Analytical and Chromatography - Sigma
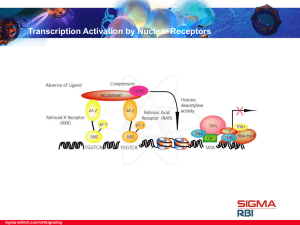
... • Retinoid X receptor (RXR) and Retinoic Acid receptor (RAR) are nuclear receptors that bind either all trans-retinoic (tRA) or 9-cis-retinoic acid (9cis-RA). In the absence of ligand, corepressors, such as Nuclear Receptor Corepressor (NCoR), Silencing Mediator of Retinoid and Thyroid Hormone Recep ...
... • Retinoid X receptor (RXR) and Retinoic Acid receptor (RAR) are nuclear receptors that bind either all trans-retinoic (tRA) or 9-cis-retinoic acid (9cis-RA). In the absence of ligand, corepressors, such as Nuclear Receptor Corepressor (NCoR), Silencing Mediator of Retinoid and Thyroid Hormone Recep ...
NUCLEIC ACID
... SIMPLE FACTS ABOUT DNA AND GENES • The information for development and specific function is stored in genes. • A gene is portion of genetic information definable according to the structure and functions. • Genes lie on chromosomes in the nuclei of the cells. • Chromosomes are made up of long chains ...
... SIMPLE FACTS ABOUT DNA AND GENES • The information for development and specific function is stored in genes. • A gene is portion of genetic information definable according to the structure and functions. • Genes lie on chromosomes in the nuclei of the cells. • Chromosomes are made up of long chains ...
Transposons: Mobile DNA DNA
... DNA transposons are able to transpose in direct, DNA-DNA manner and are present in prokaryotes and eukaryotes Two distinct mechanisms of transposition: •Replicative transposition – direct interaction between the donor transposon and the target site, resulting in copying of the donor ...
... DNA transposons are able to transpose in direct, DNA-DNA manner and are present in prokaryotes and eukaryotes Two distinct mechanisms of transposition: •Replicative transposition – direct interaction between the donor transposon and the target site, resulting in copying of the donor ...
Making Proteins - Hbwbiology.net
... Gene Regualtion and Structure - Protein synthesis in prokaryotes is controlled by on-off switches. Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes can regulate which genes are expressed. Escherichia coli - a bacterium in the human (and other animal) digestive tract that breaks down sugars. lactose - a disaccharide ...
... Gene Regualtion and Structure - Protein synthesis in prokaryotes is controlled by on-off switches. Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes can regulate which genes are expressed. Escherichia coli - a bacterium in the human (and other animal) digestive tract that breaks down sugars. lactose - a disaccharide ...
Dr Ishtiaq Regulation of gene expression
... • The second control mechanism is a response to glucose, which uses the Catabolite activator protein (CAP) to greatly increase production of β-galactosidase in the absence of glucose. • Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) is a signal molecule whose prevalence is inversely proportional to that of g ...
... • The second control mechanism is a response to glucose, which uses the Catabolite activator protein (CAP) to greatly increase production of β-galactosidase in the absence of glucose. • Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) is a signal molecule whose prevalence is inversely proportional to that of g ...
Leukaemia Section t(2;21)(p11;q22) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... Mathew S, Shurtleff SA, Raimondi SC. Novel cryptic, complex rearrangements involving ETV6-CBFA2 (TEL-AML1) genes identified by fluorescence in situ hybridization in pediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2001 Oct;32(2):188-93 ...
... Mathew S, Shurtleff SA, Raimondi SC. Novel cryptic, complex rearrangements involving ETV6-CBFA2 (TEL-AML1) genes identified by fluorescence in situ hybridization in pediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2001 Oct;32(2):188-93 ...
BB30055: Genes and genomes
... signal transduction and immune function) However, only 3 cases where a combination of 3 domain types shared by human & yeast proteins. e.g carbomyl-phosphate synthase (involved in the first 3 steps of de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis) has 7 domain types, which occurs once in human and yeast but twice ...
... signal transduction and immune function) However, only 3 cases where a combination of 3 domain types shared by human & yeast proteins. e.g carbomyl-phosphate synthase (involved in the first 3 steps of de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis) has 7 domain types, which occurs once in human and yeast but twice ...
TE content correlates positively with genome size
... • Variation in gene numbers cannot explain variation in genome size among eukaryotes • Most variation in genome size is due to variation in the amount of repetitive DNA (mostly derived from TEs) • TEs accumulate in intergenic and intronic regions ...
... • Variation in gene numbers cannot explain variation in genome size among eukaryotes • Most variation in genome size is due to variation in the amount of repetitive DNA (mostly derived from TEs) • TEs accumulate in intergenic and intronic regions ...
Coarse-Graining of Macromolecules
... Measurement of when genes are expressed. An example: the repressilator, a transcriptional regulatory network which leads to a time varying concentration of various gene products. The idea: stick an engineered set of genes into the cell and then turn them on. ...
... Measurement of when genes are expressed. An example: the repressilator, a transcriptional regulatory network which leads to a time varying concentration of various gene products. The idea: stick an engineered set of genes into the cell and then turn them on. ...
7.5 Eukaryotic Genome Regulation
... Many RNA coding genes are transcribed. Precursor RNAs fold into hairpin structures, which are cut and processed into miRNAs that regulate translation of mRNAs. ...
... Many RNA coding genes are transcribed. Precursor RNAs fold into hairpin structures, which are cut and processed into miRNAs that regulate translation of mRNAs. ...
protein processing
... MicroRNAs (miRNAs) • small single-stranded RNA molecules that can bind to mRNA • These can degrade mRNA or block its translation • Inhibition of gene expression by RNA molecules = RNA INTERFERENCE (RNAi) ...
... MicroRNAs (miRNAs) • small single-stranded RNA molecules that can bind to mRNA • These can degrade mRNA or block its translation • Inhibition of gene expression by RNA molecules = RNA INTERFERENCE (RNAi) ...
Chapter 18 notes
... Enhancers and specific transcription factors 1) proximal control elements – located close to promoter 2) distal control elements – located farther away…called enhancers a} may be upstream or downstream b} other proteins may bend DNA bringing enhancer closer to promoter c} proteins binding at enhance ...
... Enhancers and specific transcription factors 1) proximal control elements – located close to promoter 2) distal control elements – located farther away…called enhancers a} may be upstream or downstream b} other proteins may bend DNA bringing enhancer closer to promoter c} proteins binding at enhance ...
protein synthesis notes
... mRNA binds to small rRNA subunit w/start codon, AUG, in the “P” site tRNA w/ anticodon UAC and carrying a.a. methionine binds to start codon The next codon, in “A” site, binds w/ complimentary tRNA (carrying the corresponding a.a.) Enzyme forms a peptide bond between adjacent a.a. tRNA in “P” site n ...
... mRNA binds to small rRNA subunit w/start codon, AUG, in the “P” site tRNA w/ anticodon UAC and carrying a.a. methionine binds to start codon The next codon, in “A” site, binds w/ complimentary tRNA (carrying the corresponding a.a.) Enzyme forms a peptide bond between adjacent a.a. tRNA in “P” site n ...
GENE EXPRESSION - Doctor Jade Main
... Control of Transcription in Eukaryotic Cells • regulatory proteins bind to DNA to turn transcription of genes on & off • each eukaryotic gene has its own promoter & other control sequences • Activator proteins are more important in eukaryotic cells than in prokaryotic cells • in most eukaryotic org ...
... Control of Transcription in Eukaryotic Cells • regulatory proteins bind to DNA to turn transcription of genes on & off • each eukaryotic gene has its own promoter & other control sequences • Activator proteins are more important in eukaryotic cells than in prokaryotic cells • in most eukaryotic org ...
12.3 Transcription and Translation PPT
... Translation: Breaking the genetic code Translation is the process of decoding mRNA nucleotides into proteins • Proteins are made by joining amino acids into ...
... Translation: Breaking the genetic code Translation is the process of decoding mRNA nucleotides into proteins • Proteins are made by joining amino acids into ...
notes File - selu moodle
... Most common mechanism for termination is the formation of a hairpin structure In prokaryotes transcription and translation happen simultaneously. Operons are multiple genes under the control of the same promoter 15.4 Eukaryotic Transcription Promoter - -10sequence is a TATA box More initiation facto ...
... Most common mechanism for termination is the formation of a hairpin structure In prokaryotes transcription and translation happen simultaneously. Operons are multiple genes under the control of the same promoter 15.4 Eukaryotic Transcription Promoter - -10sequence is a TATA box More initiation facto ...
Genetics BIOL 335 Optional Worksheet 1 solutions 1
... 4. A mutant E coli has no activity for the enzyme isocitrate lyase. Does this result prove that the mutation is in the gene coding for isocitrate lyase? If not, what other mutations could result in the same phenotype? No, it does not. Mutations that affect gene expression could be involved. For exam ...
... 4. A mutant E coli has no activity for the enzyme isocitrate lyase. Does this result prove that the mutation is in the gene coding for isocitrate lyase? If not, what other mutations could result in the same phenotype? No, it does not. Mutations that affect gene expression could be involved. For exam ...
1, 2, 5, 6, 7 Time: 08:00
... enzymes involved in the replication of DNA. -Summarize the process of DNA replication. -Students will extract a sample of DNA. ...
... enzymes involved in the replication of DNA. -Summarize the process of DNA replication. -Students will extract a sample of DNA. ...
PCB 6528 Exam – Organelle genomes and gene expression
... [5 pt] Upstream events included: rearranged mitochondrial genomes; increased levels of mitochondrial transcripts; some novel mitochondrial gene transcripts. [5 pt] The downstream consequence was up-regulation of a suite of nuclear genes involved in: response to environmental signals; transcription f ...
... [5 pt] Upstream events included: rearranged mitochondrial genomes; increased levels of mitochondrial transcripts; some novel mitochondrial gene transcripts. [5 pt] The downstream consequence was up-regulation of a suite of nuclear genes involved in: response to environmental signals; transcription f ...
Gene Expression
... Transcription is the process of creating RNA from DNA. Transcription occurs in the cell's nucleus. RNA polymerase is the protein molecule that reads the DNA and creates the RNA intermediary. Transcription requires: DNA, RNA polymerase, ribonucleotides, and some ATP for energy. Uracil (U) is substitu ...
... Transcription is the process of creating RNA from DNA. Transcription occurs in the cell's nucleus. RNA polymerase is the protein molecule that reads the DNA and creates the RNA intermediary. Transcription requires: DNA, RNA polymerase, ribonucleotides, and some ATP for energy. Uracil (U) is substitu ...
GENETICS – BIO 300
... synteny: similar gene content & organization vastly different genome sizes due to transposons safe havens: strategy of insertion in other transposons, minimize negative effect on host transposons genes ...
... synteny: similar gene content & organization vastly different genome sizes due to transposons safe havens: strategy of insertion in other transposons, minimize negative effect on host transposons genes ...
File - MRS. WILSON Science
... Like DNA, RNA is a nucleic acid. It is made of nucleotides that consist of a phosphate group, a sugar, and a nitrogen-containing base. However, RNA differs in important ways from DNA: (1) RNA contains the sugar ribose, not deoxyribose; (2) RNA is made up of the nucleotides A, C, G, and uracil, U, wh ...
... Like DNA, RNA is a nucleic acid. It is made of nucleotides that consist of a phosphate group, a sugar, and a nitrogen-containing base. However, RNA differs in important ways from DNA: (1) RNA contains the sugar ribose, not deoxyribose; (2) RNA is made up of the nucleotides A, C, G, and uracil, U, wh ...
- PhagesDB
... Interestingly, both gp15 & gp17 give good hits as encoding a major tail subunit protein. We not that the closely related AM cluster Circum genome homologs have been annotated as capsid genes. We feel these two related homolog are in fact MCP genes. Gp96 gives really good blast hits to homologs of ta ...
... Interestingly, both gp15 & gp17 give good hits as encoding a major tail subunit protein. We not that the closely related AM cluster Circum genome homologs have been annotated as capsid genes. We feel these two related homolog are in fact MCP genes. Gp96 gives really good blast hits to homologs of ta ...























