Transition bias and substitution models
... • Mutation: Transitional mutation occurs more frequently than transversions because – Misincorporation during DNA replication occur more frequently between two purines or between two pyrimidines than between a purine and a pyrimidine – A purine is more likely to mutate chemically to another purine t ...
... • Mutation: Transitional mutation occurs more frequently than transversions because – Misincorporation during DNA replication occur more frequently between two purines or between two pyrimidines than between a purine and a pyrimidine – A purine is more likely to mutate chemically to another purine t ...
is merriam`s elk really extinct?
... the arrival of the animals from Yellowstone. There are 3 Merriam's elk specimens in existence. DNA has been successfully extracted from one such specimen housed at the University of Arizona (known as "the Jesse Burke Rack). We used sequencing of a 111-basepair (bp) portion of the mtDNA control regio ...
... the arrival of the animals from Yellowstone. There are 3 Merriam's elk specimens in existence. DNA has been successfully extracted from one such specimen housed at the University of Arizona (known as "the Jesse Burke Rack). We used sequencing of a 111-basepair (bp) portion of the mtDNA control regio ...
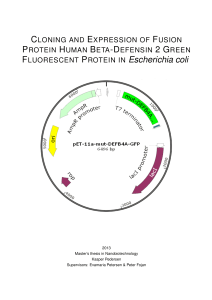
FLUORESCENT PROTEIN IN Escherichia coli
... up to a week before B-cells and T-cells have been produced to combat this infection. Here, the innate imune system will instead prevent that infection or limit it until the adaptive immune system is ready to take over [Hancock and Diamond, 2000]. The innate immune system is triggered by structures t ...
... up to a week before B-cells and T-cells have been produced to combat this infection. Here, the innate imune system will instead prevent that infection or limit it until the adaptive immune system is ready to take over [Hancock and Diamond, 2000]. The innate immune system is triggered by structures t ...
Chpt8_RecombineDNA.doc
... mediated conjugal transfer of parts of chromosomes in E. coli (Chapter 1). Recombination between two phage during a mixed infection of bacteria is another example. Also, the retrieval system for post-replicative repair (Chapter 7) involves general recombination. The mechanism of recombination has be ...
... mediated conjugal transfer of parts of chromosomes in E. coli (Chapter 1). Recombination between two phage during a mixed infection of bacteria is another example. Also, the retrieval system for post-replicative repair (Chapter 7) involves general recombination. The mechanism of recombination has be ...
K - Romanian Biotechnological Letters
... The non-conventional yeast Kluyveromyces lactis has become an excellent alternative yeast model organism [1, 2]. Reconsidered to be a distinct species [3, 4], K. lactis is an ascomyceteous budding yeast that belongs to the endoascomycetales [1]. There are important reasons for the increased attracti ...
... The non-conventional yeast Kluyveromyces lactis has become an excellent alternative yeast model organism [1, 2]. Reconsidered to be a distinct species [3, 4], K. lactis is an ascomyceteous budding yeast that belongs to the endoascomycetales [1]. There are important reasons for the increased attracti ...
209 Original Scientific Article THE INFLUENCE OF
... blastocyst what correspond with cell differentiation ...
... blastocyst what correspond with cell differentiation ...
WW Genetic Counselor English - Wonderwise
... genetic counselor. Cathy works in a hospital clinic, where she sees people of all ages. Adults and kids visit her with different kinds of health problems that might be passed on from one generation to the next. You probably know that we inherit features such as our hair or eye color from our parents ...
... genetic counselor. Cathy works in a hospital clinic, where she sees people of all ages. Adults and kids visit her with different kinds of health problems that might be passed on from one generation to the next. You probably know that we inherit features such as our hair or eye color from our parents ...
THE LAC OPERON
... Above is another diagram of the lac operon. Once the bacteria are exposed to different sugars, their operons have to either produce enzymes or not. Some control of the Lac operon is due to cAMP –cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate. cAMP is made when glucose levels are low and it acts to TURN ON or ACTIV ...
... Above is another diagram of the lac operon. Once the bacteria are exposed to different sugars, their operons have to either produce enzymes or not. Some control of the Lac operon is due to cAMP –cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate. cAMP is made when glucose levels are low and it acts to TURN ON or ACTIV ...
pdf
... measure of the genetic distance between them (reviewed in Chapter 1). The recombinant chromosomes resulting from a crossover are revealed in a mating between the heterozygous parent (A+B+/A-B-) and a homozygous recessive individual (A-B-/A-B-). Most of the germ cells contributed by the heterozygous ...
... measure of the genetic distance between them (reviewed in Chapter 1). The recombinant chromosomes resulting from a crossover are revealed in a mating between the heterozygous parent (A+B+/A-B-) and a homozygous recessive individual (A-B-/A-B-). Most of the germ cells contributed by the heterozygous ...
Binding of Hoechst with nucleic acids using fluorescence spectroscopy
... while sorption of this fluorescent dye on a surface of the hairpin oligonucleotide HP1, t-RNA and DNA. At small concentrations, this dye, adsorbed on the surface of DNA, RNA or HP1, does not show any specificity to certain nucleotides. In the case of unwound sites of DNA or HP1, it can bind inside, ...
... while sorption of this fluorescent dye on a surface of the hairpin oligonucleotide HP1, t-RNA and DNA. At small concentrations, this dye, adsorbed on the surface of DNA, RNA or HP1, does not show any specificity to certain nucleotides. In the case of unwound sites of DNA or HP1, it can bind inside, ...
Ds - e-Acharya
... on the transposition mechanism, diversity, number and rate of turnover of transposable elements in the genome at any given time. The transposable elements transpose by a mechanism that involves DNA synthesis followed by random integration at a new target site in the genome. All transposable elements ...
... on the transposition mechanism, diversity, number and rate of turnover of transposable elements in the genome at any given time. The transposable elements transpose by a mechanism that involves DNA synthesis followed by random integration at a new target site in the genome. All transposable elements ...
Gel Electrophoresis - Integrated DNA Technologies
... smaller than about 100 bases in an agarose gel because the sieving properties of agarose are not fine enough. On the other end of the scale, molecules longer than about 25,000 bp but shorter than around 2,000,000 bp will all run at the same rate. This is called limiting mobility. Nucleic acid molecu ...
... smaller than about 100 bases in an agarose gel because the sieving properties of agarose are not fine enough. On the other end of the scale, molecules longer than about 25,000 bp but shorter than around 2,000,000 bp will all run at the same rate. This is called limiting mobility. Nucleic acid molecu ...
AP & Regents Biology
... the time interval between 10 and 20 minutes. c. Account for the differences in oxygen consumption observed between: 1. germinating seeds at 22°C and at 10°C 2. germinating seeds and dry seeds. d. Describe the essential features of an experimental apparatus that could be used to measure oxygen consum ...
... the time interval between 10 and 20 minutes. c. Account for the differences in oxygen consumption observed between: 1. germinating seeds at 22°C and at 10°C 2. germinating seeds and dry seeds. d. Describe the essential features of an experimental apparatus that could be used to measure oxygen consum ...
QUESTION - Cloudfront.net
... protein synthesis and their products in order. • ANSWER : Dna is transcibed into mRNA that leaves the nucleus and goes to the ribosome where every 3 letters are read that code for amino acids. This is translation and tRNA brings the amino acids that are put together to make a protein. Answer ...
... protein synthesis and their products in order. • ANSWER : Dna is transcibed into mRNA that leaves the nucleus and goes to the ribosome where every 3 letters are read that code for amino acids. This is translation and tRNA brings the amino acids that are put together to make a protein. Answer ...
Lyons/Hewitt/Suchocki/Yeh, CONCEPTUAL INTEGRATED SCIENCE
... Copyright © 2007 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley ...
... Copyright © 2007 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley ...
Regional DNA Hypermethylation at D17S5
... Mutations. Perhaps the most striking feature of the present study is methylation of normally unmethylated CpG-rich areas can both result from and cause changes in chromatin structures (14-18). One known that several aspects of our data strongly suggest that D17S5 hyperm ethylation precedes both 17p ...
... Mutations. Perhaps the most striking feature of the present study is methylation of normally unmethylated CpG-rich areas can both result from and cause changes in chromatin structures (14-18). One known that several aspects of our data strongly suggest that D17S5 hyperm ethylation precedes both 17p ...
The Mitochondrial Genome of Chara vulgaris
... streptophyte mtDNAs suggests that introns have been gained independently in several lineages. Of the 11 introns in Chaetosphaeridium mtDNA, only the fourth intron in cox1 exhibits positional and structural conservation with one of the seven introns in Mesostigma mtDNA, and only the second intron in ...
... streptophyte mtDNAs suggests that introns have been gained independently in several lineages. Of the 11 introns in Chaetosphaeridium mtDNA, only the fourth intron in cox1 exhibits positional and structural conservation with one of the seven introns in Mesostigma mtDNA, and only the second intron in ...
B.2 Specific Aims. The term `epigenetics` literally means `above the
... modifications of gene expression potential[1]. DNA methylation is one molecular mechanism mediating epigenetic phenomena, and indicates the covalent transfer of a methyl group to the carbon at position 5 of cytosine residues,[2] usually within regions of DNA in which cytosine occurs next to a guanin ...
... modifications of gene expression potential[1]. DNA methylation is one molecular mechanism mediating epigenetic phenomena, and indicates the covalent transfer of a methyl group to the carbon at position 5 of cytosine residues,[2] usually within regions of DNA in which cytosine occurs next to a guanin ...
Geneticseasy
... Enzyme molecules are synthesized primarily from a. monosaccharides b. amino acids c. fatty acids d. phopholipids ...
... Enzyme molecules are synthesized primarily from a. monosaccharides b. amino acids c. fatty acids d. phopholipids ...
SYBR Green with low ROX
... sensitivity and amplification efficiency of various targets with the highest fluorescence signals. ...
... sensitivity and amplification efficiency of various targets with the highest fluorescence signals. ...
Initiation of recombination suppression and PAR formation during
... suppression of recombination with the X. In the early stages of sex-chromosome differentiation, it is suggested that interactions between sex-determining genes and sexually antagonistic genes can drive selection for reduced recombination via gradual reduction of crossover frequencies, due to the spr ...
... suppression of recombination with the X. In the early stages of sex-chromosome differentiation, it is suggested that interactions between sex-determining genes and sexually antagonistic genes can drive selection for reduced recombination via gradual reduction of crossover frequencies, due to the spr ...
A nomenclature for restriction enzymes, DNA methyltransferases
... their protein products are HsdR, HsdM and HsdS, respectively. The protein products can be abbreviated by omitting Hsd. The S subunit is the speci®city subunit that determines which DNA sequence is recognized. The R subunit is essential for cleavage (restriction) and the M subunit catalyzes the methy ...
... their protein products are HsdR, HsdM and HsdS, respectively. The protein products can be abbreviated by omitting Hsd. The S subunit is the speci®city subunit that determines which DNA sequence is recognized. The R subunit is essential for cleavage (restriction) and the M subunit catalyzes the methy ...
Using comparative genomic hybridization to
... duplications and deletions associated with population divergence and speciation [Anopheles gambiae: [18,19]], and genomic regions that differentiate humans from other primate species [20,21]. While most studies rely only on presence or absence metrics, a few studies have suggested that the relations ...
... duplications and deletions associated with population divergence and speciation [Anopheles gambiae: [18,19]], and genomic regions that differentiate humans from other primate species [20,21]. While most studies rely only on presence or absence metrics, a few studies have suggested that the relations ...
Extrachromosomal DNA

Extrachromosomal DNA is any DNA that is found outside of the nucleus of a cell. It is also referred to as extranuclear DNA or cytoplasmic DNA. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes but DNA found outside of the nucleus also serves important biological functions.In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids whereas in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in research of replication because it is easy to identify and isolate.Extrachromosomal DNA was found to be structurally different from nuclear DNA. Cytoplasmic DNA is less methylated than DNA found within the nucleus. It was also confirmed that the sequences of cytoplasmic DNA was different from nuclear DNA in the same organism, showing that cytoplasmic DNAs are not simply fragments of nuclear DNA.In addition to DNA found outside of the nucleus in cells, infection of viral genomes also provides an example of extrachromosomal DNA.