrical current is switched on. The small fragments travel faster, and the larger fragments cannot travel as far. DNA fingerprint produced by gel ...
Stg Chp 11 - Edublogs @ Macomb ISD
... In your textbook, read about the genetic code. Complete each statement. 4. Proteins are made up of 5. There are twenty different types of _ 6. The message of the DNA code is information for building. 7. Each set of three nitrogenous bases that codes for an amino acid is known as a ...
... In your textbook, read about the genetic code. Complete each statement. 4. Proteins are made up of 5. There are twenty different types of _ 6. The message of the DNA code is information for building. 7. Each set of three nitrogenous bases that codes for an amino acid is known as a ...
Print › Benchmark Second Nine Weeks | Quizlet | Quizlet
... . Genes for different traits are inherited independently of one another states the law of ...
... . Genes for different traits are inherited independently of one another states the law of ...
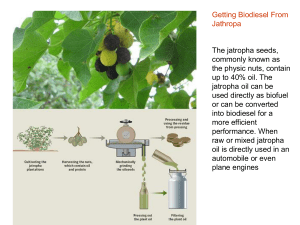
Jatropha genotyping In Gh Pu QR In Gh Pu QR 13 primer pairs
... • Results indicate very little variation between accessions from India, Ghana, Tanzania & Madagascar ...
... • Results indicate very little variation between accessions from India, Ghana, Tanzania & Madagascar ...
File
... _____ 5. Why are plasmids so widely used in recombinant DNA studies? a. because it is difficult to insert new genes into them b. because they can be used to transform bacteria c. because they naturally contain much foreign DNA d. because they cannot be cut with restriction enzymes _____ 6. Why is in ...
... _____ 5. Why are plasmids so widely used in recombinant DNA studies? a. because it is difficult to insert new genes into them b. because they can be used to transform bacteria c. because they naturally contain much foreign DNA d. because they cannot be cut with restriction enzymes _____ 6. Why is in ...
CH 3 GENETICS - TEST – GIFT GUIDE HINTS due
... Cytoplasm = is the region inside the cell between the cell membrane and the nucleus. In the cytoplasm is where protein synthesis takes place on the ribosomes Dominant = allele is one whose trait always shows up if it is in the genes Egg = female sex cell Genes = are the factors that control traits. ...
... Cytoplasm = is the region inside the cell between the cell membrane and the nucleus. In the cytoplasm is where protein synthesis takes place on the ribosomes Dominant = allele is one whose trait always shows up if it is in the genes Egg = female sex cell Genes = are the factors that control traits. ...
DNA Control (Protein Synthesis)
... the DNA but different parts of the DNA are read in different types of cells...thus making different proteins which carry out the work of the cell ...
... the DNA but different parts of the DNA are read in different types of cells...thus making different proteins which carry out the work of the cell ...
Unit 5 Free Response
... The unit of genetic organization in all living organisms is the chromosome. a. Describe the structure and function of the parts of a eukaryotic chromosome. You may wish to include a diagram as part of your description. b. Describe the adaptive (evolutionary) significance of organizing genes into chr ...
... The unit of genetic organization in all living organisms is the chromosome. a. Describe the structure and function of the parts of a eukaryotic chromosome. You may wish to include a diagram as part of your description. b. Describe the adaptive (evolutionary) significance of organizing genes into chr ...
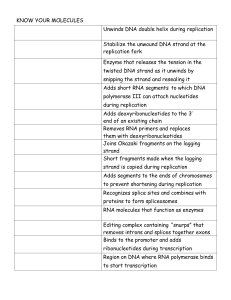
Know your molecules organizer
... Stabilize the unwound DNA strand at the replication fork Enzyme that releases the tension in the twisted DNA strand as it unwinds by snipping the strand and resealing it Adds short RNA segments to which DNA polymerase III can attach nucleotides during replication Adds deoxyribonucleotides to the 3’ ...
... Stabilize the unwound DNA strand at the replication fork Enzyme that releases the tension in the twisted DNA strand as it unwinds by snipping the strand and resealing it Adds short RNA segments to which DNA polymerase III can attach nucleotides during replication Adds deoxyribonucleotides to the 3’ ...
Extrachromosomal DNA

Extrachromosomal DNA is any DNA that is found outside of the nucleus of a cell. It is also referred to as extranuclear DNA or cytoplasmic DNA. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes but DNA found outside of the nucleus also serves important biological functions.In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids whereas in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in research of replication because it is easy to identify and isolate.Extrachromosomal DNA was found to be structurally different from nuclear DNA. Cytoplasmic DNA is less methylated than DNA found within the nucleus. It was also confirmed that the sequences of cytoplasmic DNA was different from nuclear DNA in the same organism, showing that cytoplasmic DNAs are not simply fragments of nuclear DNA.In addition to DNA found outside of the nucleus in cells, infection of viral genomes also provides an example of extrachromosomal DNA.