Interfering with the genome: A new generation of disease treatments
... type of genetic material called RNA. Like DNA, RNA is comprised of nucleic acids, although RNA nucleic acids are subtly different from those of DNA. When a gene is being expressed, the relevant section of the DNA molecule unwinds to expose the underlying code, and RNA nucleic acids then create an in ...
... type of genetic material called RNA. Like DNA, RNA is comprised of nucleic acids, although RNA nucleic acids are subtly different from those of DNA. When a gene is being expressed, the relevant section of the DNA molecule unwinds to expose the underlying code, and RNA nucleic acids then create an in ...
Airgas template
... The __________________ square can be used to describe possible combinations that can occur with transmission of single-gene dominant and recessive traits. ...
... The __________________ square can be used to describe possible combinations that can occur with transmission of single-gene dominant and recessive traits. ...
Protein Synthesis
... therefore there are easily enough codons to code for all the necessary amino acids. • The same amino acid is often specified by more than one codon. However, the reverse is ...
... therefore there are easily enough codons to code for all the necessary amino acids. • The same amino acid is often specified by more than one codon. However, the reverse is ...
(RNA and Protein Synthesis) Section 11.4 Questions
... 24. How many nitrogenous bases make up a codon? __________ 25. What does a codon code for? _________________________ 26. Several codons make what? _________________________ 27. Which amino acid does the codon UUU code for? _________________________ 28. How many different triplet codes can be made wi ...
... 24. How many nitrogenous bases make up a codon? __________ 25. What does a codon code for? _________________________ 26. Several codons make what? _________________________ 27. Which amino acid does the codon UUU code for? _________________________ 28. How many different triplet codes can be made wi ...
12.3 notes
... • DNA is double stranded, RNA is single stranded • DNA contains deoxyribose sugar, RNA contains ribose sugar • DNA has thymine; RNA has uracil ...
... • DNA is double stranded, RNA is single stranded • DNA contains deoxyribose sugar, RNA contains ribose sugar • DNA has thymine; RNA has uracil ...
Central Dogma! - Cloudfront.net
... • tRNA: Bind specific amino acids and allow info in the mRNA to be translated into a linear peptide sequence. ...
... • tRNA: Bind specific amino acids and allow info in the mRNA to be translated into a linear peptide sequence. ...
Transcription & Translation
... • The steps of translation: • 1. Initiation: mRNA enters the cytoplasm and becomes associated with ribosomes (rRNA + proteins). • tRNAs, each carrying a specific amino acid, pair up with the mRNA codons inside the ribosomes. Base pairing (A-U, G-C) between mRNA codons and tRNA anticodons determines ...
... • The steps of translation: • 1. Initiation: mRNA enters the cytoplasm and becomes associated with ribosomes (rRNA + proteins). • tRNAs, each carrying a specific amino acid, pair up with the mRNA codons inside the ribosomes. Base pairing (A-U, G-C) between mRNA codons and tRNA anticodons determines ...
Lecture 0
... • Only one strand of the DNA double helix is utilized as the physical template for RNA synthesis, and is termed the template strand. • The coding strand has a 5’-3’ sequence that is identical to the 5’3’ sequence of the RNA. ...
... • Only one strand of the DNA double helix is utilized as the physical template for RNA synthesis, and is termed the template strand. • The coding strand has a 5’-3’ sequence that is identical to the 5’3’ sequence of the RNA. ...
Origin of Life (IB)
... Debate about the origin of life A. Scientific evidence for what could have happened. B. Alternative scientific theories: 1. Panspermia- meteorites brought organic molecules formed in outer space. 2. Nucleic acid genes may have been preceded by simpler hereditary systems. ...
... Debate about the origin of life A. Scientific evidence for what could have happened. B. Alternative scientific theories: 1. Panspermia- meteorites brought organic molecules formed in outer space. 2. Nucleic acid genes may have been preceded by simpler hereditary systems. ...
Origins of Sugars in the Prebiotic World
... • If the nucleophile is the 3’-OH group of another NTP, then a nucleic acid is generated: polymer of nucleotides – Oligomers (“oligos”) short length (DNA/RNA polymers of long ...
... • If the nucleophile is the 3’-OH group of another NTP, then a nucleic acid is generated: polymer of nucleotides – Oligomers (“oligos”) short length (DNA/RNA polymers of long ...
Introduction Document
... The three dimensional form of a protein is related to its function. A folded protein has varied nooks and bulges to bind to other molecules to build group or exchange atoms. Proteins are produced in a cell structure called ribosome where the amino acids are assembled one by one from an important mol ...
... The three dimensional form of a protein is related to its function. A folded protein has varied nooks and bulges to bind to other molecules to build group or exchange atoms. Proteins are produced in a cell structure called ribosome where the amino acids are assembled one by one from an important mol ...
Gene Expression/Transcription & Translation Practice PowerPoint
... In 1917 the biologist Thomas Hunt Morgan conducted studies in which he kept some caterpillars in the dark and placed other under red, green, or blue lights. Exposure to red light produced butterflies with brightly colored wings. Exposure to green light resulted in dark-colored wings. Exposure to bl ...
... In 1917 the biologist Thomas Hunt Morgan conducted studies in which he kept some caterpillars in the dark and placed other under red, green, or blue lights. Exposure to red light produced butterflies with brightly colored wings. Exposure to green light resulted in dark-colored wings. Exposure to bl ...
PCR - University of Hawaii
... T-DNA Mutagenesis: • T-DNA=Transfer DNA • Mutagenesis=Creating mutations! • mutations are changes to the base pair sequence of genetic material (either DNA or RNA). Mutations can be caused by copying errors in the genetic material during cell division and by exposure to ultraviolet or ionizing radi ...
... T-DNA Mutagenesis: • T-DNA=Transfer DNA • Mutagenesis=Creating mutations! • mutations are changes to the base pair sequence of genetic material (either DNA or RNA). Mutations can be caused by copying errors in the genetic material during cell division and by exposure to ultraviolet or ionizing radi ...
Ch 5
... mRNA has codons – a sequence of 3 nucleotides that codes for an amino acid. tRNA has anticodons that are complementary to mRNA’s codons. AUG is the universal ‘start’ codon that tells the ribosome to start translating. There are three ‘stop’codons – UAA, UAG and UGA – that tell the ribosome to stop t ...
... mRNA has codons – a sequence of 3 nucleotides that codes for an amino acid. tRNA has anticodons that are complementary to mRNA’s codons. AUG is the universal ‘start’ codon that tells the ribosome to start translating. There are three ‘stop’codons – UAA, UAG and UGA – that tell the ribosome to stop t ...
RNA polymerase
... (transfer RNA) - transports specific amino acids to ribosome during protein synthesis (translation). Anticodon - specific sequence of 3 nucleotides; complementary to an mRNA codon. ...
... (transfer RNA) - transports specific amino acids to ribosome during protein synthesis (translation). Anticodon - specific sequence of 3 nucleotides; complementary to an mRNA codon. ...
FROM DNA TO PROTEINS: gene expression Chapter 14 LECTURE
... The gene-enzyme relationship has since been revised to the Example: In hemoglobin, each polypeptide chain is specified by a separate gene. Other genes code for RNA are not translated to polypeptides; some genes are involved in controlling other genes. THE CENTRAL DOGMA The flow of information in cel ...
... The gene-enzyme relationship has since been revised to the Example: In hemoglobin, each polypeptide chain is specified by a separate gene. Other genes code for RNA are not translated to polypeptides; some genes are involved in controlling other genes. THE CENTRAL DOGMA The flow of information in cel ...
Lecture3 (1/22/08) "Nucleic Acids, RNA, and Proteins"
... Also, notice start & stop codons. Can tell on DNA where protein starts/stops. ...
... Also, notice start & stop codons. Can tell on DNA where protein starts/stops. ...
Slides - nanoHUB
... Also, notice start & stop codons. Can tell on DNA where protein starts/stops. ...
... Also, notice start & stop codons. Can tell on DNA where protein starts/stops. ...
Document
... • Only about 1.5% of the human genome codes for proteins. (This is also true of many other multicellular eukaryotes.) • Another small fraction of DNA consists of genes for ribosomal RNA and transfer RNA. • A flood of recent data suggests that a significant amount of the remaining genome is transcrib ...
... • Only about 1.5% of the human genome codes for proteins. (This is also true of many other multicellular eukaryotes.) • Another small fraction of DNA consists of genes for ribosomal RNA and transfer RNA. • A flood of recent data suggests that a significant amount of the remaining genome is transcrib ...
Protein Synthesis Notes
... a. made in the nucleus and reused in the cytoplasm b. reads mRNA and brings the correct amino acid to make a chain of amino acids (protein). This process is called “translation” c. The code is being translated into the language of amino acids. ...
... a. made in the nucleus and reused in the cytoplasm b. reads mRNA and brings the correct amino acid to make a chain of amino acids (protein). This process is called “translation” c. The code is being translated into the language of amino acids. ...
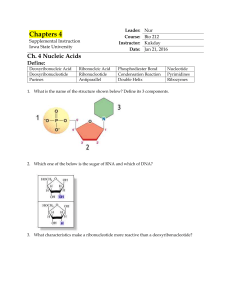
Ch. 4 Nucleic Acids Define
... We know that two strands of DNA form a double helix when they bond via hydrogen bonds. Regions in DNA rich in G and C nucleotides are harder to break apart. What might be the ...
... We know that two strands of DNA form a double helix when they bond via hydrogen bonds. Regions in DNA rich in G and C nucleotides are harder to break apart. What might be the ...
Protein Synthesis
... Enzymes control all the chemical reactions of an organism. By encoding the instructions for making proteins, DNA controls cells. ...
... Enzymes control all the chemical reactions of an organism. By encoding the instructions for making proteins, DNA controls cells. ...
RNA

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA it is more often found in nature as a single-strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double-strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the letters G, U, A, and C to denote the nitrogenous bases guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function whereby mRNA molecules direct the assembly of proteins on ribosomes. This process uses transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) links amino acids together to form proteins.