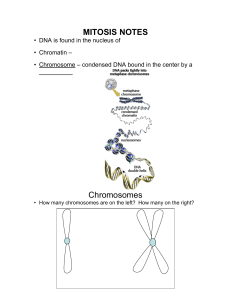
Biobowl 3
... 1. When a DNA molecule replicates, a chromosome is then made up of two sister _______. 2. Eukaryotic DNA molecules are associated with ____________ proteins. 3. In general, the division of the cytoplasm, known as _______, occurs during telophase of mitosis. 4. In animals, meiosis produces ______ (na ...
... 1. When a DNA molecule replicates, a chromosome is then made up of two sister _______. 2. Eukaryotic DNA molecules are associated with ____________ proteins. 3. In general, the division of the cytoplasm, known as _______, occurs during telophase of mitosis. 4. In animals, meiosis produces ______ (na ...
Heredity Notes - Madison County Schools / Overview
... can divide. Why? You don’t want to lose half of yourself do you? ...
... can divide. Why? You don’t want to lose half of yourself do you? ...
Intro Biology Review for Final
... Review for Final Note: Please remember that the final will be comprehensive. The final will be fill in the blank and multiple choice questions. Most questions will come straight from the powerpoints, so I would review those first and as you are doing this, please pay attention to the following list ...
... Review for Final Note: Please remember that the final will be comprehensive. The final will be fill in the blank and multiple choice questions. Most questions will come straight from the powerpoints, so I would review those first and as you are doing this, please pay attention to the following list ...
File
... a small portion of the cytoplasm – When conditions improve can germinate and return to normal cell division – Bacteria causing tetanus, botulism, and anthrax ...
... a small portion of the cytoplasm – When conditions improve can germinate and return to normal cell division – Bacteria causing tetanus, botulism, and anthrax ...
Syllabus Checklist
... This is the knowledge that you should understand upon completing this section: 11.1 DNA ...
... This is the knowledge that you should understand upon completing this section: 11.1 DNA ...
Suggested answers to Exercise - Bio-662
... Biotechnology is any technological application that involves the use of organisms, biological systems or processes in producing goods or providing services. 1m The making of cheese / yoghurt / wine involves the use of microorganisms and is thus considered as an early biotechnology. 1m Restriction en ...
... Biotechnology is any technological application that involves the use of organisms, biological systems or processes in producing goods or providing services. 1m The making of cheese / yoghurt / wine involves the use of microorganisms and is thus considered as an early biotechnology. 1m Restriction en ...
You Asked for it….. - Mr. Smith’s Science Page
... proteins •These are the simplest cells •Examples are bacteria, like those that cause strep throat. ...
... proteins •These are the simplest cells •Examples are bacteria, like those that cause strep throat. ...
W09micr430Lec17 - Cal State LA
... amount of sigma factor σ32, also called σH or RpoH. σ32 recognizes promoters of genes in a major heat shock regulon – the σ32 regulon. During growth at 30 ºC, σ32 can be degraded by several proteases. However, if σ32 is bound to RNAP, it is protected from degradation. ...
... amount of sigma factor σ32, also called σH or RpoH. σ32 recognizes promoters of genes in a major heat shock regulon – the σ32 regulon. During growth at 30 ºC, σ32 can be degraded by several proteases. However, if σ32 is bound to RNAP, it is protected from degradation. ...
Transcription is the process by which RNA polymerase copies a
... scientists also noticed that DNA is like a zipper – in it can be split into a two single strands by separating the hydrogen bonds between the base pairs. Check out this video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0CMIgZQakHY ...
... scientists also noticed that DNA is like a zipper – in it can be split into a two single strands by separating the hydrogen bonds between the base pairs. Check out this video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0CMIgZQakHY ...
chloroplasts passive transport active transport osmosis
... What makes up an atom? What are the 4 types of marcomolecules that make up all living things? Unit 2: Cells Vocab cell prokaryote eukaryote cytoplasm cell membrane golgi appartus endoplasmic reticulum nucleus chromosome DNA mitochondria ...
... What makes up an atom? What are the 4 types of marcomolecules that make up all living things? Unit 2: Cells Vocab cell prokaryote eukaryote cytoplasm cell membrane golgi appartus endoplasmic reticulum nucleus chromosome DNA mitochondria ...
Bacteria Genetics - MBBS Students Club
... Bacterial Genetics • Genetic material of bacterial cell is single DNA molecule with specific molecular weight and base pairs. • Molecular weight of DNA varies from smallest free living wall-less organism, (Mycoplasma) from 3x109 base pairs and encode 100,000 proteins to E. coli with Mol weight 5x10 ...
... Bacterial Genetics • Genetic material of bacterial cell is single DNA molecule with specific molecular weight and base pairs. • Molecular weight of DNA varies from smallest free living wall-less organism, (Mycoplasma) from 3x109 base pairs and encode 100,000 proteins to E. coli with Mol weight 5x10 ...
Entry Test Sample for MS in Bioinformatics Program Weightage Distribution:
... a) Discrete Quantitative Question Each multiple-choice question will consist of a question statement which requires you to perform some calculations for selecting exactly one of the available choices. ...
... a) Discrete Quantitative Question Each multiple-choice question will consist of a question statement which requires you to perform some calculations for selecting exactly one of the available choices. ...
The Living World
... A protective outer layer that will form the placenta Inner cell mass that will form the embryo The inner cell mass consists of embryonic stem cells These are pluripotent Capable of forming the entire organism As development proceeds, cells lose their pluripotency They become committed to o ...
... A protective outer layer that will form the placenta Inner cell mass that will form the embryo The inner cell mass consists of embryonic stem cells These are pluripotent Capable of forming the entire organism As development proceeds, cells lose their pluripotency They become committed to o ...
Study Guide Genetics Final 2014
... 2. How is an autosome different from a sex chromosome? 3. How is an X different from a y chromosome? 4. Use a Punnet square to show how gender is passed from parent to offspring. Which parent’s chromosome determines the sex of a child? Why? 5. Compare and contrast dominant and recessive alleles. Wha ...
... 2. How is an autosome different from a sex chromosome? 3. How is an X different from a y chromosome? 4. Use a Punnet square to show how gender is passed from parent to offspring. Which parent’s chromosome determines the sex of a child? Why? 5. Compare and contrast dominant and recessive alleles. Wha ...
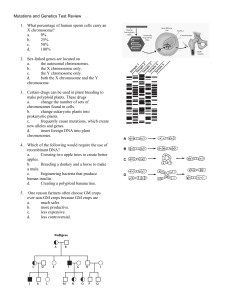
Mutations and Genetics Test Review 1. What percentage of human
... Mutations and Genetics Test Review 1. What percentage of human sperm cells carry an X chromosome? a. ...
... Mutations and Genetics Test Review 1. What percentage of human sperm cells carry an X chromosome? a. ...
From DNA to Protein Name: What does DNA stand for? What is DNA
... what would the nucleotide sequence on the complementary strand of DNA? ...
... what would the nucleotide sequence on the complementary strand of DNA? ...
File
... Because only certain sections of DNA code for a protein and what were those sections called? ...
... Because only certain sections of DNA code for a protein and what were those sections called? ...
Genetics Introduction:
... tRNA transfers amino acids from cytoplasms pool to a ribosome Ribosome adds each AA carried by tRNA to the growing end of the polypeptide chain In the triplet code, 3 consecutive bases specify an AA, creating 4 3 (64) possible code words The genetic instructions for a PP chain are written in DNA as ...
... tRNA transfers amino acids from cytoplasms pool to a ribosome Ribosome adds each AA carried by tRNA to the growing end of the polypeptide chain In the triplet code, 3 consecutive bases specify an AA, creating 4 3 (64) possible code words The genetic instructions for a PP chain are written in DNA as ...
Lesson Plan
... Opening: Study for Test (Jeopardy Review) Students take DNA, RNA Test New Material: Gene expression (introns, exons, lac genes) Guided Practice: Gene expression handout Assessment and Closing: Explain gene expression in 1 paragraph using important terms from your notes. New Material: Meiosis Notes ...
... Opening: Study for Test (Jeopardy Review) Students take DNA, RNA Test New Material: Gene expression (introns, exons, lac genes) Guided Practice: Gene expression handout Assessment and Closing: Explain gene expression in 1 paragraph using important terms from your notes. New Material: Meiosis Notes ...
Extrachromosomal DNA

Extrachromosomal DNA is any DNA that is found outside of the nucleus of a cell. It is also referred to as extranuclear DNA or cytoplasmic DNA. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes but DNA found outside of the nucleus also serves important biological functions.In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids whereas in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in research of replication because it is easy to identify and isolate.Extrachromosomal DNA was found to be structurally different from nuclear DNA. Cytoplasmic DNA is less methylated than DNA found within the nucleus. It was also confirmed that the sequences of cytoplasmic DNA was different from nuclear DNA in the same organism, showing that cytoplasmic DNAs are not simply fragments of nuclear DNA.In addition to DNA found outside of the nucleus in cells, infection of viral genomes also provides an example of extrachromosomal DNA.