dna
... Steps in Replication 2. A molecule of DNA POLYMERASE binds to one of the strands of DNA and begins to move in the 3’ to 5’ direction along it. This produces a new strand of DNA that is called the LEADING STRAND. DNA in the leading strand is synthesized in the 5’ to 3’ direction which is the ONLY wa ...
... Steps in Replication 2. A molecule of DNA POLYMERASE binds to one of the strands of DNA and begins to move in the 3’ to 5’ direction along it. This produces a new strand of DNA that is called the LEADING STRAND. DNA in the leading strand is synthesized in the 5’ to 3’ direction which is the ONLY wa ...
See DNA Essay possibilities
... (b) All humans are nearly identical genetically in coding sequences and have many proteins that are identical in structure and function. Nevertheless, each human has a unique DNA fingerprint. Explain this apparent contradiction. ...
... (b) All humans are nearly identical genetically in coding sequences and have many proteins that are identical in structure and function. Nevertheless, each human has a unique DNA fingerprint. Explain this apparent contradiction. ...
- mrsolson.com
... 4. Paula is blood type A– and has a child who is B+; Paula requests that Bernie undergo a paternity test as a possible father of the child. If Bernie is the father, what are his possible blood types? a. AB+ or B+ c. A+ or B+ b. AB– or O+ d. AB– or AB+ 5. A man with type A blood and a woman with type ...
... 4. Paula is blood type A– and has a child who is B+; Paula requests that Bernie undergo a paternity test as a possible father of the child. If Bernie is the father, what are his possible blood types? a. AB+ or B+ c. A+ or B+ b. AB– or O+ d. AB– or AB+ 5. A man with type A blood and a woman with type ...
DNA STRUCTURE - Teachers Network
... How does this shape allow the DNA to be copied easily? 2. The 4 bases that make up DNA are: _________________________, _________________________, _________________________, _________________________. The base-pairing rules are: A pairs with ____. T pairs with ____. ...
... How does this shape allow the DNA to be copied easily? 2. The 4 bases that make up DNA are: _________________________, _________________________, _________________________, _________________________. The base-pairing rules are: A pairs with ____. T pairs with ____. ...
ThemesHwk1-1KEY
... E.g.: A sea turtle is a sea turtle's egg's way of making another sea turtle." Living things make more of themselves, either directly through cell division or by using cell division to create "founder" cells that merge into a new being. What is physically passed along – copied, then divided - are chr ...
... E.g.: A sea turtle is a sea turtle's egg's way of making another sea turtle." Living things make more of themselves, either directly through cell division or by using cell division to create "founder" cells that merge into a new being. What is physically passed along – copied, then divided - are chr ...
Ch.12 - Jamestown Public Schools
... molecule separates into 2 strands, then produces 2 new complimentary strands following base pairing rules Each strand of the double helix serves as a template, or model, for the new strand ...
... molecule separates into 2 strands, then produces 2 new complimentary strands following base pairing rules Each strand of the double helix serves as a template, or model, for the new strand ...
Eukaryotic Genomes Chapter 19
... gene duplications that occur as errors during DNA replication and recombination. ► The differences in genes arise from mutations that accumulate in the gene copies over generations. These mutations may even lead to enough changes to form pseudogenes, DNA segments that have sequences similar to rea ...
... gene duplications that occur as errors during DNA replication and recombination. ► The differences in genes arise from mutations that accumulate in the gene copies over generations. These mutations may even lead to enough changes to form pseudogenes, DNA segments that have sequences similar to rea ...
document
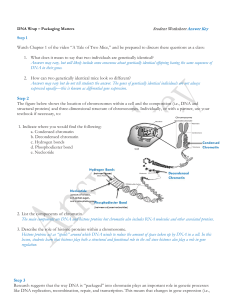
... 2. List the components of chromatin. The main components are DNA and histone proteins but chromatin also includes RNA molecules and other associated proteins. 3. Describe the role of histone proteins within a chromosome. Histone proteins act as “spools” around which DNA winds to reduce the amount of ...
... 2. List the components of chromatin. The main components are DNA and histone proteins but chromatin also includes RNA molecules and other associated proteins. 3. Describe the role of histone proteins within a chromosome. Histone proteins act as “spools” around which DNA winds to reduce the amount of ...
Level 2 Biology - No Brain Too Small
... large that substances cannot diffuse fast enough to carry out cell processes. Therefore cells divide to have a high surface-to-volume ratio. This enables efficient chemical reactions. Mitosis occurs during periods of growth and repair during infancy / childhood / early development in animals followi ...
... large that substances cannot diffuse fast enough to carry out cell processes. Therefore cells divide to have a high surface-to-volume ratio. This enables efficient chemical reactions. Mitosis occurs during periods of growth and repair during infancy / childhood / early development in animals followi ...
Biotechnology - clevengerscience
... • Mice with human genes for animal testing • Livestock with extra copies of growth hormone genes to improve food supply • Chicken with a gene resistant to the bacteria ...
... • Mice with human genes for animal testing • Livestock with extra copies of growth hormone genes to improve food supply • Chicken with a gene resistant to the bacteria ...
DNA WebQuest
... Carefully view and read each part of this animation. Complete the statements and questions below: 1. Protein Synthesis is the making of __________________ from instructions coded for in the DNA. 2. There are many types of proteins and a variety of functions which include: hormones (send signals), tr ...
... Carefully view and read each part of this animation. Complete the statements and questions below: 1. Protein Synthesis is the making of __________________ from instructions coded for in the DNA. 2. There are many types of proteins and a variety of functions which include: hormones (send signals), tr ...
to view fulltext PDF - Indian Academy of Sciences
... such processes the polymer might undergo a conformational change through stretching and bending. The flexibility of DNA is thus an important parameter defining the molecular interactions. In higher biological systems DNA is in a highly condensed state (called the chromosome) due to its self-assembly ...
... such processes the polymer might undergo a conformational change through stretching and bending. The flexibility of DNA is thus an important parameter defining the molecular interactions. In higher biological systems DNA is in a highly condensed state (called the chromosome) due to its self-assembly ...
1 - TeacherWeb
... _____ birds are more closely related to reptiles than mammals _____ amphibians produce an amniotic egg _____ hair evolved in an ancestor shared by mammals, birds, and reptiles _____ birds would be most similar to mammals when comparing DNA nucleotide or amino acid sequences ...
... _____ birds are more closely related to reptiles than mammals _____ amphibians produce an amniotic egg _____ hair evolved in an ancestor shared by mammals, birds, and reptiles _____ birds would be most similar to mammals when comparing DNA nucleotide or amino acid sequences ...
Georgia Department of Education Study Guide Domain III Genetic
... What are the components of a DNA nucleotide? (3 parts) What are the 4 nitrogen bases found in DNA? Define double helix. Why is DNA called a double helix? The two strands of nucleotides are held together by what? The “sides of the ladder” of DNA consist of what? (2 items should be listed). What is th ...
... What are the components of a DNA nucleotide? (3 parts) What are the 4 nitrogen bases found in DNA? Define double helix. Why is DNA called a double helix? The two strands of nucleotides are held together by what? The “sides of the ladder” of DNA consist of what? (2 items should be listed). What is th ...
Chapter 2
... b. chemical units composed of a sugar-acetate group. c. base compounds. d. nucleotide bases. 4. “Pleiotropic” refers to: a. a simple mapping between genes and proteins b. one gene playing multiple roles at different developmental times. c. the cellular machinery that influences the expression of gen ...
... b. chemical units composed of a sugar-acetate group. c. base compounds. d. nucleotide bases. 4. “Pleiotropic” refers to: a. a simple mapping between genes and proteins b. one gene playing multiple roles at different developmental times. c. the cellular machinery that influences the expression of gen ...
Mutation - TeacherWeb
... Full set in somatic cells NOT sex cells DNA codes for protein. Influences appearance Involved in bodily processes Involved in bodily repair ...
... Full set in somatic cells NOT sex cells DNA codes for protein. Influences appearance Involved in bodily processes Involved in bodily repair ...
Genomics
... Proteins are responsible for an endless number of tasks within the cell. The complete set of proteins in a cell can be referred to as its proteome and the study of protein structure and function and what every protein in the cell is doing is known as proteomics. The proteome is highly dynamic and it ...
... Proteins are responsible for an endless number of tasks within the cell. The complete set of proteins in a cell can be referred to as its proteome and the study of protein structure and function and what every protein in the cell is doing is known as proteomics. The proteome is highly dynamic and it ...
DNA and the Genetic Code
... Transcription is the synthesis of messenger RNA (mRNA) from DNA. The two DNA strands separate from one another. One strand is used for replication, the other for transcription. mRNA is the complement strand of the original DNA except with T replaced by U (uracil). mRNA carries the genetic informatio ...
... Transcription is the synthesis of messenger RNA (mRNA) from DNA. The two DNA strands separate from one another. One strand is used for replication, the other for transcription. mRNA is the complement strand of the original DNA except with T replaced by U (uracil). mRNA carries the genetic informatio ...
to 3
... B. DNA has A,T,C,G, and U nucleotides. C. DNA has two strands, which are antiparallel to each other. D. DNA has two strands, which are parallel to each other. E. DNA has two strands, which are composed of 25% of each kind of nucleotides. ...
... B. DNA has A,T,C,G, and U nucleotides. C. DNA has two strands, which are antiparallel to each other. D. DNA has two strands, which are parallel to each other. E. DNA has two strands, which are composed of 25% of each kind of nucleotides. ...
Chapter 8 Microbial Genetics
... Diagram and describe how enzymes speed up biochemical reactions, and how they affect the energy required for a reaction to occur. Describe 3 different physical and chemical factors that can influence enzyme activity? ...
... Diagram and describe how enzymes speed up biochemical reactions, and how they affect the energy required for a reaction to occur. Describe 3 different physical and chemical factors that can influence enzyme activity? ...
Sample Exam 1
... 40. For the following substances describe the possible effect on DNA replication (lagging and leading strand) is they were mutated so that they would not function. (2 points each) a. ligase b. single stranded binding protein c. DNA polymerase I d. Gyrase ...
... 40. For the following substances describe the possible effect on DNA replication (lagging and leading strand) is they were mutated so that they would not function. (2 points each) a. ligase b. single stranded binding protein c. DNA polymerase I d. Gyrase ...
Extrachromosomal DNA

Extrachromosomal DNA is any DNA that is found outside of the nucleus of a cell. It is also referred to as extranuclear DNA or cytoplasmic DNA. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes but DNA found outside of the nucleus also serves important biological functions.In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids whereas in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in research of replication because it is easy to identify and isolate.Extrachromosomal DNA was found to be structurally different from nuclear DNA. Cytoplasmic DNA is less methylated than DNA found within the nucleus. It was also confirmed that the sequences of cytoplasmic DNA was different from nuclear DNA in the same organism, showing that cytoplasmic DNAs are not simply fragments of nuclear DNA.In addition to DNA found outside of the nucleus in cells, infection of viral genomes also provides an example of extrachromosomal DNA.