Genetics Packet 2017
... understanding of the different types of cloning is key to making an informed stance on the current issues surrounding cloning. The following are three of the types of cloning being most discussed in the media today: (1) recombinant DNA technology or DNA cloning, (2) reproductive cloning, and (3) the ...
... understanding of the different types of cloning is key to making an informed stance on the current issues surrounding cloning. The following are three of the types of cloning being most discussed in the media today: (1) recombinant DNA technology or DNA cloning, (2) reproductive cloning, and (3) the ...
HST.161 Molecular Biology and Genetics in Modern Medicine
... the phosphodiester linkage via the formation of a glycol intermediate to break the RNA chain. The 2’ position of the DNA chain is an H which can’t carry out this reaction Deamination of cytosine will lead to uracil not thymine making it possible for DNA repair enzymes to distinguish a damaged base; ...
... the phosphodiester linkage via the formation of a glycol intermediate to break the RNA chain. The 2’ position of the DNA chain is an H which can’t carry out this reaction Deamination of cytosine will lead to uracil not thymine making it possible for DNA repair enzymes to distinguish a damaged base; ...
Sequence ID: ref|WP_006700522.1
... Kinetic and Spectroscopic Studies of Bicupin Oxalate Oxidase and Putative Active Site Mutants ...
... Kinetic and Spectroscopic Studies of Bicupin Oxalate Oxidase and Putative Active Site Mutants ...
Initiation of transcription by Pol II Separate basal and activated
... Activated transcription by Pol II enhancers are sequences 5’ to TATAA transcriptional activators bind them • have distinct DNA binding and activation domains • activation domain interacts with mediator • helps assemble initiation complex on TATAA ...
... Activated transcription by Pol II enhancers are sequences 5’ to TATAA transcriptional activators bind them • have distinct DNA binding and activation domains • activation domain interacts with mediator • helps assemble initiation complex on TATAA ...
... Choice B: The version of Phosphofructose kinase (PFK) in the muscle is different than that from the liver. Although both catalyze the same reaction, they are regulated differently. Based on your knowledge of PFK in the liver, and your knowledge of liver and muscle function, suggest how PFK in the mu ...
Topic 2
... blood. Porcine and bovine insulin, extracted from the pancreases of pigs and cattle, have both been widely used. Porcine insulin has only one difference in amino acid sequence from human insulin and bovine insulin has three differences. Shark insulin, which has been used for treating diabetics in Ja ...
... blood. Porcine and bovine insulin, extracted from the pancreases of pigs and cattle, have both been widely used. Porcine insulin has only one difference in amino acid sequence from human insulin and bovine insulin has three differences. Shark insulin, which has been used for treating diabetics in Ja ...
Chapter 20~ DNA Technology & Genomics
... ◦ insert recombinant plasmid into bacteria ◦ grow recombinant bacteria in agar cultures bacteria make lots of copies of plasmid “cloning” the plasmid ...
... ◦ insert recombinant plasmid into bacteria ◦ grow recombinant bacteria in agar cultures bacteria make lots of copies of plasmid “cloning” the plasmid ...
Ten novel interaction partners for the histone H2A protein
... known to bind H2A, while 10 of these proteins were novel interactors for H2A. Two of these novel proteins, Cac1 and Paf1, have potential roles in gene expression in association with H2A. INTRODUCTION Protein-protein interactions play an important role in almost all cell activities. The focus of this ...
... known to bind H2A, while 10 of these proteins were novel interactors for H2A. Two of these novel proteins, Cac1 and Paf1, have potential roles in gene expression in association with H2A. INTRODUCTION Protein-protein interactions play an important role in almost all cell activities. The focus of this ...
Manipulating Plant Histone Genes to Improve Agrobacterium
... indicate a similar level of virulence on other species: The tumorigenic parent of A. tumefaciens EHA101, A277, does not show hyper-virulence on Arabidopsis root segments.7 Additionally, scientists have increased Agrobacterium virulence by generating strains with extra copies of the vir gene transcri ...
... indicate a similar level of virulence on other species: The tumorigenic parent of A. tumefaciens EHA101, A277, does not show hyper-virulence on Arabidopsis root segments.7 Additionally, scientists have increased Agrobacterium virulence by generating strains with extra copies of the vir gene transcri ...
Conservation of the three-dimensional structure in non
... consisting of six alpha helices [12]. The number of helices can be altered in different families of globin-like proteins. These helices are not randomly distributed in the protein, but they are oriented following standard helixhelix packing rules in order to form a globular structure. Globin-like fo ...
... consisting of six alpha helices [12]. The number of helices can be altered in different families of globin-like proteins. These helices are not randomly distributed in the protein, but they are oriented following standard helixhelix packing rules in order to form a globular structure. Globin-like fo ...
PCR of GFP - the BIOTECH Project
... 1. Label the PCR tube so that you can distinguish the samples in the tube. 2. Add 7.5 µl primer of each primer to each tube. If necessary, gently tap you tube on the counter to get all of the liquid to the bottom of the tube. 3. Add 15 µl GoTaq (green solution). Close the tubes and centrifuge briefl ...
... 1. Label the PCR tube so that you can distinguish the samples in the tube. 2. Add 7.5 µl primer of each primer to each tube. If necessary, gently tap you tube on the counter to get all of the liquid to the bottom of the tube. 3. Add 15 µl GoTaq (green solution). Close the tubes and centrifuge briefl ...
DETERMINATIVE DEGREE AND NUCLEOTIDE CONTENT OF DNA
... Thorough study of the genetic code in abstract way is useful for various DNA model constructions and indispensable for deep understanding of genes organization and expression [1]. In this direction the study of symmetries [2, 3], application of group theory [4] and implication of supersymmetry [5] a ...
... Thorough study of the genetic code in abstract way is useful for various DNA model constructions and indispensable for deep understanding of genes organization and expression [1]. In this direction the study of symmetries [2, 3], application of group theory [4] and implication of supersymmetry [5] a ...
Nucleic Acids
... D. A tRNA brings an amino acid to its codon on mRNA. B. The ribosome moves along a mRNA to add amino acids to the growing peptide chain. C. A completed polypeptide is released. ...
... D. A tRNA brings an amino acid to its codon on mRNA. B. The ribosome moves along a mRNA to add amino acids to the growing peptide chain. C. A completed polypeptide is released. ...
Nucleic Acids - notescentre.com
... D. A tRNA brings an amino acid to its codon on mRNA. B. The ribosome moves along a mRNA to add amino acids to the growing peptide chain. C. A completed polypeptide is released. ...
... D. A tRNA brings an amino acid to its codon on mRNA. B. The ribosome moves along a mRNA to add amino acids to the growing peptide chain. C. A completed polypeptide is released. ...
PDS 803482 Ron Blood and Cell DNA Mini
... Ron’s Blood and Cell DNA Mini Kit is designed for quick preparation of pure DNA. The kit contains spin columns, buffers and reagents necessary for cell lysis, DNA binding, washing and elution of DNA into small volume. Each kit contains a manual with detailed protocols of DNA extraction and purificat ...
... Ron’s Blood and Cell DNA Mini Kit is designed for quick preparation of pure DNA. The kit contains spin columns, buffers and reagents necessary for cell lysis, DNA binding, washing and elution of DNA into small volume. Each kit contains a manual with detailed protocols of DNA extraction and purificat ...
gen-305-presentation-14-16
... recombinant DNA. In this case, the ends are ‘sticky’ in that they have a short, single-stranded end that can base-pair with another piece of DNA cut with the same enzyme. ...
... recombinant DNA. In this case, the ends are ‘sticky’ in that they have a short, single-stranded end that can base-pair with another piece of DNA cut with the same enzyme. ...
Biology 30 - Patricia Schwandt Courses
... How many nucleotides are there in each codon? If there were only one, there could only be four codes, representing only four different amino acids. How many different codons can be made if there are two nucleotides in each, for example, AA, AT, AC, AG, and so on? Will this be enough to represent al ...
... How many nucleotides are there in each codon? If there were only one, there could only be four codes, representing only four different amino acids. How many different codons can be made if there are two nucleotides in each, for example, AA, AT, AC, AG, and so on? Will this be enough to represent al ...
Chapter 3 Proteins: - California State University San Marcos
... ►Released 3’ OH end used as primer for RT that generates ssDNA copy of element linked to target ►Leads to synthesis of second DNA strand that is inserted where original nick was made ...
... ►Released 3’ OH end used as primer for RT that generates ssDNA copy of element linked to target ►Leads to synthesis of second DNA strand that is inserted where original nick was made ...
Chapter 16 Lecture Notes
... It takes E. coli less than an hour to copy each of the 4.6 million nucleotide pairs in its single chromosome and divide to form two identical daughter cells. ...
... It takes E. coli less than an hour to copy each of the 4.6 million nucleotide pairs in its single chromosome and divide to form two identical daughter cells. ...
CHAPTER 16 THE MOLECULE BASIS OF INHERITANCE
... It takes E. coli less than an hour to copy each of the 4.6 million nucleotide pairs in its single chromosome and divide to form two identical daughter cells. ...
... It takes E. coli less than an hour to copy each of the 4.6 million nucleotide pairs in its single chromosome and divide to form two identical daughter cells. ...
Chapter 16 Outline
... It takes E. coli less than an hour to copy each of the 4.6 million nucleotide pairs in its single chromosome and divide to form two identical daughter cells. ...
... It takes E. coli less than an hour to copy each of the 4.6 million nucleotide pairs in its single chromosome and divide to form two identical daughter cells. ...
Methods for measuring rates of protein binding to insoluble scaffolds
... of 10 mm in human cells. The first level of packaging is the nucleosome, formed by the wrapping of DNA around a nucleosomal core consisting of an octamer complex with two molecules each of histones H2A, H2B, H3, and H4 [Luger et al., 1997; Richmond et al., 1984]. This forms a chromatin structure tha ...
... of 10 mm in human cells. The first level of packaging is the nucleosome, formed by the wrapping of DNA around a nucleosomal core consisting of an octamer complex with two molecules each of histones H2A, H2B, H3, and H4 [Luger et al., 1997; Richmond et al., 1984]. This forms a chromatin structure tha ...
Monohybrid Crosses
... At the end of replication, there are 2 new identical strands of DNA- 1 side is from the original DNA strand (template)- The other side is the newly formed strand that was “copied” Replication is the process in which a DNA model is copied and that replication occurs during the S (synthesis) phase of ...
... At the end of replication, there are 2 new identical strands of DNA- 1 side is from the original DNA strand (template)- The other side is the newly formed strand that was “copied” Replication is the process in which a DNA model is copied and that replication occurs during the S (synthesis) phase of ...
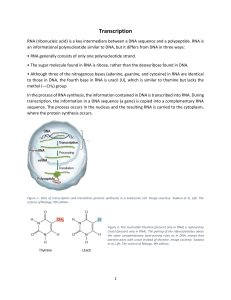
Transcription and RNA processing
... In prokaryotes, several adjacent genes sometimes share one promoter; however, in eukaryotes, each gene has its own promoter, which usually precedes the coding region. Eukaryotic genes undergo a systematic process called RNA processing to produce a mature mRNA from pre mRNA. Eukaryotic genes may cont ...
... In prokaryotes, several adjacent genes sometimes share one promoter; however, in eukaryotes, each gene has its own promoter, which usually precedes the coding region. Eukaryotic genes undergo a systematic process called RNA processing to produce a mature mRNA from pre mRNA. Eukaryotic genes may cont ...
Nucleosome

A nucleosome is a basic unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes, consisting of a segment of DNA wound in sequence around eight histone protein cores. This structure is often compared to thread wrapped around a spool.Nucleosomes form the fundamental repeating units of eukaryotic chromatin, which is used to pack the large eukaryotic genomes into the nucleus while still ensuring appropriate access to it (in mammalian cells approximately 2 m of linear DNA have to be packed into a nucleus of roughly 10 µm diameter). Nucleosomes are folded through a series of successively higher order structures to eventually form a chromosome; this both compacts DNA and creates an added layer of regulatory control, which ensures correct gene expression. Nucleosomes are thought to carry epigenetically inherited information in the form of covalent modifications of their core histones.Nucleosomes were observed as particles in the electron microscope by Don and Ada Olins and their existence and structure (as histone octamers surrounded by approximately 200 base pairs of DNA) were proposed by Roger Kornberg. The role of the nucleosome as a general gene repressor was demonstrated by Lorch et al. in vitro and by Han and Grunstein in vivo.The nucleosome core particle consists of approximately 147 base pairs of DNA wrapped in 1.67 left-handed superhelical turns around a histone octamer consisting of 2 copies each of the core histones H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. Core particles are connected by stretches of ""linker DNA"", which can be up to about 80 bp long. Technically, a nucleosome is defined as the core particle plus one of these linker regions; however the word is often synonymous with the core particle. Genome-wide nucleosome positioning maps are now available for many model organisms including mouse liver and brain.Linker histones such as H1 and its isoforms are involved in chromatin compaction and sit at the base of the nucleosome near the DNA entry and exit binding to the linker region of the DNA. Non-condensed nucleosomes without the linker histone resemble ""beads on a string of DNA"" under an electron microscope.In contrast to most eukaryotic cells, mature sperm cells largely use protamines to package their genomic DNA, most likely to achieve an even higher packaging ratio. Histone equivalents and a simplified chromatin structure have also been found in Archea, suggesting that eukaryotes are not the only organisms that use nucleosomes.