Transcription and RNA processing
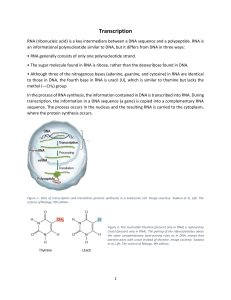
... In prokaryotes, several adjacent genes sometimes share one promoter; however, in eukaryotes, each gene has its own promoter, which usually precedes the coding region. Eukaryotic genes undergo a systematic process called RNA processing to produce a mature mRNA from pre mRNA. Eukaryotic genes may cont ...
... In prokaryotes, several adjacent genes sometimes share one promoter; however, in eukaryotes, each gene has its own promoter, which usually precedes the coding region. Eukaryotic genes undergo a systematic process called RNA processing to produce a mature mRNA from pre mRNA. Eukaryotic genes may cont ...
Folate and DNA methylation during in utero development and aging
... DNA methylation is the addition of a methyl group to a cytosine residue present in a CpG dinucleotide [2]. CpG dinucleotides occur at low abundance throughout the human DNA genome and tend to concentrate in regions known as CpG islands found in the promoter regions of genes. A CpG island is a region ...
... DNA methylation is the addition of a methyl group to a cytosine residue present in a CpG dinucleotide [2]. CpG dinucleotides occur at low abundance throughout the human DNA genome and tend to concentrate in regions known as CpG islands found in the promoter regions of genes. A CpG island is a region ...
... Restriction endonucleases can easily distinguish between these two sequences due to the formation of hydrogen bonds in the major groove. If restriction endonucleases bound in the minor groove would they be able to differentiate between an AT and a TA basepair? Begin by marking all non-watson crick h ...
Coffee, B, Zhang, F, Warren, ST and Reines, D: Acetylated histones are associated with the FMR1 gene in normal but not fragile X syndrome cells. Nature Genetics 22:98-101 (1999).
... Cell culture and drug treatments. EBV-transformed lymphoblastoid cell lines were derived from normal males or males with the typical clinical phenotype of fragile X syndrome. In normal cells, the FMR1 repeat is of normal length and methylation status, whereas those cells derived from patients exhibi ...
... Cell culture and drug treatments. EBV-transformed lymphoblastoid cell lines were derived from normal males or males with the typical clinical phenotype of fragile X syndrome. In normal cells, the FMR1 repeat is of normal length and methylation status, whereas those cells derived from patients exhibi ...
Your Spitting Image Guide DOC - University of Maryland School of
... DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is found inside the nucleus of a cell in tight bundles called chromosomes and contains all of our genetic information. This information is necessary to make a complete organism. Every cell in the human body, except red blood cells, has DNA. A person’s genetic information ...
... DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is found inside the nucleus of a cell in tight bundles called chromosomes and contains all of our genetic information. This information is necessary to make a complete organism. Every cell in the human body, except red blood cells, has DNA. A person’s genetic information ...
Misconceptions, misunderstandings and questions students
... among the molecules that give each cell type its characteristic properties. One type of property a cell type has is regulated growth to create an organ of a given size. Clearly, this is important if cells are going to cooperate to make a functioning body where all the parts form in correct relations ...
... among the molecules that give each cell type its characteristic properties. One type of property a cell type has is regulated growth to create an organ of a given size. Clearly, this is important if cells are going to cooperate to make a functioning body where all the parts form in correct relations ...
A conserved repetitive DNA element located in the centromeres of
... cereal species, including rice, wheat, barley, rye, and oats. However, it did not hybridize to any specific chromosomal regions of the several dicot species analyzed, including Vicia faba, tomato, tobacco, soybean, and Arabidopsis thaliana. The BAC clone 52A4 was digested with various restriction en ...
... cereal species, including rice, wheat, barley, rye, and oats. However, it did not hybridize to any specific chromosomal regions of the several dicot species analyzed, including Vicia faba, tomato, tobacco, soybean, and Arabidopsis thaliana. The BAC clone 52A4 was digested with various restriction en ...
NT-99476a - Interchim
... and D. M. J. Lilley, Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg, pp. 53-70, 1997. 2)Ishihama, A.: Promoter selectivity of prokaryotic RNA polymerases. Trends in Genet. 4, 282-286 (1988). 3)L. H. DeRiemer and C. F. Meares. J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm., 18, 1517 (1981). 4)T. M. Rana, and C. F. Meares, J. Am. Chem. ...
... and D. M. J. Lilley, Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg, pp. 53-70, 1997. 2)Ishihama, A.: Promoter selectivity of prokaryotic RNA polymerases. Trends in Genet. 4, 282-286 (1988). 3)L. H. DeRiemer and C. F. Meares. J. Labelled Compd. Radiopharm., 18, 1517 (1981). 4)T. M. Rana, and C. F. Meares, J. Am. Chem. ...
nuclear morphology and the ultra
... which can be drawn are limited by this fact. Nevertheless it seems probable that the nuclear membrane is an important locus of DNA synthesis in cells which have no readily discernible peripheral rim of heterochromatin. This may represent activity at the end of heterochromatic decondensation as the l ...
... which can be drawn are limited by this fact. Nevertheless it seems probable that the nuclear membrane is an important locus of DNA synthesis in cells which have no readily discernible peripheral rim of heterochromatin. This may represent activity at the end of heterochromatic decondensation as the l ...
File
... TA-5´ (b) 4 (c) ClaI: cannot be determined; TaqI: yes 5. A new restriction enzyme is discovered that recognizes an 8-base restriction sequence. About how many fragments of the Wombat genome (approximately 4.2 × 108 in size) would you expect if you digested it with this enzyme? Answer: An 8-base reco ...
... TA-5´ (b) 4 (c) ClaI: cannot be determined; TaqI: yes 5. A new restriction enzyme is discovered that recognizes an 8-base restriction sequence. About how many fragments of the Wombat genome (approximately 4.2 × 108 in size) would you expect if you digested it with this enzyme? Answer: An 8-base reco ...
SAMIE: STATISTICAL ALGORITHM FOR MODELING
... In the present report, we focus on SELEX data from studies on EGRderived proteins. According to \one-to-one" model of interaction 6 , amino acids at positions -1, 3 and 6 (with respect to the beginning of the -helix) contact bases at positions 3, 2 and 1 respectively; whereas amino acid at position ...
... In the present report, we focus on SELEX data from studies on EGRderived proteins. According to \one-to-one" model of interaction 6 , amino acids at positions -1, 3 and 6 (with respect to the beginning of the -helix) contact bases at positions 3, 2 and 1 respectively; whereas amino acid at position ...
DNA Structure: Gumdrop Modeling
... 2. Once you have your 6 nucleotides, pick up one of your “A” nucleotides (yellow). Q2. What is the complementary (matching) base for “A”? What color is that base? T (thymine); it is pink 3. Use a toothpick to bond the “A” nucleotide with its complementary nucleotide. Note that they should be connect ...
... 2. Once you have your 6 nucleotides, pick up one of your “A” nucleotides (yellow). Q2. What is the complementary (matching) base for “A”? What color is that base? T (thymine); it is pink 3. Use a toothpick to bond the “A” nucleotide with its complementary nucleotide. Note that they should be connect ...
Mossbourne Community Academy A
... Describe how you would expect the number of lysosomes in a pupa to change with the age of the pupa. Give a reason for your answer. ...
... Describe how you would expect the number of lysosomes in a pupa to change with the age of the pupa. Give a reason for your answer. ...
Making the connection: DNA to Protein Engagement Exploration
... • The genetic information encoded in DNA has assembled a protein with an abnormal amino acid sequence and therefore an altered function. Standards addressed in this module (AAAS Project 2061): • Genes are segments of DNA molecules. Inserting, deleting, or substituting DNA segments can alter genes. A ...
... • The genetic information encoded in DNA has assembled a protein with an abnormal amino acid sequence and therefore an altered function. Standards addressed in this module (AAAS Project 2061): • Genes are segments of DNA molecules. Inserting, deleting, or substituting DNA segments can alter genes. A ...
general introduction
... reduces the replication error rate to about 1:109. As a comparison, this is similar to typing 1000 books of 300 pages each with in total only one single typing error. Mutations Mutations are defined as permanent changes in the nucleotide sequence and comprise various types. Mutations are necessary f ...
... reduces the replication error rate to about 1:109. As a comparison, this is similar to typing 1000 books of 300 pages each with in total only one single typing error. Mutations Mutations are defined as permanent changes in the nucleotide sequence and comprise various types. Mutations are necessary f ...
Microbial Genetics Thesaurus
... altered so that they need to have a supply of a nutrient that is normally found only in the laboratory. When some potentially dangerous experiments are undergone by scientists, the organisms involved may be genetically engineered or extremely toxic to other organisms in some way. In such examples, t ...
... altered so that they need to have a supply of a nutrient that is normally found only in the laboratory. When some potentially dangerous experiments are undergone by scientists, the organisms involved may be genetically engineered or extremely toxic to other organisms in some way. In such examples, t ...
Facilitation of chromatin dynamics by SARs Craig M Hart and Ulrich
... tobacco plant cell lines [22]. The SAR effect is only observed following stable integration into the genome in all biological systems tested [22–24]. These cis-acting elements hence appear to require a chromatin environment as transiently transfected DNA is known to be poorly organized into nucleoso ...
... tobacco plant cell lines [22]. The SAR effect is only observed following stable integration into the genome in all biological systems tested [22–24]. These cis-acting elements hence appear to require a chromatin environment as transiently transfected DNA is known to be poorly organized into nucleoso ...
Chapter 12
... bring about the combining of genes from two different cells • This discovery led to the development of recombinant DNA technology – a set of techniques for combining genes from ...
... bring about the combining of genes from two different cells • This discovery led to the development of recombinant DNA technology – a set of techniques for combining genes from ...
Leukaemia Section t(2;8)(p23;p11) KAT6A/ASXL2 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... KAT6A is a histone acetyltransferase (HAT). KAT6A has intrinsic HAT activity; KAT6A also forms complexes with MEAF6 (1p34), ING5 (2q37), and BRPF1 (3p25) to acetylate histones H3. KAT6A is a transcriptional co-activator; it interacts with RUNX1 (21q22) and SPI1/PU.1 (11p11) to regulate the expressio ...
... KAT6A is a histone acetyltransferase (HAT). KAT6A has intrinsic HAT activity; KAT6A also forms complexes with MEAF6 (1p34), ING5 (2q37), and BRPF1 (3p25) to acetylate histones H3. KAT6A is a transcriptional co-activator; it interacts with RUNX1 (21q22) and SPI1/PU.1 (11p11) to regulate the expressio ...
Review Common Themes in Mechanisms of Gene Silencing
... involved in stabilizing such sequences. Most repetitive DNA elements are somehow recognized and inactivated by either transcriptional or posttranscriptional mechanisms (reviewed in Henikoff, 1998; Hsieh and Fire, 2000). Transcriptional inactivation of repetitive DNA is likely to involve silencing me ...
... involved in stabilizing such sequences. Most repetitive DNA elements are somehow recognized and inactivated by either transcriptional or posttranscriptional mechanisms (reviewed in Henikoff, 1998; Hsieh and Fire, 2000). Transcriptional inactivation of repetitive DNA is likely to involve silencing me ...
Monohybrid Crosses
... At the end of replication, there are 2 new identical strands of DNA- 1 side is from the original DNA strand (template)- The other side is the newly formed strand that was “copied” Replication is the process in which a DNA model is copied and that replication occurs during the S (synthesis) phase of ...
... At the end of replication, there are 2 new identical strands of DNA- 1 side is from the original DNA strand (template)- The other side is the newly formed strand that was “copied” Replication is the process in which a DNA model is copied and that replication occurs during the S (synthesis) phase of ...
Nucleosome

A nucleosome is a basic unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes, consisting of a segment of DNA wound in sequence around eight histone protein cores. This structure is often compared to thread wrapped around a spool.Nucleosomes form the fundamental repeating units of eukaryotic chromatin, which is used to pack the large eukaryotic genomes into the nucleus while still ensuring appropriate access to it (in mammalian cells approximately 2 m of linear DNA have to be packed into a nucleus of roughly 10 µm diameter). Nucleosomes are folded through a series of successively higher order structures to eventually form a chromosome; this both compacts DNA and creates an added layer of regulatory control, which ensures correct gene expression. Nucleosomes are thought to carry epigenetically inherited information in the form of covalent modifications of their core histones.Nucleosomes were observed as particles in the electron microscope by Don and Ada Olins and their existence and structure (as histone octamers surrounded by approximately 200 base pairs of DNA) were proposed by Roger Kornberg. The role of the nucleosome as a general gene repressor was demonstrated by Lorch et al. in vitro and by Han and Grunstein in vivo.The nucleosome core particle consists of approximately 147 base pairs of DNA wrapped in 1.67 left-handed superhelical turns around a histone octamer consisting of 2 copies each of the core histones H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. Core particles are connected by stretches of ""linker DNA"", which can be up to about 80 bp long. Technically, a nucleosome is defined as the core particle plus one of these linker regions; however the word is often synonymous with the core particle. Genome-wide nucleosome positioning maps are now available for many model organisms including mouse liver and brain.Linker histones such as H1 and its isoforms are involved in chromatin compaction and sit at the base of the nucleosome near the DNA entry and exit binding to the linker region of the DNA. Non-condensed nucleosomes without the linker histone resemble ""beads on a string of DNA"" under an electron microscope.In contrast to most eukaryotic cells, mature sperm cells largely use protamines to package their genomic DNA, most likely to achieve an even higher packaging ratio. Histone equivalents and a simplified chromatin structure have also been found in Archea, suggesting that eukaryotes are not the only organisms that use nucleosomes.























