AP Biology - TeacherWeb
... 5. IF cells carry all of the genetic differences, why then are cells so unique – what is responsible for this? 6. In the diagram below – highlight all of the potential locations for gene expression regulation in eukaryotic cells. How does this compare with prokaryotic cells? ...
... 5. IF cells carry all of the genetic differences, why then are cells so unique – what is responsible for this? 6. In the diagram below – highlight all of the potential locations for gene expression regulation in eukaryotic cells. How does this compare with prokaryotic cells? ...
DNA Technology
... organism, containing the recombinant DNA, into the organism into eukaryote. Waiting until the eukaryotes genome has been changed by the invading ...
... organism, containing the recombinant DNA, into the organism into eukaryote. Waiting until the eukaryotes genome has been changed by the invading ...
Biologists have learned to manipulate DNA
... C. The fragments stick together by base-pairing – a complementary strand D. DNA ligase pastes the fragments together to form recombinant DNA molecule III. Cloning Recombinant DNA A. The Process of cloning recombinant DNA 1. Restriction enzymes cuts plasmid in one place, human DNA cut in many places ...
... C. The fragments stick together by base-pairing – a complementary strand D. DNA ligase pastes the fragments together to form recombinant DNA molecule III. Cloning Recombinant DNA A. The Process of cloning recombinant DNA 1. Restriction enzymes cuts plasmid in one place, human DNA cut in many places ...
Nedmolecularbio1of32013 40 KB
... -Mutations usually either occur during/due to errors in replication, or are perpetuated by replication. Mutations that are passed along can alter the code, and ultimately protein structure. -Each 3-base codon of DNA is converted to an amino acid (one is start) or a stop. 20 aa possible. -DNA bases a ...
... -Mutations usually either occur during/due to errors in replication, or are perpetuated by replication. Mutations that are passed along can alter the code, and ultimately protein structure. -Each 3-base codon of DNA is converted to an amino acid (one is start) or a stop. 20 aa possible. -DNA bases a ...
File
... of its X chromosomes to become inactivated (obviously), which usually results in the early deaths of males since they only have a single X chromosome. Not every cell in an organism’s body has to have an inactivated X chromosome which is how tricolor cats form. In the cells with inactivated X chromos ...
... of its X chromosomes to become inactivated (obviously), which usually results in the early deaths of males since they only have a single X chromosome. Not every cell in an organism’s body has to have an inactivated X chromosome which is how tricolor cats form. In the cells with inactivated X chromos ...
Study Guide for DNA Structure and Replication
... o Nitrogen base(s): o Chromosome: o Sugar phosphate backbone: o Cell Nucleus: o Eukaryotic: o Prokaryotic: o DNA Replication: The structure of DNA Know all living organisms have DNA, including prokaryotes such as bacteria, fungi, plants, animals, and also many viruses Recognize that in eukaryote ...
... o Nitrogen base(s): o Chromosome: o Sugar phosphate backbone: o Cell Nucleus: o Eukaryotic: o Prokaryotic: o DNA Replication: The structure of DNA Know all living organisms have DNA, including prokaryotes such as bacteria, fungi, plants, animals, and also many viruses Recognize that in eukaryote ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Ch. 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene
... specify amino acids. They’re called… • Codons • 3 base codons in DNA are transcribed into complementary RNA codon, then translated into amino acids that form a polypeptide chain. ...
... specify amino acids. They’re called… • Codons • 3 base codons in DNA are transcribed into complementary RNA codon, then translated into amino acids that form a polypeptide chain. ...
Document
... One circular chromosome 16.5 kb in size Located inside the mitochondrial organelle Most cells contain at least 1000 mtDNA molecules • Mature oocyte has more than 100,000 copies of mtDNA ...
... One circular chromosome 16.5 kb in size Located inside the mitochondrial organelle Most cells contain at least 1000 mtDNA molecules • Mature oocyte has more than 100,000 copies of mtDNA ...
Ligation and Transformation
... • Competent cells are those capable of taking up the plasmid • Cells most likely to become competent are in log growth phase ...
... • Competent cells are those capable of taking up the plasmid • Cells most likely to become competent are in log growth phase ...
Lecture 1, Part I
... chromosomal structural integrity and regulating when, where, and in what quantity proteins are made (regulatory regions). • The terms exon and intron refer to coding (translated into a protein) and non-coding DNA, respectively. ...
... chromosomal structural integrity and regulating when, where, and in what quantity proteins are made (regulatory regions). • The terms exon and intron refer to coding (translated into a protein) and non-coding DNA, respectively. ...
Protein Synthesis - science4warriors
... amino acids into proteins from DNA to the rest of the cell • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): makes up the major part of the ribosome • Transfer RNA (tRNA): transfers amino acids to ribosomes during protein ...
... amino acids into proteins from DNA to the rest of the cell • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): makes up the major part of the ribosome • Transfer RNA (tRNA): transfers amino acids to ribosomes during protein ...
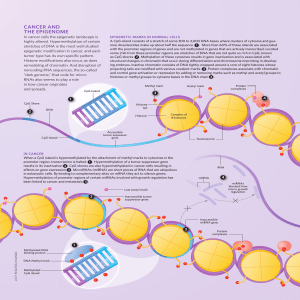
CaNCer aND THe ePIGeNOMe
... epigenetic modification in cancer, and each tumor type has its own specific pattern. Histone modifications also occur, as does remodeling of chromatin. And disruption of noncoding RNA sequences, the so-called “dark genome,” that code for microRNAs also seems to play a role in how cancer originates a ...
... epigenetic modification in cancer, and each tumor type has its own specific pattern. Histone modifications also occur, as does remodeling of chromatin. And disruption of noncoding RNA sequences, the so-called “dark genome,” that code for microRNAs also seems to play a role in how cancer originates a ...
MB 206 Microbial Biotechnology2
... into host genome Phage M13 – allows cloned DNA to be isolated in single-stranded form Cosmids hybrids of plasmid-bacteriophage l Artificial chromosomes - Cloning of very large genomic fragments - BACs (bacterial artificial chromosomes) - YACs (yeast artificial chromosomes ...
... into host genome Phage M13 – allows cloned DNA to be isolated in single-stranded form Cosmids hybrids of plasmid-bacteriophage l Artificial chromosomes - Cloning of very large genomic fragments - BACs (bacterial artificial chromosomes) - YACs (yeast artificial chromosomes ...
CALL FOR PROPOSALS 2008
... axeny, specific information on genome size (bibliographic references or techniques for estimation of size), G+C content, information on ploidy, polymorphism level (details and methods of estimation), repeat structure with details about how these are known, etc. ...
... axeny, specific information on genome size (bibliographic references or techniques for estimation of size), G+C content, information on ploidy, polymorphism level (details and methods of estimation), repeat structure with details about how these are known, etc. ...
Semiconservative
... The regulation of amino acids such as arginine involves repression when arginine accumulates, and no repression when arginine is being used. ...
... The regulation of amino acids such as arginine involves repression when arginine accumulates, and no repression when arginine is being used. ...
Unit 4: Genetic Engineering and Gene Expression
... 14. What does it mean to not “express” a trait even though one might possess the DNA in their genes? Why do we say a gene is “turned on” or “turned off”? Expressed = turned on = the gene is read/transcribed, so the protein is being produced Not expressed = turned off = the gene is NOT being transcri ...
... 14. What does it mean to not “express” a trait even though one might possess the DNA in their genes? Why do we say a gene is “turned on” or “turned off”? Expressed = turned on = the gene is read/transcribed, so the protein is being produced Not expressed = turned off = the gene is NOT being transcri ...
Answers to Exam Practice Questions 1. Mitosis produces two
... 17. Many proteins are enzymes which catalyze and regulate chemical reactions. A gene that codes for an enzyme to produce pigment can control the color of a flower. Another gene could control the production of red blood cells. 18. Most mutations have little to no effect on the individual, however mu ...
... 17. Many proteins are enzymes which catalyze and regulate chemical reactions. A gene that codes for an enzyme to produce pigment can control the color of a flower. Another gene could control the production of red blood cells. 18. Most mutations have little to no effect on the individual, however mu ...
Study Guide
... • In general, when studying a biological event, one should try not to disrupt the event in the process of measuring it. In this particular study, you might wonder whether DNA polymerase can still function when GFP is attached to one of its subunits. This paragraph has the answer. • How did the locat ...
... • In general, when studying a biological event, one should try not to disrupt the event in the process of measuring it. In this particular study, you might wonder whether DNA polymerase can still function when GFP is attached to one of its subunits. This paragraph has the answer. • How did the locat ...
Genetics - DNA
... Each chromosome contains many genes. We inherit two copies of each chromosome (one from each parent) and this is why our chromosomes can be arranged into homologous pairs. A Gene is a section of DNA that contains a specific sequence of bases. This sequence codes for a chain of amino acids that folds ...
... Each chromosome contains many genes. We inherit two copies of each chromosome (one from each parent) and this is why our chromosomes can be arranged into homologous pairs. A Gene is a section of DNA that contains a specific sequence of bases. This sequence codes for a chain of amino acids that folds ...
Biology Final Exam Vocabulary Review
... 7. ____________________ is the exchange of chromosome segments between homologous chromosomes during meiosis. 8. A(n)__________________ is an image of the chromosomes in a cell, arranged as homologous pairs based on size, shape, and banding pattern. 9. __________________ describes the failure of hom ...
... 7. ____________________ is the exchange of chromosome segments between homologous chromosomes during meiosis. 8. A(n)__________________ is an image of the chromosomes in a cell, arranged as homologous pairs based on size, shape, and banding pattern. 9. __________________ describes the failure of hom ...
src
... It was found that cDNAsarc binds to DNA from all vertebrate classes, including mammals, but not to the DNA from sea urchins, fruit flies, or bacteria. Conclusion: The src gene is not only present in the RNA of the ASV genome and the genome of the chicken cells it can infect, but a homologous gene is ...
... It was found that cDNAsarc binds to DNA from all vertebrate classes, including mammals, but not to the DNA from sea urchins, fruit flies, or bacteria. Conclusion: The src gene is not only present in the RNA of the ASV genome and the genome of the chicken cells it can infect, but a homologous gene is ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... 2. It uses the bacterium’s RNA polymerase to transcribe early genes 3. One early protein shuts down host (bacterial) gene transcription 4. Another protein stimulates viral genome replication 5. Another protein stimulates late gene transcription 6. New viral capsid proteins and a protein lyses the ho ...
... 2. It uses the bacterium’s RNA polymerase to transcribe early genes 3. One early protein shuts down host (bacterial) gene transcription 4. Another protein stimulates viral genome replication 5. Another protein stimulates late gene transcription 6. New viral capsid proteins and a protein lyses the ho ...
Extrachromosomal DNA

Extrachromosomal DNA is any DNA that is found outside of the nucleus of a cell. It is also referred to as extranuclear DNA or cytoplasmic DNA. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes but DNA found outside of the nucleus also serves important biological functions.In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids whereas in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in research of replication because it is easy to identify and isolate.Extrachromosomal DNA was found to be structurally different from nuclear DNA. Cytoplasmic DNA is less methylated than DNA found within the nucleus. It was also confirmed that the sequences of cytoplasmic DNA was different from nuclear DNA in the same organism, showing that cytoplasmic DNAs are not simply fragments of nuclear DNA.In addition to DNA found outside of the nucleus in cells, infection of viral genomes also provides an example of extrachromosomal DNA.