Atomic-Structure-Concise-Notes
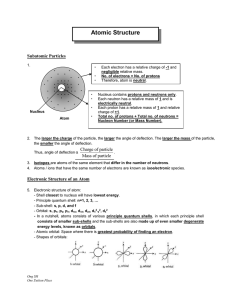
... - In a nutshell, atoms consists of various principle quantum shells, in which each principle shell consists of smaller sub-shells and the sub-shells are also made up of even smaller degenerate energy levels, known as orbitals. - Atomic orbital: Space where there is greatest probability of finding an ...
... - In a nutshell, atoms consists of various principle quantum shells, in which each principle shell consists of smaller sub-shells and the sub-shells are also made up of even smaller degenerate energy levels, known as orbitals. - Atomic orbital: Space where there is greatest probability of finding an ...
faster than light? - Particle Physics and Particle Astrophysics
... in the face of the thoroughly established facts of interference” [His paper on the measurement of h] “…this work resulted, contrary to my own expectation, in the first direct experimental proof…” [Nobel lecture] ...
... in the face of the thoroughly established facts of interference” [His paper on the measurement of h] “…this work resulted, contrary to my own expectation, in the first direct experimental proof…” [Nobel lecture] ...
File Vocabulary PPT set #1
... all objects to resist any change in motion – Things want to keep doing what they are doing ...
... all objects to resist any change in motion – Things want to keep doing what they are doing ...
Wave packets Uncertainty - cranson
... around the sun. de Broglie’s atom treats electrons more as waves with wave patterns that fit symmetrically within the atom. In both cases, the energy levels of the electrons must go up by an incremental quantity (quantum). ...
... around the sun. de Broglie’s atom treats electrons more as waves with wave patterns that fit symmetrically within the atom. In both cases, the energy levels of the electrons must go up by an incremental quantity (quantum). ...
pdf
... into protons and neutrons, and how those in turn stack up to form atomic nuclei. It forces the electrons orbiting the nucleus to occupy different orbits and is thus at the heart of all chemistry. It can decide whether some solid-state material is an insulator or a conductor. On astronomical scales, ...
... into protons and neutrons, and how those in turn stack up to form atomic nuclei. It forces the electrons orbiting the nucleus to occupy different orbits and is thus at the heart of all chemistry. It can decide whether some solid-state material is an insulator or a conductor. On astronomical scales, ...
ATAR Year 12 sample course outline - SCSA
... non-commercial purposes in educational institutions, provided that the School Curriculum and Standards Authority is acknowledged as the copyright owner, and that the Authority’s moral rights are not infringed. Copying or communication for any other purpose can be done only within the terms of the Co ...
... non-commercial purposes in educational institutions, provided that the School Curriculum and Standards Authority is acknowledged as the copyright owner, and that the Authority’s moral rights are not infringed. Copying or communication for any other purpose can be done only within the terms of the Co ...
Chapter 4: Struct of Atom
... S Classical and quantum domains are different S Planck’s constant helps with deciding where we are: e.g., energy of a baseball is classical while the energy of a moving electron is quantum S h = 6.626 x 10^-34 J-s -> E of baseball =(1/2)mv^2 is ~Joules and m ~ 0.1 kg while v ~ 90 mph ~ 40 m/s so ...
... S Classical and quantum domains are different S Planck’s constant helps with deciding where we are: e.g., energy of a baseball is classical while the energy of a moving electron is quantum S h = 6.626 x 10^-34 J-s -> E of baseball =(1/2)mv^2 is ~Joules and m ~ 0.1 kg while v ~ 90 mph ~ 40 m/s so ...
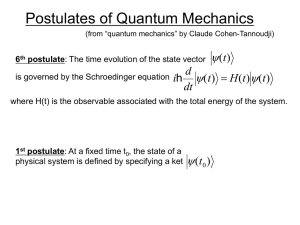
chem6V19_postulates
... where H(t) is the observable associated with the total energy of the system. ...
... where H(t) is the observable associated with the total energy of the system. ...
L35 - University of Iowa Physics
... depends on speed As speed increases, so does mass Speed can never exceed the speed of light, c ...
... depends on speed As speed increases, so does mass Speed can never exceed the speed of light, c ...
ATOMIC STRUCTURE Chapter 7
... Photoelectric Effect Albert Einstein (1879-1955) Photoelectric effect demonstrates the particle nature of light. (Kotz, figure 7.6) No e- observed until light of a certain minimum E is used. Number of e- ejected does NOT depend on frequency, rather it depends on light intensity. ...
... Photoelectric Effect Albert Einstein (1879-1955) Photoelectric effect demonstrates the particle nature of light. (Kotz, figure 7.6) No e- observed until light of a certain minimum E is used. Number of e- ejected does NOT depend on frequency, rather it depends on light intensity. ...
Energy levels, photons and spectral lines
... Observations of gas emission and absorption spectrum → ? ...
... Observations of gas emission and absorption spectrum → ? ...
Introduction to Quantum Physics
... The number of photoelectrons emitted per second is independent of the intensity of the light for all the different wavelengths. The number of photoelectrons emitted per second is directly proportional to the frequency for all the different wavelengths. The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectron ...
... The number of photoelectrons emitted per second is independent of the intensity of the light for all the different wavelengths. The number of photoelectrons emitted per second is directly proportional to the frequency for all the different wavelengths. The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectron ...
Lectuer 15
... - The z component of the angular momentum is determined completely by m through L z = m ħ. - The quantum number m is called the magnetic quantum number because the energy of a hydrogen atom in a magnetic field depends on m. - The (2 Ɩ + 1) – fold degeneracy in the absence of a magnetic field is spli ...
... - The z component of the angular momentum is determined completely by m through L z = m ħ. - The quantum number m is called the magnetic quantum number because the energy of a hydrogen atom in a magnetic field depends on m. - The (2 Ɩ + 1) – fold degeneracy in the absence of a magnetic field is spli ...
Lecture 29B - UCSD Department of Physics
... The electron cloud model is quite different from the Bohr model. The electron cloud structure does not change with time and remains the same on average. The atom does not radiate when it is in one particular quantum state. ...
... The electron cloud model is quite different from the Bohr model. The electron cloud structure does not change with time and remains the same on average. The atom does not radiate when it is in one particular quantum state. ...













![L 35 Modern Physics [1] - University of Iowa Physics](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001147028_1-f00aa7577568b42bc32948cbade9023a-300x300.png)