BiochemReview
... Bonding, Salt Bridges, Van der Waals Forces, and Disulfide Bonds. – The strongest covalent bonds are disulfide bonds. – The strongest non-covalent bonds are salt bridges. – The force that contributes the most to tertiary structure is HYDROPHOBIC forces. • Hydrophobic residues put in core of protein ...
... Bonding, Salt Bridges, Van der Waals Forces, and Disulfide Bonds. – The strongest covalent bonds are disulfide bonds. – The strongest non-covalent bonds are salt bridges. – The force that contributes the most to tertiary structure is HYDROPHOBIC forces. • Hydrophobic residues put in core of protein ...
DNA and Protein Synthesis Notes 2015
... DNA – Structure Questions 1.What pair of scientists are largely credited for discovering the shape of the DNA molecule? 2.Name the scientist whose photographs helped solve the mystery of DNA’s structure 3.DNA is in the shape of a _______ _______. 4.What are the sides of the DNA molecule made of? ...
... DNA – Structure Questions 1.What pair of scientists are largely credited for discovering the shape of the DNA molecule? 2.Name the scientist whose photographs helped solve the mystery of DNA’s structure 3.DNA is in the shape of a _______ _______. 4.What are the sides of the DNA molecule made of? ...
PD-PR-083: Laboratory protocol for manual
... for a minimum of 2 hours, or in a 50°C water incubator for a minimum of 1 hour. ...
... for a minimum of 2 hours, or in a 50°C water incubator for a minimum of 1 hour. ...
17.1 – Isolating the Genetic Material
... → transforming principle: genetic information that can be transferred. In 1928, Fred Griffith discovered that dead pathogenic (disease-causing) bacteria could pass on their pathogenic properties to live non-pathogenic bacteria → Griffith died before discovering what the transforming factor was 5) Ma ...
... → transforming principle: genetic information that can be transferred. In 1928, Fred Griffith discovered that dead pathogenic (disease-causing) bacteria could pass on their pathogenic properties to live non-pathogenic bacteria → Griffith died before discovering what the transforming factor was 5) Ma ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... multiple transpositions of P element • Damaging chromosomal mutations are caused that render the hybrids sterile • P elements have practical value as mutagenic and transforming agents in genetic experiments with Drosophila ...
... multiple transpositions of P element • Damaging chromosomal mutations are caused that render the hybrids sterile • P elements have practical value as mutagenic and transforming agents in genetic experiments with Drosophila ...
Overview of recombinant technology
... The enhanced survival of UV-irradiated bacteria following exposure visible light is now known to be due to PHOTOLYASE, an enzyme that is encoded by E. coli genes phrA and phrB. This enzyme binds to pyrimidine dimers and uses energy from visible light (370 nm) to split the dimers apart. Phr- mutants ...
... The enhanced survival of UV-irradiated bacteria following exposure visible light is now known to be due to PHOTOLYASE, an enzyme that is encoded by E. coli genes phrA and phrB. This enzyme binds to pyrimidine dimers and uses energy from visible light (370 nm) to split the dimers apart. Phr- mutants ...
Presenting: DNA and RNA
... from the presence of abnormal molecules of the protein hemoglobin in red blood cells. A person with the sicklecell trait may have a child with the same condition because the child receives from the parent ...
... from the presence of abnormal molecules of the protein hemoglobin in red blood cells. A person with the sicklecell trait may have a child with the same condition because the child receives from the parent ...
Bmi1 (D42B3) Rabbit mAb - Cell Signaling Technology
... Background: The polycomb group (PcG) of proteins contributes to the maintenance of cell identity, stem cell self-renewal, cell cycle regulation, and oncogenesis by maintaining the silenced state of genes that promote cell lineage specification, cell death, and cell-cycle arrest (1-4). PcG proteins e ...
... Background: The polycomb group (PcG) of proteins contributes to the maintenance of cell identity, stem cell self-renewal, cell cycle regulation, and oncogenesis by maintaining the silenced state of genes that promote cell lineage specification, cell death, and cell-cycle arrest (1-4). PcG proteins e ...
Teacher resource 1
... Ser-Cys-Ile-Glu-Asn-Cys-Glu-stop-Ile-Ser-Ser-Arg-Ala-Arg-Gly-Tyr-Val SCIENCE ISSRARGYV ...
... Ser-Cys-Ile-Glu-Asn-Cys-Glu-stop-Ile-Ser-Ser-Arg-Ala-Arg-Gly-Tyr-Val SCIENCE ISSRARGYV ...
Study Guide
... ❏ How do organ systems work together to maintain homeostasis? Organ systems work together using signal molecules, proteins and communication between cells and tissues in order to maintain all aspects of the body at a set point. Negative feedback loops are often used to keep body at the setpoin ...
... ❏ How do organ systems work together to maintain homeostasis? Organ systems work together using signal molecules, proteins and communication between cells and tissues in order to maintain all aspects of the body at a set point. Negative feedback loops are often used to keep body at the setpoin ...
DNA - benanbiology
... • Two polynucleotide strands wrap around each other to form a DNA double helix – The two strands are associated because particular bases always hydrogen bond to one another – A pairs with T, and C pairs with G, producing base pairs ...
... • Two polynucleotide strands wrap around each other to form a DNA double helix – The two strands are associated because particular bases always hydrogen bond to one another – A pairs with T, and C pairs with G, producing base pairs ...
R N A & PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... information from DNA in the cells nucleus and carry it to the ribosomes. They serve as messengers to the cell. Transfer RNA (tRNA)~ the function of transfer RNA is to deliver amino acids one by one to protein chains growing at ribosomes. ...
... information from DNA in the cells nucleus and carry it to the ribosomes. They serve as messengers to the cell. Transfer RNA (tRNA)~ the function of transfer RNA is to deliver amino acids one by one to protein chains growing at ribosomes. ...
An in vitro RNA synthesis reaction was set up and allowed to
... added and RNA synthesis was allowed to continue. Then the RNA molecules were isolated from the reaction mixture and analyzed for the presence of radioactive nucleotides at the 5' and the 3' ends. Based on what you know about RNA synthesis, which end of the RNA molecules were found to be radioactive? ...
... added and RNA synthesis was allowed to continue. Then the RNA molecules were isolated from the reaction mixture and analyzed for the presence of radioactive nucleotides at the 5' and the 3' ends. Based on what you know about RNA synthesis, which end of the RNA molecules were found to be radioactive? ...
000 EXAM 2 study guide
... 4. Consider the Chi-square analysis - you will not do a Chi-square problem, but please understand what it accomplishes. Why is one of these hypotheses more appropriate for a null hypothesis? Options: "the genes are linked" , "the genes are not linked". 5. Understand Mitotic Recombination and Cancer ...
... 4. Consider the Chi-square analysis - you will not do a Chi-square problem, but please understand what it accomplishes. Why is one of these hypotheses more appropriate for a null hypothesis? Options: "the genes are linked" , "the genes are not linked". 5. Understand Mitotic Recombination and Cancer ...
幻灯片 1 - University of Texas at Austin
... •Not only does this order make you a human rather than a dog or a daffodil, it also makes each person unique. •Sequences of DNA differ from person to person, but every cell within the same person contains the same sequence of DNA. So, your hair, blood, skin and all of the other cells in your body ar ...
... •Not only does this order make you a human rather than a dog or a daffodil, it also makes each person unique. •Sequences of DNA differ from person to person, but every cell within the same person contains the same sequence of DNA. So, your hair, blood, skin and all of the other cells in your body ar ...
D>3 Round 5 - High School Quizbowl Packet Archive
... 1. This story by Bret Harte is about a prostitute in the mining camps of California who gives birth to a baby who the gold rushers name Thomas. 2. This grisly tale by Richard Connell is about a literal man hunt, in which Sanger Rainsford eludes the crazed General Zaroff on an obscure Caribbean islan ...
... 1. This story by Bret Harte is about a prostitute in the mining camps of California who gives birth to a baby who the gold rushers name Thomas. 2. This grisly tale by Richard Connell is about a literal man hunt, in which Sanger Rainsford eludes the crazed General Zaroff on an obscure Caribbean islan ...
Bio Unit 7b DNA packet
... 16. tRNA brings amino acids to the nucleus or ribosome? 17. A polypeptide is a sequence of proteins or amino acids? 18. tRNA has codons or anti-codons? 19. tRNA transfers amino acids during translation or transcription? 20. Ribosomes are the site where translation or transcription takes place? ...
... 16. tRNA brings amino acids to the nucleus or ribosome? 17. A polypeptide is a sequence of proteins or amino acids? 18. tRNA has codons or anti-codons? 19. tRNA transfers amino acids during translation or transcription? 20. Ribosomes are the site where translation or transcription takes place? ...
DNA, The Genetic Material
... Replication units – zones on chromosomes where replication starts. By having many replication units the replication process is more rapid. Human chromosomes have an average of 200 million nucleotide pairs. To compact the DNA, it is wrapped around proteins called histones (they’re positive in charge ...
... Replication units – zones on chromosomes where replication starts. By having many replication units the replication process is more rapid. Human chromosomes have an average of 200 million nucleotide pairs. To compact the DNA, it is wrapped around proteins called histones (they’re positive in charge ...
Teacher Guide - the BIOTECH Project
... child and, with his parents’ permission, we can help him confirm or deny his current biological parentage. Some questions to get you thinking about today’s lab: What is DNA and what does it do? deoxyribonucleic acid, makes you who you are, codes for proteins, etc. What are chromosomes and how many c ...
... child and, with his parents’ permission, we can help him confirm or deny his current biological parentage. Some questions to get you thinking about today’s lab: What is DNA and what does it do? deoxyribonucleic acid, makes you who you are, codes for proteins, etc. What are chromosomes and how many c ...
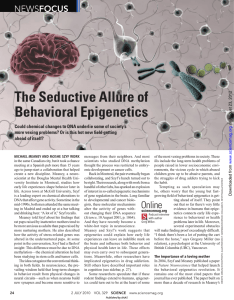
The Seductive Allure of Behavioral Epigenetics. Science.
... behavior. Nestler cautions that Epigenetic breakdown. Several epigenetic mechanisms alter gene activity to find increased methylation any treatments for human drug in neurons, with potentially important effects on brain function and behav- of the glucocorticoid receptor addicts are a long way off, b ...
... behavior. Nestler cautions that Epigenetic breakdown. Several epigenetic mechanisms alter gene activity to find increased methylation any treatments for human drug in neurons, with potentially important effects on brain function and behav- of the glucocorticoid receptor addicts are a long way off, b ...
Nucleosomes released from oviduct nuclei during brief micrococcal
... HMG17). The H4:HMG14:HMG17:HMGY ratios was found to be 2.0/0.9/0.5/0.5, i.e., nearly two molecules of HMG per nucleosome. This may be an overestimate since we are not sure that all the histone is displaced from the DNA by the protamine sulphate, i.e. there could be preferential dissociation of HMG p ...
... HMG17). The H4:HMG14:HMG17:HMGY ratios was found to be 2.0/0.9/0.5/0.5, i.e., nearly two molecules of HMG per nucleosome. This may be an overestimate since we are not sure that all the histone is displaced from the DNA by the protamine sulphate, i.e. there could be preferential dissociation of HMG p ...
Nucleosome

A nucleosome is a basic unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes, consisting of a segment of DNA wound in sequence around eight histone protein cores. This structure is often compared to thread wrapped around a spool.Nucleosomes form the fundamental repeating units of eukaryotic chromatin, which is used to pack the large eukaryotic genomes into the nucleus while still ensuring appropriate access to it (in mammalian cells approximately 2 m of linear DNA have to be packed into a nucleus of roughly 10 µm diameter). Nucleosomes are folded through a series of successively higher order structures to eventually form a chromosome; this both compacts DNA and creates an added layer of regulatory control, which ensures correct gene expression. Nucleosomes are thought to carry epigenetically inherited information in the form of covalent modifications of their core histones.Nucleosomes were observed as particles in the electron microscope by Don and Ada Olins and their existence and structure (as histone octamers surrounded by approximately 200 base pairs of DNA) were proposed by Roger Kornberg. The role of the nucleosome as a general gene repressor was demonstrated by Lorch et al. in vitro and by Han and Grunstein in vivo.The nucleosome core particle consists of approximately 147 base pairs of DNA wrapped in 1.67 left-handed superhelical turns around a histone octamer consisting of 2 copies each of the core histones H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. Core particles are connected by stretches of ""linker DNA"", which can be up to about 80 bp long. Technically, a nucleosome is defined as the core particle plus one of these linker regions; however the word is often synonymous with the core particle. Genome-wide nucleosome positioning maps are now available for many model organisms including mouse liver and brain.Linker histones such as H1 and its isoforms are involved in chromatin compaction and sit at the base of the nucleosome near the DNA entry and exit binding to the linker region of the DNA. Non-condensed nucleosomes without the linker histone resemble ""beads on a string of DNA"" under an electron microscope.In contrast to most eukaryotic cells, mature sperm cells largely use protamines to package their genomic DNA, most likely to achieve an even higher packaging ratio. Histone equivalents and a simplified chromatin structure have also been found in Archea, suggesting that eukaryotes are not the only organisms that use nucleosomes.