Chapter 3
... Make sure you know the significance of cytokinesis 14. Identify and describe the steps that result in DNA replication Know why it is called semi-conservative replication Role of DNA polymerase and helicase 15. Describe the events that take place in transcription 16. Describe the events that ta ...
... Make sure you know the significance of cytokinesis 14. Identify and describe the steps that result in DNA replication Know why it is called semi-conservative replication Role of DNA polymerase and helicase 15. Describe the events that take place in transcription 16. Describe the events that ta ...
genetics-1 - MacsScienceSpace
... chosen from, the list below, that is best described by that d) DNA, messenger RNA, transfer RNA, phrase. [A number may be used more than once or not at all.] polypeptide 35) Sometimes a section of a chromosome is lost during meiosis. This loss results in a change in genetic material known as a) a de ...
... chosen from, the list below, that is best described by that d) DNA, messenger RNA, transfer RNA, phrase. [A number may be used more than once or not at all.] polypeptide 35) Sometimes a section of a chromosome is lost during meiosis. This loss results in a change in genetic material known as a) a de ...
The human genome
... There are two kinds of distance metric for chromosome. Physical distances are measured in terms of number of base pairs (abbreviated as bp) Between two points. The units for physical distances are bp and kb (1000 bp). Genetic distances are defined as the expected numbers of crossovers between two p ...
... There are two kinds of distance metric for chromosome. Physical distances are measured in terms of number of base pairs (abbreviated as bp) Between two points. The units for physical distances are bp and kb (1000 bp). Genetic distances are defined as the expected numbers of crossovers between two p ...
Protein Synthesis (Transcription and Translation)
... • A point mutation is a change in a single base pair in DNA. • A change in a single nitrogenous base can change the entire structure of a protein because a change in a single amino acid can affect the shape of the protein. ...
... • A point mutation is a change in a single base pair in DNA. • A change in a single nitrogenous base can change the entire structure of a protein because a change in a single amino acid can affect the shape of the protein. ...
BLAST - Georgia State University
... The Motif Finding Problem: Formulation The Motif Finding Problem: Given a set of DNA sequences, find a set of lmers, one from each sequence, that maximizes the consensus score • Input: A t x n matrix of DNA, and l, the length of the pattern to find • Output: An array of t starting positions s = (s1 ...
... The Motif Finding Problem: Formulation The Motif Finding Problem: Given a set of DNA sequences, find a set of lmers, one from each sequence, that maximizes the consensus score • Input: A t x n matrix of DNA, and l, the length of the pattern to find • Output: An array of t starting positions s = (s1 ...
Chapter 13 Genetics and Biotechnology
... A carrier, called a vector transfers the recombinant DNA into a bacterial cell called the host cell. Plasmids (small, circular double-stranded DNA molecules that occur naturally in bacteria) and viruses are commonly used vectors because they can be cut with restriction enzymes. If a plasmid and a DN ...
... A carrier, called a vector transfers the recombinant DNA into a bacterial cell called the host cell. Plasmids (small, circular double-stranded DNA molecules that occur naturally in bacteria) and viruses are commonly used vectors because they can be cut with restriction enzymes. If a plasmid and a DN ...
Science Pacing Resource Companion
... B.5.2 Describe how hereditary information passed from parents to offspring is encoded in the regions of DNA molecules called genes. SWBAT: Compare how genes affect heredity. B.5.3 Describe the process by which DNA directs the production of protein within a cell. SWBAT: Produce a protein from a g ...
... B.5.2 Describe how hereditary information passed from parents to offspring is encoded in the regions of DNA molecules called genes. SWBAT: Compare how genes affect heredity. B.5.3 Describe the process by which DNA directs the production of protein within a cell. SWBAT: Produce a protein from a g ...
Final Exam Review
... Name the phases of interphase. When is DNA duplicated? Review the stages of mitosis using diagrams of the process and lists of the characteristics of each stage. What is cytokinesis and how does it differ in plants and animals? What is the difference between sexual and asexual reproduction? Review t ...
... Name the phases of interphase. When is DNA duplicated? Review the stages of mitosis using diagrams of the process and lists of the characteristics of each stage. What is cytokinesis and how does it differ in plants and animals? What is the difference between sexual and asexual reproduction? Review t ...
Genetics 321 - Western Washington University
... …a pair of chromosomes containing the same linear gene sequence, each derived from one parent, – homologous chromosomes carry the same complement of genes, – the DNA sequence of the genes on homologous chromosomes may ...
... …a pair of chromosomes containing the same linear gene sequence, each derived from one parent, – homologous chromosomes carry the same complement of genes, – the DNA sequence of the genes on homologous chromosomes may ...
Lecture 6 - EukDNAexpression2007 - Cal State LA
... Both strands serve as templates for transcription by the host cell DNA dependent RNA polymerase II. Therefore, the strands are called the right and the left strand to indicate the direction of transcription. Immediate early gene – expression of E1A, the immediate early gene, is needed for the ex ...
... Both strands serve as templates for transcription by the host cell DNA dependent RNA polymerase II. Therefore, the strands are called the right and the left strand to indicate the direction of transcription. Immediate early gene – expression of E1A, the immediate early gene, is needed for the ex ...
Cell Division and Mitosis Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis DNA
... 16. Why is regeneration important for some organisms? In what way could regeneration of nerve cells be beneficial for humans? 17. What types of organisms are polyploidy? Why are they important? 18. What happens to chromosomes in meiosis I and meiosis II? 19. Describe several different ways that orga ...
... 16. Why is regeneration important for some organisms? In what way could regeneration of nerve cells be beneficial for humans? 17. What types of organisms are polyploidy? Why are they important? 18. What happens to chromosomes in meiosis I and meiosis II? 19. Describe several different ways that orga ...
MITOSIS COLORING
... the cytoplasm) and the nucleolus is visible. At this time the cell grows, the DNA replicates, and organelles grow in preparation for cell division. Color the centrioles red and the nuclear membrane yellow. Shade the chromatin blue. 2. Prophase. This is the first step of mitosis. The nuc ...
... the cytoplasm) and the nucleolus is visible. At this time the cell grows, the DNA replicates, and organelles grow in preparation for cell division. Color the centrioles red and the nuclear membrane yellow. Shade the chromatin blue. 2. Prophase. This is the first step of mitosis. The nuc ...
DNA Transcription
... We’ve seen how DNA is replicated, but still haven’t learned exactly how genes work! The first step in understanding how genes work is to know how to “decode” the DNA. ...
... We’ve seen how DNA is replicated, but still haven’t learned exactly how genes work! The first step in understanding how genes work is to know how to “decode” the DNA. ...
Document
... buffer (salt, pH) for enzyme to work. Mimics cellular conditions of bacteria they come from. ...
... buffer (salt, pH) for enzyme to work. Mimics cellular conditions of bacteria they come from. ...
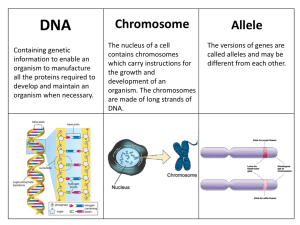
Chromosome Allele - GZ @ Science Class Online
... DNA Containing genetic information to enable an organism to manufacture all the proteins required to develop and maintain an organism when necessary. ...
... DNA Containing genetic information to enable an organism to manufacture all the proteins required to develop and maintain an organism when necessary. ...
Chromosomes come in pairs
... sequences can be transposed -inserted on other chromosomes. Transposition events sometimes occur in plants, eg flax, during times of ecological stress. It is a quick way to disrupt the phenotype, giving rise to new morphologies and physiologies in ...
... sequences can be transposed -inserted on other chromosomes. Transposition events sometimes occur in plants, eg flax, during times of ecological stress. It is a quick way to disrupt the phenotype, giving rise to new morphologies and physiologies in ...
Chapter 12
... § DNA containing the gene of interest is isolated § Plasmid DNA is treated with restriction enzyme that cuts in one place, opening the circle § DNA with the target gene is treated with the same enzyme and many fragments are produced § Plasmid and target DNA are mixed and associate with each other § ...
... § DNA containing the gene of interest is isolated § Plasmid DNA is treated with restriction enzyme that cuts in one place, opening the circle § DNA with the target gene is treated with the same enzyme and many fragments are produced § Plasmid and target DNA are mixed and associate with each other § ...
GENETICS
... sequence of nitrogenous bases of DNA is rewritten so that the same information appears in the nitrogenous bases of mRNA ...
... sequence of nitrogenous bases of DNA is rewritten so that the same information appears in the nitrogenous bases of mRNA ...
Creating a Fingerprint from DNA Evidence
... Restriction enzymes were discovered in bacteria cells. It appears that bacteria use these enzymes as a type of immune system. Any foreign DNA that enters a bacteria cell, from a virus perhaps, if the same sequence of bases is present on the foreign DNA as can be recognized by the enzyme, then the fo ...
... Restriction enzymes were discovered in bacteria cells. It appears that bacteria use these enzymes as a type of immune system. Any foreign DNA that enters a bacteria cell, from a virus perhaps, if the same sequence of bases is present on the foreign DNA as can be recognized by the enzyme, then the fo ...
Saturday Review – Biology
... ____ 34. The apparatus above was used to collect the oxygen that was produced by Elodea. Which factor was most responsible for the production of oxygen by Elodea? F. Sugar was present in the liquid. G. The liquid contained enough oxygen for the plant to absorb. H. The presence of light stimulated ph ...
... ____ 34. The apparatus above was used to collect the oxygen that was produced by Elodea. Which factor was most responsible for the production of oxygen by Elodea? F. Sugar was present in the liquid. G. The liquid contained enough oxygen for the plant to absorb. H. The presence of light stimulated ph ...
Extrachromosomal DNA

Extrachromosomal DNA is any DNA that is found outside of the nucleus of a cell. It is also referred to as extranuclear DNA or cytoplasmic DNA. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes but DNA found outside of the nucleus also serves important biological functions.In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids whereas in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in research of replication because it is easy to identify and isolate.Extrachromosomal DNA was found to be structurally different from nuclear DNA. Cytoplasmic DNA is less methylated than DNA found within the nucleus. It was also confirmed that the sequences of cytoplasmic DNA was different from nuclear DNA in the same organism, showing that cytoplasmic DNAs are not simply fragments of nuclear DNA.In addition to DNA found outside of the nucleus in cells, infection of viral genomes also provides an example of extrachromosomal DNA.