13. DNA Replication
... in simplest form, the concept that each strand of DNA serves as the template for synthesis of the daughter strand (Fig. 6.8) experimental evidence for the model Meselson and Stahl 1958 ...
... in simplest form, the concept that each strand of DNA serves as the template for synthesis of the daughter strand (Fig. 6.8) experimental evidence for the model Meselson and Stahl 1958 ...
CP Biology Second Semester Final Exam Review Guide
... 3. What is a scientific theory? 4. Describe the Galapagos Islands (why is life there so diverse?) 5. Why were Darwin’s ideas so controversial at the time? 6. What did James Hutton propose? 7. What did Charles Lyell propose? 8. How did the above scientists help shape Darwin’s theory? 9. Describe AND ...
... 3. What is a scientific theory? 4. Describe the Galapagos Islands (why is life there so diverse?) 5. Why were Darwin’s ideas so controversial at the time? 6. What did James Hutton propose? 7. What did Charles Lyell propose? 8. How did the above scientists help shape Darwin’s theory? 9. Describe AND ...
Chapter 9 DNA and the Molecular Structure of Chromosomes
... molecules of DNA segregated into about 50 domains. ...
... molecules of DNA segregated into about 50 domains. ...
Biology Homework Chapter 8
... 1. How does the movement of chromosomes during meiosis explain the principle of independent ...
... 1. How does the movement of chromosomes during meiosis explain the principle of independent ...
Genetic Engineering
... bacterial cells. These enzymes are now known to be part of the natural defence system of bacteria against bacterial viruses. They cut the virus DNA into small fragments and stop the infection process. There are many different types of restriction endonuclease, each one cutting the DNA at a specific ...
... bacterial cells. These enzymes are now known to be part of the natural defence system of bacteria against bacterial viruses. They cut the virus DNA into small fragments and stop the infection process. There are many different types of restriction endonuclease, each one cutting the DNA at a specific ...
PDF
... epigenetic reprogramming, so how does this demethylation impact gene expression and TE repression in PGCs? Richard Meehan and co-workers (p. 3623) show that DNA methylation at the promoters of germline-specific genes couples genome-defence mechanisms to epigenetic reprogramming in mouse PGCs. The re ...
... epigenetic reprogramming, so how does this demethylation impact gene expression and TE repression in PGCs? Richard Meehan and co-workers (p. 3623) show that DNA methylation at the promoters of germline-specific genes couples genome-defence mechanisms to epigenetic reprogramming in mouse PGCs. The re ...
Flagella as a Platform for Epitope-Based Vaccines
... The flagella expression system The general concept of our approach is to use conserved epi– topes derived from the pathogen as immunogens. Each epitope is expressed in Salmonella flagellin; the resultant recombinant flagella can be easily cleaved and purified for administration. This Salmonella is a ...
... The flagella expression system The general concept of our approach is to use conserved epi– topes derived from the pathogen as immunogens. Each epitope is expressed in Salmonella flagellin; the resultant recombinant flagella can be easily cleaved and purified for administration. This Salmonella is a ...
Exam 2
... C. be ½ tall and ½ dwarf D. be ¾ tall and ¼ dwarf E. all be short ____17. Edward was found to be heterozygous (Ss) for sickle-cell anemia. The alleles represented by the letters S and s are A. on the X and Y chromosomes. B. linked. C. on homologous chromosomes. D. both present in each of Edward’s sp ...
... C. be ½ tall and ½ dwarf D. be ¾ tall and ¼ dwarf E. all be short ____17. Edward was found to be heterozygous (Ss) for sickle-cell anemia. The alleles represented by the letters S and s are A. on the X and Y chromosomes. B. linked. C. on homologous chromosomes. D. both present in each of Edward’s sp ...
Chapter 12 Outline - Navarro College Shortcuts
... One of the least recognized of the body systems, the lymphatic system has been gaining ground in recognition and understanding over the past two decades, largely due to research into AIDS, cancer, and autoimmune disorders. Its importance in fighting disease and maintaining healthy homeostatic balanc ...
... One of the least recognized of the body systems, the lymphatic system has been gaining ground in recognition and understanding over the past two decades, largely due to research into AIDS, cancer, and autoimmune disorders. Its importance in fighting disease and maintaining healthy homeostatic balanc ...
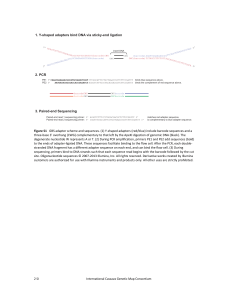
Figure S1 - G3: Genes | Genomes | Genetics
... degenerate nucleotide W represents A or T. (2) During PCR amplification, primers PE1 and PE2 add sequences (bold) to the ends of adapter‐ligated DNA. These sequences facilitate binding to the flow cell. After the PCR, each double‐ stranded DNA fragment has a different adapter sequence on each end, ...
... degenerate nucleotide W represents A or T. (2) During PCR amplification, primers PE1 and PE2 add sequences (bold) to the ends of adapter‐ligated DNA. These sequences facilitate binding to the flow cell. After the PCR, each double‐ stranded DNA fragment has a different adapter sequence on each end, ...
DNA Challenge DNA Challenge
... enzyme breaks the hydrogen bonds enzyme breaks the hydrogen bonds allowing the DNA to separate? ...
... enzyme breaks the hydrogen bonds enzyme breaks the hydrogen bonds allowing the DNA to separate? ...
Molecular Genetics
... The attachment point on the chromosome for the spindle fibres. The visible crossing-over of non-sister chromatids. A duplicated chromosome joined to its pair. It becomes visible at prophase. When chromatids separate at anaphase they are referred to as chromosomes. The genetic material during the res ...
... The attachment point on the chromosome for the spindle fibres. The visible crossing-over of non-sister chromatids. A duplicated chromosome joined to its pair. It becomes visible at prophase. When chromatids separate at anaphase they are referred to as chromosomes. The genetic material during the res ...
The antibody in real life
... parts…in many instances it's the cellular components that are more important than antibodies," Dr. Michel Nussenzweig, professor of immunology at Rockefeller. Many leukocytes are capable of recognition, learning and memory, many of which do not need antibodies to function in destruction and eliminat ...
... parts…in many instances it's the cellular components that are more important than antibodies," Dr. Michel Nussenzweig, professor of immunology at Rockefeller. Many leukocytes are capable of recognition, learning and memory, many of which do not need antibodies to function in destruction and eliminat ...
Primary DNA Molecular Structure
... Hydrostatic forces are very important to the molecular structure of DNA. Hydrostatic forces arise because of hydrogen bonding between the hydrogen and oxygen atoms in water. Polar molecules, because of thier charge, can interact with water without disrupting the ubiquitous latice of hydrogen bonds t ...
... Hydrostatic forces are very important to the molecular structure of DNA. Hydrostatic forces arise because of hydrogen bonding between the hydrogen and oxygen atoms in water. Polar molecules, because of thier charge, can interact with water without disrupting the ubiquitous latice of hydrogen bonds t ...
General Defence System - leavingcertbiology.net
... • All microorganisms have antigens on their surfaces that make it foreign to the body • Antigens are foreign molecules capable of eliciting an antibody response • An antibody is a protein produced by lymphocytes in response to an antigen • Antigens are found in bacterial cell walls, viral coats, for ...
... • All microorganisms have antigens on their surfaces that make it foreign to the body • Antigens are foreign molecules capable of eliciting an antibody response • An antibody is a protein produced by lymphocytes in response to an antigen • Antigens are found in bacterial cell walls, viral coats, for ...
DNA
... After completing all activities and assignments in this unit, students will be able to: • Describe mitosis and meiosis and explain their importance. • Construct and identify the parts of a model of a DNA molecule. • Describe how DNA copies itself. PA Science and Technology Standards covered in this ...
... After completing all activities and assignments in this unit, students will be able to: • Describe mitosis and meiosis and explain their importance. • Construct and identify the parts of a model of a DNA molecule. • Describe how DNA copies itself. PA Science and Technology Standards covered in this ...
8.1 study guide KEY
... Which type of enzyme destroys the ability of the transforming principle to function? ...
... Which type of enzyme destroys the ability of the transforming principle to function? ...
10/02 Chromatin and Chromosome structure
... •Compaction has to be undone to allow transcription •This can be seen in extreme circumstances as DNA puffs •Can be determined enzymatically by Dnase ...
... •Compaction has to be undone to allow transcription •This can be seen in extreme circumstances as DNA puffs •Can be determined enzymatically by Dnase ...
DNA
... They did this by using extracts from the heatkilled cells and digesting specific classes of molecules with enzymes Enzyme ...
... They did this by using extracts from the heatkilled cells and digesting specific classes of molecules with enzymes Enzyme ...
DNA vaccination

DNA vaccination is a technique for protecting an animal against disease by injecting it with genetically engineered DNA so cells directly produce an antigen, resulting in a protective immunological response. Several DNA vaccines have been released for veterinary use, and there has been promising research using the vaccines for viral, bacterial and parasitic diseases, as well as to several tumour types. Although only one DNA vaccine has been approved for human use, DNA vaccines may have a number of potential advantages over conventional vaccines, including the ability to induce a wider range of immune response types.