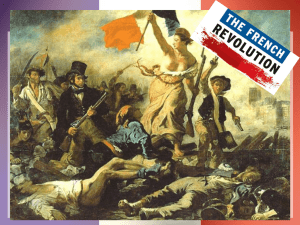
French Revolution
... Catholic Church. A Civil Constitution was put into place, in which the bishops and priests were to be elected by the people and paid by the state. ...
... Catholic Church. A Civil Constitution was put into place, in which the bishops and priests were to be elected by the people and paid by the state. ...
and internal threats (of traitors inside France threatening to frustrate
... CONCLUSION OF REIGN OF TERROR THE REIGN OF TERROR ULTIMATELY WEAKENED THE REVOLUTIONARY GOVERNMENT, WHILE TEMPORARILY ENDING INTERNAL OPPOSITION. THE JACOBINS EXPANDED THE SIZE OF THE ARMY, AND CARNOT REPLACED MANY NOBLE RANKED OFFICERS WITH SOLDIERS WHO HAD DEMONSTRATED THEIR PATRIOTISM, IF NOT TH ...
... CONCLUSION OF REIGN OF TERROR THE REIGN OF TERROR ULTIMATELY WEAKENED THE REVOLUTIONARY GOVERNMENT, WHILE TEMPORARILY ENDING INTERNAL OPPOSITION. THE JACOBINS EXPANDED THE SIZE OF THE ARMY, AND CARNOT REPLACED MANY NOBLE RANKED OFFICERS WITH SOLDIERS WHO HAD DEMONSTRATED THEIR PATRIOTISM, IF NOT TH ...
Chapter 1 The French Revolution
... 21ST September, 1792: The Convention abolished the monarchy and declared France a republic. 21st January, 1793: Louis XVI was executed publicly at the Place de la Concorde. Queen Marie Antoinette met with the same fate shortly after. The Reign of Terror ...
... 21ST September, 1792: The Convention abolished the monarchy and declared France a republic. 21st January, 1793: Louis XVI was executed publicly at the Place de la Concorde. Queen Marie Antoinette met with the same fate shortly after. The Reign of Terror ...
french_revolution_notes
... Second Estate - The Nobility Third Estate - The Commoners (95+%) Bourgeoisie (dominate the delegates) ...
... Second Estate - The Nobility Third Estate - The Commoners (95+%) Bourgeoisie (dominate the delegates) ...
The French Revolution - Mat
... March on Versailles • Despite these changes, King Louis XVI sill refused to accept the Declaration of Rights and recognize the National Assembly • March on Versailles led by women who were upset with harsh economic conditions and bread shortages • Marched to the King’s palace and demanded he move t ...
... March on Versailles • Despite these changes, King Louis XVI sill refused to accept the Declaration of Rights and recognize the National Assembly • March on Versailles led by women who were upset with harsh economic conditions and bread shortages • Marched to the King’s palace and demanded he move t ...
The French Revolution - Jenks Public Schools
... IV. Dawn of a New Era (cont.) • The Reign of Terror (July, 1793 – July, 1794) • Those suspected of treason were hunted down and punished (often times the victims were innocent) • 85% of the 40,000 were commoners • The Committee of Public Safety & Robespierre • Church was turned into a “temple of re ...
... IV. Dawn of a New Era (cont.) • The Reign of Terror (July, 1793 – July, 1794) • Those suspected of treason were hunted down and punished (often times the victims were innocent) • 85% of the 40,000 were commoners • The Committee of Public Safety & Robespierre • Church was turned into a “temple of re ...
Estates-General
... How did French citizens react to the King’s actions at the Estate-General? The Third Estate met to write a new ...
... How did French citizens react to the King’s actions at the Estate-General? The Third Estate met to write a new ...
U7frenchrevPP
... – July 14, 1789 a mob searching for gunpowder stormed The Bastille, a Paris prison. – Mob overwhelmed the guards. – Took control of the building. – Hacked the guards and prison commanders to death. – Paraded around the city with their heads on pikes. – Became a great symbolic act of Revolution to th ...
... – July 14, 1789 a mob searching for gunpowder stormed The Bastille, a Paris prison. – Mob overwhelmed the guards. – Took control of the building. – Hacked the guards and prison commanders to death. – Paraded around the city with their heads on pikes. – Became a great symbolic act of Revolution to th ...
The French Revolution Begins Economic and social inequalities in
... • got locked out of their meeting because they spoke out • Broke into a tennis court - Sieyès persuades them to make major changes in French government • Tennis Court Oath — delegates decide to write new constitution for France ...
... • got locked out of their meeting because they spoke out • Broke into a tennis court - Sieyès persuades them to make major changes in French government • Tennis Court Oath — delegates decide to write new constitution for France ...
Causes of the French Revolution
... • Louis tried again to regain control this time by using the army and firing Necker • The National Assembly wanted a limited monarchy • Louis sided with conservative aristocrats ...
... • Louis tried again to regain control this time by using the army and firing Necker • The National Assembly wanted a limited monarchy • Louis sided with conservative aristocrats ...
French Revolution - Auburn High School
... 1. Why did revolutionaries fear that the Revolution was in danger? • Leaders driven to preserve and extend revolution • France was at war w/ much of Europe. • Peasants were revolting. (Sept. massacres) ...
... 1. Why did revolutionaries fear that the Revolution was in danger? • Leaders driven to preserve and extend revolution • France was at war w/ much of Europe. • Peasants were revolting. (Sept. massacres) ...
File
... • Louis was recognized on the route to Varennes, and Louis and his family was captured and brought back to Paris. ...
... • Louis was recognized on the route to Varennes, and Louis and his family was captured and brought back to Paris. ...
Jonathan Wang
... and India due to the __________________(22). France was no longer a dominant colonial power. From 1648 to 1653, the Fronde, a series of peasant rebellions occurred against ___________(23), who was ruling as regent of ______________(24). The peasants were angry because their rights were steadily decr ...
... and India due to the __________________(22). France was no longer a dominant colonial power. From 1648 to 1653, the Fronde, a series of peasant rebellions occurred against ___________(23), who was ruling as regent of ______________(24). The peasants were angry because their rights were steadily decr ...
DAY 114: Summation Questions From Play
... D. She was not descended from royalty. 9. Why did the nobles and clergy force Louis XVI to dismiss Jacques Necker? A. He was caught smuggling thousands of dollars from the government. B. They suspected that he was planning a revolt against the French government. C. He proposed that Louis XVI impose ...
... D. She was not descended from royalty. 9. Why did the nobles and clergy force Louis XVI to dismiss Jacques Necker? A. He was caught smuggling thousands of dollars from the government. B. They suspected that he was planning a revolt against the French government. C. He proposed that Louis XVI impose ...
French Revolution
... popped up in major French cities. Calls for a constitutional monarchy were more typical than an all-out revolution of the existing political structure. ...
... popped up in major French cities. Calls for a constitutional monarchy were more typical than an all-out revolution of the existing political structure. ...
APWH Ch 23 Revolutions
... • The Convention abolished the monarchy – As long as the royal family lived, the monarchy could be restored – Put the royal couple on trial for treason • Convictions were a foregone conclusion ...
... • The Convention abolished the monarchy – As long as the royal family lived, the monarchy could be restored – Put the royal couple on trial for treason • Convictions were a foregone conclusion ...
THE FRENCH REVOLUTION
... Emigres – Nobles who fled France during the peasant uprisings and hoped to restore the old system Sans-culottes – Workers and small shopkeepers who wanted a greater voice in the French government. ...
... Emigres – Nobles who fled France during the peasant uprisings and hoped to restore the old system Sans-culottes – Workers and small shopkeepers who wanted a greater voice in the French government. ...
Chapter 6 notes Sections 1 - 2
... Estate; the nobility, or Second Estate; and the rest of the population, or Third Estate. • In 1789, France faced social discontent, a severe financial crisis, and serious food shortages. • Louis XVI called on the Estates General to carry out reforms, but members of the Third Estate defied the king a ...
... Estate; the nobility, or Second Estate; and the rest of the population, or Third Estate. • In 1789, France faced social discontent, a severe financial crisis, and serious food shortages. • Louis XVI called on the Estates General to carry out reforms, but members of the Third Estate defied the king a ...
French Revolution Part 2 Reform, Radicals, and
... Church and State Church was seen as oppositional to the Revolution Assembly took over church property onNovember 2, 1789. Assembly sold church property to pay for government debt Priest had to be elected and paid by the state ...
... Church and State Church was seen as oppositional to the Revolution Assembly took over church property onNovember 2, 1789. Assembly sold church property to pay for government debt Priest had to be elected and paid by the state ...
Print › AP European History Chapter 19 Spielvogel | Quizlet | Quizlet
... composed of the Third Estate whose goal was to draw up a new constitution for France ...
... composed of the Third Estate whose goal was to draw up a new constitution for France ...
French Revolution Recall Guide File
... Committee of Public Safety; who headed it; what was it for Bastille: What was it; why was it important; effects ...
... Committee of Public Safety; who headed it; what was it for Bastille: What was it; why was it important; effects ...
French Revolution PPT
... -Coup d’etat against the Jacobin Club in control of the Committee of Public Safety. -Began with the vote in the National Convention to execute Maximilien Robespierre and other leaders of the Jacobin Club. -Robespierre is killed by the guillotine on July 28, 1794. -The National Convention is now cont ...
... -Coup d’etat against the Jacobin Club in control of the Committee of Public Safety. -Began with the vote in the National Convention to execute Maximilien Robespierre and other leaders of the Jacobin Club. -Robespierre is killed by the guillotine on July 28, 1794. -The National Convention is now cont ...
French Revolution Powerpoint
... Bourgeoisie-these were merchants and artisans. They believed in the ideas of the Enlightenment. They paid high taxes and were not allowed the social recognition of the 2nd estate. Workers- these were the cooks, servants, and blue collar workers. They were paid low wages and often had to resort to st ...
... Bourgeoisie-these were merchants and artisans. They believed in the ideas of the Enlightenment. They paid high taxes and were not allowed the social recognition of the 2nd estate. Workers- these were the cooks, servants, and blue collar workers. They were paid low wages and often had to resort to st ...
Louis XVI and the Legislative Assembly

The French Revolution was a period in the history of France covering the years 1789 to 1799, in which republicans overthrew the Bourbon monarchy and the Roman Catholic Church in France perforce underwent radical restructuring. This article covers the one-year period from 1 October 1791 to September 1792, during which France was governed by the Legislative Assembly, operating under the French Constitution of 1791, between the periods of the National Constituent Assembly and of the National Convention.