The Quantization of Wave Fields
... How(w(,1' "'. dOI'H not appear in the lagrangian density, so that i ie; identil,ally 1,"1'0. It � � � therefore impossible to satisfy the � � � � � � � � � of tho conuHutllliOIl rdatjoflS (54.28) (or the corresponding classical I'O[:-;SOIIbradwL n'ild,ioll), so that ljI*, i caIUlOt be regarded as a ...
... How(w(,1' "'. dOI'H not appear in the lagrangian density, so that i ie; identil,ally 1,"1'0. It � � � therefore impossible to satisfy the � � � � � � � � � of tho conuHutllliOIl rdatjoflS (54.28) (or the corresponding classical I'O[:-;SOIIbradwL n'ild,ioll), so that ljI*, i caIUlOt be regarded as a ...
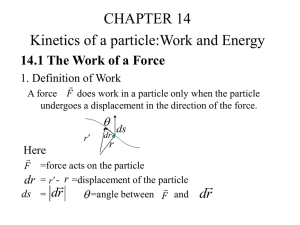
II. Forces
... 2. Types of waves. A wave is a disturbance of a medium which transports energy through the medium without permanently transporting matter. In a wave, particles of the medium are temporarily displaced and then return to their original position. A. Waves in which the particles of the medium move in a ...
... 2. Types of waves. A wave is a disturbance of a medium which transports energy through the medium without permanently transporting matter. In a wave, particles of the medium are temporarily displaced and then return to their original position. A. Waves in which the particles of the medium move in a ...
Word
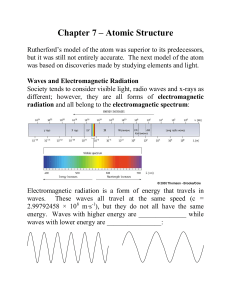
... A simple model of the atom explains why the electrons have discrete energy levels. The quantum properties of the electron are responsible for limiting its energy in the atom to certain discrete energy levels. Any quantum particle confined to a limited region of space can exist only in one of a numbe ...
... A simple model of the atom explains why the electrons have discrete energy levels. The quantum properties of the electron are responsible for limiting its energy in the atom to certain discrete energy levels. Any quantum particle confined to a limited region of space can exist only in one of a numbe ...
...detail
... 1. Determination of acceleration due to gravity with the help of a Kater’s pendulum. 2. Determination of Young’s modulus of a material in the form of a bar by the method of flexure. 3. Determination of coefficient of viscosity of water by Poiseuilli’s method. 4. Determination of coefficient of visco ...
... 1. Determination of acceleration due to gravity with the help of a Kater’s pendulum. 2. Determination of Young’s modulus of a material in the form of a bar by the method of flexure. 3. Determination of coefficient of viscosity of water by Poiseuilli’s method. 4. Determination of coefficient of visco ...
Quantum Numbers and Atomic Orbitals
... closed shell of electrons is very stable) • Valence are the electrons that are higher in energy – outside the closed shell ...
... closed shell of electrons is very stable) • Valence are the electrons that are higher in energy – outside the closed shell ...
What is Time in Quantum Mechanics?
... True “geometrical quantization” must join two branches of mathematics: geometry and probability. While geometrical part is well developed, the probabilistic part is, till now, mostly neglected. Quantum theory is a theory of measurements, and measurements are irreversible processes that do not necess ...
... True “geometrical quantization” must join two branches of mathematics: geometry and probability. While geometrical part is well developed, the probabilistic part is, till now, mostly neglected. Quantum theory is a theory of measurements, and measurements are irreversible processes that do not necess ...
Optics and Interferometry with Na2 Molecules
... of the apparatus. A similar contrast reduction is observed with atoms. We have used this separated beam molecule interferometer to measure the ratio of the real to imaginary parts of the index of refraction for the Na2 de Broglie waves passing through a Ne gas cell in one path of the interferometer, ...
... of the apparatus. A similar contrast reduction is observed with atoms. We have used this separated beam molecule interferometer to measure the ratio of the real to imaginary parts of the index of refraction for the Na2 de Broglie waves passing through a Ne gas cell in one path of the interferometer, ...
2 - School of Physics
... An example from hep An example from hep • SM without higgs predicts that after a set of cuts 64 events will remain, but in reality 80 events are found, is it the higgs signal? • No, because 80‐64 = 16 = 2 * sqrt(64) • Remember that RMS for a poisson distribution is sq ( ea ) sqrt(mean) ...
... An example from hep An example from hep • SM without higgs predicts that after a set of cuts 64 events will remain, but in reality 80 events are found, is it the higgs signal? • No, because 80‐64 = 16 = 2 * sqrt(64) • Remember that RMS for a poisson distribution is sq ( ea ) sqrt(mean) ...
Path integrals and the classical approximation
... lution according to i(d/dt) ψ(t) = H ψ(t) . Here H is an operator on the space of states. Possible measurements and symmetry operations are represented by other operators. In the simplest case, this formulation is the same as the one particle Schrödinger equation. This is the Schrödinger picture ...
... lution according to i(d/dt) ψ(t) = H ψ(t) . Here H is an operator on the space of states. Possible measurements and symmetry operations are represented by other operators. In the simplest case, this formulation is the same as the one particle Schrödinger equation. This is the Schrödinger picture ...
1. dia
... The spin quantum number (s) It defines the value of the spin angular momentum of the electron. It is imagined as the electron (like the Earth) not just revolving around its orbit but it is spinning around its own axis. The electron’s own angular momentums can only be: ...
... The spin quantum number (s) It defines the value of the spin angular momentum of the electron. It is imagined as the electron (like the Earth) not just revolving around its orbit but it is spinning around its own axis. The electron’s own angular momentums can only be: ...
chapter46
... Field particles are also called gauge bosons The interacting particles continually emit and absorb field particles The emission of a field particle by one particle and its absorption by another manifests itself as a force between the two interacting particles The force is mediated, or carried, by th ...
... Field particles are also called gauge bosons The interacting particles continually emit and absorb field particles The emission of a field particle by one particle and its absorption by another manifests itself as a force between the two interacting particles The force is mediated, or carried, by th ...
Glossary File
... Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory in Batavia, Illinois (near Chicago). Named for particle physics pioneer Enrico Fermi. ...
... Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory in Batavia, Illinois (near Chicago). Named for particle physics pioneer Enrico Fermi. ...
JCE0597 p605 Numerical Methods for Finding Momentum Space
... condensate to obtain the velocity (and momentum, p = m v) distribution of the original condensate. Owing to the position/momentum symmetry mentioned above, this is equivalent to the spatial distribution. Thus, a single spectroscopic measurement provides both the momentum and position wave functions ...
... condensate to obtain the velocity (and momentum, p = m v) distribution of the original condensate. Owing to the position/momentum symmetry mentioned above, this is equivalent to the spatial distribution. Thus, a single spectroscopic measurement provides both the momentum and position wave functions ...
The Future of Computer Science
... A.-Ambainis 2011: Massive generalization of collision lower bound. If f is any problem whatsoever that’s symmetric under permuting the inputs and outputs, and has sufficiently many outputs (like the collision problem), then f’s classical query complexity (f’s quantum query complexity)7 Compare to ...
... A.-Ambainis 2011: Massive generalization of collision lower bound. If f is any problem whatsoever that’s symmetric under permuting the inputs and outputs, and has sufficiently many outputs (like the collision problem), then f’s classical query complexity (f’s quantum query complexity)7 Compare to ...