
DNA - EPHS Knowles Biology
... 18. What type of RNA is made from messenger RNA? 19. What type of RNA is made during transcription? 20. Where does mRNA take the triplicate code after it leaves the nucleus? 21. Name two things tRNA carries. 22. Where does translation occur in the cell? 23. When codons are matched with anticodons am ...
... 18. What type of RNA is made from messenger RNA? 19. What type of RNA is made during transcription? 20. Where does mRNA take the triplicate code after it leaves the nucleus? 21. Name two things tRNA carries. 22. Where does translation occur in the cell? 23. When codons are matched with anticodons am ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS and CONSTRUCTION SITE ANALOGY
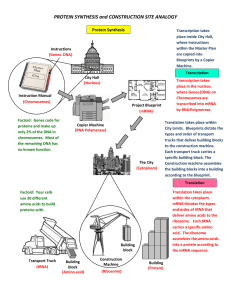
... where Genes (DNA) on Chromosomes are transcribed into mRNA by RNA Polymerase. Translation takes place within City Limits. Blueprints dictate the types and order of transport trucks that deliver building blocks to the construction machine. Each transport truck carries a specific building block. The C ...
... where Genes (DNA) on Chromosomes are transcribed into mRNA by RNA Polymerase. Translation takes place within City Limits. Blueprints dictate the types and order of transport trucks that deliver building blocks to the construction machine. Each transport truck carries a specific building block. The C ...
BUILDING THE LIFE MOLECULES: DNA AND RNA The
... The dissemination area of the Centro de Biotecnologia Molecular Estrutural (CBME) have been developing a program of new tools to help teaching and learning of structural molecular biology area at all levels, from elementary to graduate schools. In this way, we have developed a kit denoted Building t ...
... The dissemination area of the Centro de Biotecnologia Molecular Estrutural (CBME) have been developing a program of new tools to help teaching and learning of structural molecular biology area at all levels, from elementary to graduate schools. In this way, we have developed a kit denoted Building t ...
Genetics: The Science of Heredity
... 1. Initiation: DNA is unzipped and the enzyme RNA polymerase runs along the template strand of the DNA. – The template strand of DNA can be identified by finding the promotor region: nucleotide sequence T A C at the 3’ end (If the strand is written backwards it may look like C A T at the 3’ end). Th ...
... 1. Initiation: DNA is unzipped and the enzyme RNA polymerase runs along the template strand of the DNA. – The template strand of DNA can be identified by finding the promotor region: nucleotide sequence T A C at the 3’ end (If the strand is written backwards it may look like C A T at the 3’ end). Th ...
Transcription & Translation
... c. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) 1. structural RNA component of ribosomes 2. Ribosomes = rRNA and Protein ...
... c. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) 1. structural RNA component of ribosomes 2. Ribosomes = rRNA and Protein ...
RNA Interference Case Study - activity
... molecular genetics and ask you to weigh up the pros and cons of different therapeutic protocols. RNA Interference Case Study Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver which may be caused by viruses, alcohol and drugs. Symptoms include jaundice, fever, nausea and high levels of liver enzymes in the b ...
... molecular genetics and ask you to weigh up the pros and cons of different therapeutic protocols. RNA Interference Case Study Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver which may be caused by viruses, alcohol and drugs. Symptoms include jaundice, fever, nausea and high levels of liver enzymes in the b ...
Genetics Introduction:
... o DNA sugar= deoxyribose, RNA sugar= ribose o RNA contains pyrimidine uracil (U) in place of T o DNA double stranded, RNA single stranded ...
... o DNA sugar= deoxyribose, RNA sugar= ribose o RNA contains pyrimidine uracil (U) in place of T o DNA double stranded, RNA single stranded ...
DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis Webquest
... 1. What are the monomers (subunits or building blocks) of DNA and RNA? 2. What are the monomers (subunits or building blocks) of proteins? 3. What are genes made of? 4. What are the polypeptide chains that ribosomes synthesize made out of? Step 4: Steps of Protein Synthesis. Go to http://slideplayer ...
... 1. What are the monomers (subunits or building blocks) of DNA and RNA? 2. What are the monomers (subunits or building blocks) of proteins? 3. What are genes made of? 4. What are the polypeptide chains that ribosomes synthesize made out of? Step 4: Steps of Protein Synthesis. Go to http://slideplayer ...
Translation - Net Start Class
... transcribed from DNA in the nucleus and released in the cytoplasm ...
... transcribed from DNA in the nucleus and released in the cytoplasm ...
5. Protein Synthesis
... 5. Information flows from DNA to ________ to proteins. 6. What holds base pairs together? 7. What is the process of a cells making an exact copy of its DNA called? 8. What is a codon? 9. What is an anticodon and where is it found? 10. Briefly describe transcription. 11. Briefly describe translation. ...
... 5. Information flows from DNA to ________ to proteins. 6. What holds base pairs together? 7. What is the process of a cells making an exact copy of its DNA called? 8. What is a codon? 9. What is an anticodon and where is it found? 10. Briefly describe transcription. 11. Briefly describe translation. ...
Biology 12
... Transport of molecules in and out of cell: Proteins act as channels in cell membranes Hormones: control many aspects of homeostasis. (e.g. insulin) 9. What are two similarities between RNA and DNA? are polymers form from dehydration synthesis made up of nucleotides. has a backbone of the ...
... Transport of molecules in and out of cell: Proteins act as channels in cell membranes Hormones: control many aspects of homeostasis. (e.g. insulin) 9. What are two similarities between RNA and DNA? are polymers form from dehydration synthesis made up of nucleotides. has a backbone of the ...
Glossary of Bacterial Genetics
... chromosomes are in the nucleus and can be visualized with an optical microscope as threads or rods during meiosis and mitosis; in bacteria, the chromosome is usually a single circle of DNA that cannot be visualized with an optical microscope ...
... chromosomes are in the nucleus and can be visualized with an optical microscope as threads or rods during meiosis and mitosis; in bacteria, the chromosome is usually a single circle of DNA that cannot be visualized with an optical microscope ...
Chapter 10 Vocabulary Review
... results when the two strands of a DNA double helix separate so that the DNA molecule can be replicated ...
... results when the two strands of a DNA double helix separate so that the DNA molecule can be replicated ...
In the nucleus
... The codon of mRNA is translated into the amino acid sequence of a protein. Step 1- Processed mRNA leaves the nucleus and enters the cytoplasm and joins with 2 ribosome subunits. The mRNA start codon (AUG) signals a tRNA molecule carrying methionine and attaches at the anticodon at the P site. St ...
... The codon of mRNA is translated into the amino acid sequence of a protein. Step 1- Processed mRNA leaves the nucleus and enters the cytoplasm and joins with 2 ribosome subunits. The mRNA start codon (AUG) signals a tRNA molecule carrying methionine and attaches at the anticodon at the P site. St ...
[Type the document title] Microbial Genetics Molecular biology is the
... RNA Functions Three major RNAs:mRNA (messenger RNA): DNA transcript. tRNA(transfer RNA): transfer amino acid during protein synthesis. rRNA(ribosomal RNA): make up ribosomes. ...
... RNA Functions Three major RNAs:mRNA (messenger RNA): DNA transcript. tRNA(transfer RNA): transfer amino acid during protein synthesis. rRNA(ribosomal RNA): make up ribosomes. ...
Gene Expression
... • Eukaryotes modify the pre-messenger RNA. • The intervening sequences (Introns) are cut out and the expressed sequences (Exons) are spliced back together. This way, more than one protein can be made from a single gene! • Now it is mature mRNA ...
... • Eukaryotes modify the pre-messenger RNA. • The intervening sequences (Introns) are cut out and the expressed sequences (Exons) are spliced back together. This way, more than one protein can be made from a single gene! • Now it is mature mRNA ...
Key to Protein Synthesis Vocabulary
... carrying the growing polypeptide chain; P stands for peptidyl-tRNA site a change in a gene at a single nucleotide pair the modified 3’ end of an mRNA molecule consisting of the addition of 50 to 150 adenine nucleotides an aggregation of several ribosomes attached to one messenger RNA molecule an ini ...
... carrying the growing polypeptide chain; P stands for peptidyl-tRNA site a change in a gene at a single nucleotide pair the modified 3’ end of an mRNA molecule consisting of the addition of 50 to 150 adenine nucleotides an aggregation of several ribosomes attached to one messenger RNA molecule an ini ...
Protein Synthesis
... The Polypeptide chain is put together. Ribosome's moves along the chain and decodes the mRNA and attaches the amino acids together by peptide bonds. The tRNA will bring in the next amino acid, pair up with the codon on the mRNA and attach the next amino acid together ...
... The Polypeptide chain is put together. Ribosome's moves along the chain and decodes the mRNA and attaches the amino acids together by peptide bonds. The tRNA will bring in the next amino acid, pair up with the codon on the mRNA and attach the next amino acid together ...
Chapter 3 Protein Synthesis
... It’s replaced by Uracil – iii. RNA has Ribose and DNA has Deoxyribose sugar ...
... It’s replaced by Uracil – iii. RNA has Ribose and DNA has Deoxyribose sugar ...
Protein Synthesis and Mutations Review Sheet 2014
... Directions: Write the answers to each of the questions on a separate sheet of paper or flash cards. For the terms, either use them in your answers or separately define or describe their relation to the concepts of protein synthesis or mutations. Protein Synthesis: Chapter 8.4 and 8.5 1. What are thr ...
... Directions: Write the answers to each of the questions on a separate sheet of paper or flash cards. For the terms, either use them in your answers or separately define or describe their relation to the concepts of protein synthesis or mutations. Protein Synthesis: Chapter 8.4 and 8.5 1. What are thr ...
Chapter 3 Protein Synthesis Life Science RNA – Ribonucleic Acid
... replaced by Uracil • iii. RNA has Ribose and DNA has Deoxyribose sugar ...
... replaced by Uracil • iii. RNA has Ribose and DNA has Deoxyribose sugar ...
Lecture 2a – Origin of Life and the transition from the RNA world to
... Eigen’s theory is very useful in understanding the origin of life. The theory essentially shows that a selfreplicating molecule must be shorter (in terms of base pairs) than the reciprocal of the error rate for copying each base. It is thought that the first self-replicating molecule was an RNA (or ...
... Eigen’s theory is very useful in understanding the origin of life. The theory essentially shows that a selfreplicating molecule must be shorter (in terms of base pairs) than the reciprocal of the error rate for copying each base. It is thought that the first self-replicating molecule was an RNA (or ...
Nucleic Acids DNA & RNA
... •Happens during the S phase of Interphase. •Ensures each daughter cells is an exact copy of the parent cell. •Assisted by enzymes called DNA polmerase. ...
... •Happens during the S phase of Interphase. •Ensures each daughter cells is an exact copy of the parent cell. •Assisted by enzymes called DNA polmerase. ...
RNA

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the letters G, U, A, and C to denote the nitrogenous bases guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function whereby mRNA molecules direct the assembly of proteins on ribosomes. This process uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) links amino acids together to form proteins.













![[Type the document title] Microbial Genetics Molecular biology is the](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010247892_1-83bf00ba7ef17902054c2b83fe295408-300x300.png)







