Lecture 4, Exam III Worksheet Answers
... start/stop transcribing? What direction does it work in? RNA polymerase; larger than DNA polymerase, can take two nucleotides and add them together. Can make the beginning of a nucleotide without needing primase to make a primer; doesn’t need topoisomerase; doesn’t need helicase, because it has its ...
... start/stop transcribing? What direction does it work in? RNA polymerase; larger than DNA polymerase, can take two nucleotides and add them together. Can make the beginning of a nucleotide without needing primase to make a primer; doesn’t need topoisomerase; doesn’t need helicase, because it has its ...
name
... 6. Amino Acid chart based on anticodons (p. 367) 7. mutation – 8. Chromosome mutation (p.374)– a. deletion – b. duplication – c. translocation – d. inversion – 9. Gene mutation – a. frameshift mutation – b. point mutation – 10. cancer – uncontrolled cell division 11. causes of cancer a. mutagen b. c ...
... 6. Amino Acid chart based on anticodons (p. 367) 7. mutation – 8. Chromosome mutation (p.374)– a. deletion – b. duplication – c. translocation – d. inversion – 9. Gene mutation – a. frameshift mutation – b. point mutation – 10. cancer – uncontrolled cell division 11. causes of cancer a. mutagen b. c ...
Slide 1 - Piscataway High School
... Each strand acts as a template to make a new one. Both strands are copied at the same time, but in the opposite direction. ...
... Each strand acts as a template to make a new one. Both strands are copied at the same time, but in the opposite direction. ...
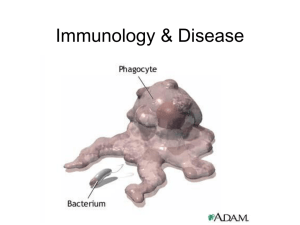
Protection against Disease
... There is a 3D fit between the amino acid chain in the antibody and the antigen This is similar to that between an enzyme and substrate-although not so precise ...
... There is a 3D fit between the amino acid chain in the antibody and the antigen This is similar to that between an enzyme and substrate-although not so precise ...
Genes
... heredity. Each gene is a segment of double-stranded DNA that holds the recipe for making a specific molecule, usually a protein. ...
... heredity. Each gene is a segment of double-stranded DNA that holds the recipe for making a specific molecule, usually a protein. ...
DNA and RNA Review
... 10. What does FIGURE 1 (picture on the right) show? 11. How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids? 12. Explain why it is possible for an amino acid to be specified by more than one kind of codon? ...
... 10. What does FIGURE 1 (picture on the right) show? 11. How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids? 12. Explain why it is possible for an amino acid to be specified by more than one kind of codon? ...
Immune Worksheet Session 27- 4/7/11
... 4) What are responsible for resetting the body’s thermostat upward? Where do these come from? ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY (general): 1) What are the 3 key characteristics of the adaptive immune response? 2) Name and define the two overlapping arms of adaptive immunity: ...
... 4) What are responsible for resetting the body’s thermostat upward? Where do these come from? ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY (general): 1) What are the 3 key characteristics of the adaptive immune response? 2) Name and define the two overlapping arms of adaptive immunity: ...
09/06
... Inserting a gene into a recombinant DNA plasmid Vector is a cloning vehicle. Both vector and donor DNA are cut with the same restriction enzyme. ...
... Inserting a gene into a recombinant DNA plasmid Vector is a cloning vehicle. Both vector and donor DNA are cut with the same restriction enzyme. ...
Quiz 2 Practice - philipdarrenjones.com
... a. half of the membrane is permeable and the other half is not. b. only large molecules can pass through. c. the cell regulates what passes in and out. d. the membrane is permeable part of the time. 8. The process whereby small molecules pass through a membrane by moving from an area of high concent ...
... a. half of the membrane is permeable and the other half is not. b. only large molecules can pass through. c. the cell regulates what passes in and out. d. the membrane is permeable part of the time. 8. The process whereby small molecules pass through a membrane by moving from an area of high concent ...
9B2.1 anti-glass INVESTIGATOR Name Gerald M. Rubin
... Ellis, M.C., O'Neill, E.M., and Rubin, G.M. (1993). Expression of Drosophila glass protein and evidence for negative regulation of its activity in non-neuronal cells by another DNA-binding protein. Development 119, 855-865. ...
... Ellis, M.C., O'Neill, E.M., and Rubin, G.M. (1993). Expression of Drosophila glass protein and evidence for negative regulation of its activity in non-neuronal cells by another DNA-binding protein. Development 119, 855-865. ...
What do Genes Look Like - Effingham County Schools
... Ex: German Shepard x German Shepard = German Shepard VII. _______________________________ – Desired genes are removed from one organism and added or recombined into another organism. This forms a transgenic organism with recombinant DNA A. This is used to make proteins not normally made by the cel ...
... Ex: German Shepard x German Shepard = German Shepard VII. _______________________________ – Desired genes are removed from one organism and added or recombined into another organism. This forms a transgenic organism with recombinant DNA A. This is used to make proteins not normally made by the cel ...
Ch. 43 - Immune System
... B Lymphocytes are 1 type of white blood cells or phagocytes (attack viruses in our bodies) Made in bone marrow Create a humoral response (means, “in the fluid” or in the ...
... B Lymphocytes are 1 type of white blood cells or phagocytes (attack viruses in our bodies) Made in bone marrow Create a humoral response (means, “in the fluid” or in the ...
Product Information Sheet - Sigma
... principally found in the cell nucleus, although it also occurs in the mitochondrion. The Watson-Crick structure provided a consistent basis for explaining protein synthesis. Biosynthesis of proteins occurs one amino acid at time forming the protein chain. Each amino acid has one or more “codons” of ...
... principally found in the cell nucleus, although it also occurs in the mitochondrion. The Watson-Crick structure provided a consistent basis for explaining protein synthesis. Biosynthesis of proteins occurs one amino acid at time forming the protein chain. Each amino acid has one or more “codons” of ...
MICROBIO320 Short Answers – These should be typically 1
... Complete the following Diagram of B Cell DNA Gene rearrangement (4 pts) The final Mature B cell will display IgA1 immunoglobulin with V3D1J2 specificity. How many individual rearrangement steps will be required to produce this heavy chain? ...
... Complete the following Diagram of B Cell DNA Gene rearrangement (4 pts) The final Mature B cell will display IgA1 immunoglobulin with V3D1J2 specificity. How many individual rearrangement steps will be required to produce this heavy chain? ...
... Two examples shown are plant cells and animal cells, but fungi and protists are also eukaryotic Notice, plants have chloroplasts (for photosynthesis) and cell walls made of cellulose. Animal cells don't have these parts. Also, plant cells have a larger vacuole for storage. Both plants and animals ha ...
You Asked for it….. - Mr. Smith’s Science Page
... Two examples shown are plant cells and animal cells, but fungi and protists are also eukaryotic Notice, plants have chloroplasts (for photosynthesis) and cell walls made of cellulose. Animal cells don't have these parts. Also, plant cells have a larger vacuole for storage. Both plants and animals ha ...
... Two examples shown are plant cells and animal cells, but fungi and protists are also eukaryotic Notice, plants have chloroplasts (for photosynthesis) and cell walls made of cellulose. Animal cells don't have these parts. Also, plant cells have a larger vacuole for storage. Both plants and animals ha ...
DNA vaccination

DNA vaccination is a technique for protecting an animal against disease by injecting it with genetically engineered DNA so cells directly produce an antigen, resulting in a protective immunological response. Several DNA vaccines have been released for veterinary use, and there has been promising research using the vaccines for viral, bacterial and parasitic diseases, as well as to several tumour types. Although only one DNA vaccine has been approved for human use, DNA vaccines may have a number of potential advantages over conventional vaccines, including the ability to induce a wider range of immune response types.