LEARNING GOALS - PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Main Idea
... mRNA carries information from the DNA to the ribosome. tRNA molecules bind specific amino acids and allow information in the mRNA to be translated to a linear peptide sequence. rRNA molecules are functional building blocks of ribosomes. The role of RNAi includes regulation of gene expression at the ...
... mRNA carries information from the DNA to the ribosome. tRNA molecules bind specific amino acids and allow information in the mRNA to be translated to a linear peptide sequence. rRNA molecules are functional building blocks of ribosomes. The role of RNAi includes regulation of gene expression at the ...
Chapter 10
... polymerases then unwind and separate the 2 strands of the double helix, exposing the DNA nucleotides on each strand. ...
... polymerases then unwind and separate the 2 strands of the double helix, exposing the DNA nucleotides on each strand. ...
New Title
... As you read, complete the flowchart below to show protein synthesis. Put the steps of the process in separate boxes in the flowchart in the order in which they occur. Protein Synthesis DNA provides code to form messenger RNA. ...
... As you read, complete the flowchart below to show protein synthesis. Put the steps of the process in separate boxes in the flowchart in the order in which they occur. Protein Synthesis DNA provides code to form messenger RNA. ...
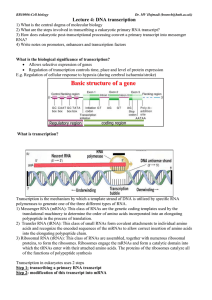
Lecture 4: DNA transcription
... Performed by spliceosomes (large RNA-protein complex made of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins) Recognise exon-intron boundaries and splice exons together by transesterification reactions Cell type-specific splicing ...
... Performed by spliceosomes (large RNA-protein complex made of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins) Recognise exon-intron boundaries and splice exons together by transesterification reactions Cell type-specific splicing ...
17-Gene to Protein
... Processing of RNA • Three types of RNA: mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA • eukaryotes have three polymerases • RNA polymerase II responsible for mRNA synthesis • Transcription subdivided into three stages: Initiation, elongation and termination • RNA must be processed before it can function ...
... Processing of RNA • Three types of RNA: mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA • eukaryotes have three polymerases • RNA polymerase II responsible for mRNA synthesis • Transcription subdivided into three stages: Initiation, elongation and termination • RNA must be processed before it can function ...
amino acids
... In what part of the cell does transcription take place? RNA makes proteins. Where are proteins made in the cell? ...
... In what part of the cell does transcription take place? RNA makes proteins. Where are proteins made in the cell? ...
Gene Expression
... Transcription is the process of creating RNA from DNA. Transcription occurs in the cell's nucleus. RNA polymerase is the protein molecule that reads the DNA and creates the RNA intermediary. Transcription requires: DNA, RNA polymerase, ribonucleotides, and some ATP for energy. Uracil (U) is substitu ...
... Transcription is the process of creating RNA from DNA. Transcription occurs in the cell's nucleus. RNA polymerase is the protein molecule that reads the DNA and creates the RNA intermediary. Transcription requires: DNA, RNA polymerase, ribonucleotides, and some ATP for energy. Uracil (U) is substitu ...
Lecture 15 Biol302 Spring 2011
... whether it is an expression of certain structural principles that are shared by many desoxypentose nucleic acids, despite far-reaching differences in their individual composition and the absence of a recognizable periodicity in their nucleotide sequence’’. He then added ‘‘It is believed that the tim ...
... whether it is an expression of certain structural principles that are shared by many desoxypentose nucleic acids, despite far-reaching differences in their individual composition and the absence of a recognizable periodicity in their nucleotide sequence’’. He then added ‘‘It is believed that the tim ...
Gene Expression
... RNA molecule is not needed to produce the polypeptide. The sections of m RNA which do not code for translation of polypeptide are called introns. ...
... RNA molecule is not needed to produce the polypeptide. The sections of m RNA which do not code for translation of polypeptide are called introns. ...
Document
... • carries the amino acid elements of a protein to the appropriate place as coded for by the mRNA. ...
... • carries the amino acid elements of a protein to the appropriate place as coded for by the mRNA. ...
Chapter 17 Molecular Genetics
... molecule is transferred to messenger RNA. – Messenger RNA molecules carry this information to the cytoplasm, where proteins are synthesized. – Messenger RNA serves as a template for protein synthesis. – Ribosomes are required to produce proteins on the mRNA template. ...
... molecule is transferred to messenger RNA. – Messenger RNA molecules carry this information to the cytoplasm, where proteins are synthesized. – Messenger RNA serves as a template for protein synthesis. – Ribosomes are required to produce proteins on the mRNA template. ...
Protein Synthesis
... • Clover-leaf shape • Single stranded molecule with attachment site at one end for an amino acid • Found out in the cytoplasm • Brings amino acid to ribosome ...
... • Clover-leaf shape • Single stranded molecule with attachment site at one end for an amino acid • Found out in the cytoplasm • Brings amino acid to ribosome ...
Chapter 3, Section 4 The DNA Connection
... • Contains a different sugar molecule. • Nitrogen base is different. • RNA contains uracil instead of thymine. ...
... • Contains a different sugar molecule. • Nitrogen base is different. • RNA contains uracil instead of thymine. ...
Biology 105
... Types of RNA Messenger RNA (mRNA) – carries specific info for making a protein Transfer RNA (tRNA) – bonds with only one specific amino acid and carries it to the ribosome Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – part of the structure of ribosomes and catalyzes functions during protein synthesis ...
... Types of RNA Messenger RNA (mRNA) – carries specific info for making a protein Transfer RNA (tRNA) – bonds with only one specific amino acid and carries it to the ribosome Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – part of the structure of ribosomes and catalyzes functions during protein synthesis ...
Positive Strand RNA Viruses
... methylated cap structure typical of eucaryotic mRNAs • It has a "ribosome landing pad" (known as the internal ribosome entry site or IRES) which enables ribosomes to bind without having to recognize a 5' methylated cap structure • Most host cell translation is cap-dependent, so this inhibits a lot o ...
... methylated cap structure typical of eucaryotic mRNAs • It has a "ribosome landing pad" (known as the internal ribosome entry site or IRES) which enables ribosomes to bind without having to recognize a 5' methylated cap structure • Most host cell translation is cap-dependent, so this inhibits a lot o ...
Answers section 4
... Lecture 15. 1. A 2. 3’-poly A tail, 5’-cap, splicing 3. D 4. D (E is the same as D – a mistake in typing) 5. A 6. if you are given 3’-CAT-5’ as the template strand of DNA, then the mRNA will be 5’GUA-3’. The mRNA will be 5’-CAU-3’ if it is the coding strand of DNA that you are given. 7. A 8. B 9. A ...
... Lecture 15. 1. A 2. 3’-poly A tail, 5’-cap, splicing 3. D 4. D (E is the same as D – a mistake in typing) 5. A 6. if you are given 3’-CAT-5’ as the template strand of DNA, then the mRNA will be 5’GUA-3’. The mRNA will be 5’-CAU-3’ if it is the coding strand of DNA that you are given. 7. A 8. B 9. A ...
RNA PP
... • During transcription, RNA polymerase binds to DNA and separates the DNA strands. RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a template from which nucleotides are assembled into a strand of RNA. • So, RNA is making a single-stranded copy from DNA that takes information out of the ...
... • During transcription, RNA polymerase binds to DNA and separates the DNA strands. RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a template from which nucleotides are assembled into a strand of RNA. • So, RNA is making a single-stranded copy from DNA that takes information out of the ...
Study Questions for Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein
... spliced out and exons are then joined together to make a continuous coding sequence 12) Introns (non-coding regions) were once thought to be “junk DNA” but now it is thought that they do have biological and/or evolutionary importance. List 3 potential functions of introns. 1. Increase opportunity fo ...
... spliced out and exons are then joined together to make a continuous coding sequence 12) Introns (non-coding regions) were once thought to be “junk DNA” but now it is thought that they do have biological and/or evolutionary importance. List 3 potential functions of introns. 1. Increase opportunity fo ...
Protein Synthesis A gene is a segment of DNA that is located on a
... RNA is usually single stranded not double stranded RNA is much shorter than DNA, usually the length of one gene Adenine pairs with uracil and cytosine pairs with guanine ...
... RNA is usually single stranded not double stranded RNA is much shorter than DNA, usually the length of one gene Adenine pairs with uracil and cytosine pairs with guanine ...
Central dogma: from genome to proteins
... Several important differences between the bacterial and eucaryotic RNA polymerases. • .While bacterial RNA polymerase (with s factor as one of its subunits) is able to initiate transcription on a DNA template in vitro without the help of additional proteins, eucaryotic RNA polymerases cannot. They ...
... Several important differences between the bacterial and eucaryotic RNA polymerases. • .While bacterial RNA polymerase (with s factor as one of its subunits) is able to initiate transcription on a DNA template in vitro without the help of additional proteins, eucaryotic RNA polymerases cannot. They ...
Section: Gene Regulation and Structure
... tRNA that is complementary to one of the codons of the genetic code ...
... tRNA that is complementary to one of the codons of the genetic code ...
RNA
... • During transcription, RNA polymerase binds to DNA and separates the DNA strands. RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a template from which nucleotides are assembled into a strand of RNA. • So, RNA is making a single-stranded copy from DNA that takes information out of the ...
... • During transcription, RNA polymerase binds to DNA and separates the DNA strands. RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a template from which nucleotides are assembled into a strand of RNA. • So, RNA is making a single-stranded copy from DNA that takes information out of the ...
RNA

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the letters G, U, A, and C to denote the nitrogenous bases guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function whereby mRNA molecules direct the assembly of proteins on ribosomes. This process uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) links amino acids together to form proteins.