DNA Specificity of the Bicoid Activator Protein Is Determined by
... LexA-Bicoid mutant A, contained a Thr-Ala substitution at position 1 and still activated a Bicoid site target. LexABicoid mutant A5 contained a Lys+Ala substitution at position 5 and also activated a Bicoid site target but at reduced levels. However, activation by this mutant was also reduced using ...
... LexA-Bicoid mutant A, contained a Thr-Ala substitution at position 1 and still activated a Bicoid site target. LexABicoid mutant A5 contained a Lys+Ala substitution at position 5 and also activated a Bicoid site target but at reduced levels. However, activation by this mutant was also reduced using ...
Lesson 1 – Introduction to Biotechnology
... The spores are much better adapted to survival under harsh conditions such as drought and excessive heat than are vegetative cells. Simple cell division occurs when the cell divides evenly creating an exact genetic duplicate of itself. Budding also produces a duplicate, but cytoplasm and intracellul ...
... The spores are much better adapted to survival under harsh conditions such as drought and excessive heat than are vegetative cells. Simple cell division occurs when the cell divides evenly creating an exact genetic duplicate of itself. Budding also produces a duplicate, but cytoplasm and intracellul ...
Adaptive value of sex in microbial pathogens
... 1995; Gandon and Otto, 2007). Data from pathogens bearing on the host–parasite model will be discussed below. Because of these and other problems with the negative epistasis model, some workers in this area favor selection and chance effects in finite populations as the main sources of genetic assoc ...
... 1995; Gandon and Otto, 2007). Data from pathogens bearing on the host–parasite model will be discussed below. Because of these and other problems with the negative epistasis model, some workers in this area favor selection and chance effects in finite populations as the main sources of genetic assoc ...
SNP Analysis of the PTC Gene Using PCR
... (Figure 2). This fact was discovered in 1931 in a series of events that involved impressive scientific curiosity and questionable laboratory safety. A chemist named Arthur Fox was mixing a powdered chemical when he accidentally let a bit of the powder blow into the air. A nearby colleague exclaimed h ...
... (Figure 2). This fact was discovered in 1931 in a series of events that involved impressive scientific curiosity and questionable laboratory safety. A chemist named Arthur Fox was mixing a powdered chemical when he accidentally let a bit of the powder blow into the air. A nearby colleague exclaimed h ...
Recent advances in the genome-wide study of DNA replication
... ORIs compared with other studied yeasts. In this kind of yeast, two different types of ORIs exist simultaneously. In addition to an A/T-rich type more reminiscent of typical budding and fission yeast origins, there is also a G/C-rich type of replication origins associated with transcription start si ...
... ORIs compared with other studied yeasts. In this kind of yeast, two different types of ORIs exist simultaneously. In addition to an A/T-rich type more reminiscent of typical budding and fission yeast origins, there is also a G/C-rich type of replication origins associated with transcription start si ...
Carcinoembryonic Antigens - The Journal of Cell Biology
... cated by the proposed domain structure illustrated in Fig. 3 and by the sequence relationships detailed in Table I. As is typical for other CEA isoantigens, the TM1-CEA polypeptide initiates with a M-amino acid leader sequence that ends at a short side-chain amino acid, alanine. The proposed NH2-ter ...
... cated by the proposed domain structure illustrated in Fig. 3 and by the sequence relationships detailed in Table I. As is typical for other CEA isoantigens, the TM1-CEA polypeptide initiates with a M-amino acid leader sequence that ends at a short side-chain amino acid, alanine. The proposed NH2-ter ...
biotransformation - University of California, Berkeley
... The elimination of xenobiotics often depends on their conversion to water-soluble chemicals through biotransformation, catalyzed by multiple enzymes primarily in the liver with contributions from other tissues. Biotransformation changes the properties of a xenobiotic usually from a lipophilic form ( ...
... The elimination of xenobiotics often depends on their conversion to water-soluble chemicals through biotransformation, catalyzed by multiple enzymes primarily in the liver with contributions from other tissues. Biotransformation changes the properties of a xenobiotic usually from a lipophilic form ( ...
Illustrating Python via Bioinformatics Examples
... The instructions to the computer how the analysis is going to be performed are specified using the Python1 programming language. The forthcoming examples are simple illustrations of the type of problem settings and corresponding Python implementations that are encountered in bioinformatics. However, ...
... The instructions to the computer how the analysis is going to be performed are specified using the Python1 programming language. The forthcoming examples are simple illustrations of the type of problem settings and corresponding Python implementations that are encountered in bioinformatics. However, ...
Document
... Self-organization and evolution An attractive aspect of ‘self-organization’ is that it implies that organism, as a physical structure, has a possibility to adapt before and independent from natural selection and thus provides an alternative model for natural evolution: ...
... Self-organization and evolution An attractive aspect of ‘self-organization’ is that it implies that organism, as a physical structure, has a possibility to adapt before and independent from natural selection and thus provides an alternative model for natural evolution: ...
Specialized Transduction
... volume have seen fit to respect tradition. The term specialized transduction originally called attention to the propensity of coliphage λ, the first discovered specialized transducer, to mediate transfer of only a limited set of host genes (47, 48). Generalized transduction, discovered first in Salm ...
... volume have seen fit to respect tradition. The term specialized transduction originally called attention to the propensity of coliphage λ, the first discovered specialized transducer, to mediate transfer of only a limited set of host genes (47, 48). Generalized transduction, discovered first in Salm ...
Protein Acetylation as an Integral Part of Metabolism in Cancer
... tissues, biological systems and also across cancer types and grades. In a variety of primary cancer tissues it has been shown that lower cellular levels of histone acetylation, suggesting reduced gene expression, can be associated with more aggressive cancers and poorer clinical outcomes [26,27,28] ...
... tissues, biological systems and also across cancer types and grades. In a variety of primary cancer tissues it has been shown that lower cellular levels of histone acetylation, suggesting reduced gene expression, can be associated with more aggressive cancers and poorer clinical outcomes [26,27,28] ...
DNA Base Sequence Homology in Rhizoctonia solani Kuihn: Inter
... AG-10 (12). Some of these anastomosis groups are further subdivided based on pathogenicity (AG-1, AG-2), colony morphology (AG-1), thiamine requirement (AG-2, AG-9), and/or DNA homology (AG-4, AG-6) into intraspecific groups (ISG) (11). The ISG is derived by combining anastomosis group affiliation w ...
... AG-10 (12). Some of these anastomosis groups are further subdivided based on pathogenicity (AG-1, AG-2), colony morphology (AG-1), thiamine requirement (AG-2, AG-9), and/or DNA homology (AG-4, AG-6) into intraspecific groups (ISG) (11). The ISG is derived by combining anastomosis group affiliation w ...
Developmental Validation of the Quantifiler Real-Time
... sex determination using the amplification of homologous but distinct regions of the X and Y chromosomes (4,5). The Quantifiler kits were designed for the quantification of human nuclear DNA, and their genomic targets reflect the particular roles for which the kits were intended. The Quantifiler Huma ...
... sex determination using the amplification of homologous but distinct regions of the X and Y chromosomes (4,5). The Quantifiler kits were designed for the quantification of human nuclear DNA, and their genomic targets reflect the particular roles for which the kits were intended. The Quantifiler Huma ...
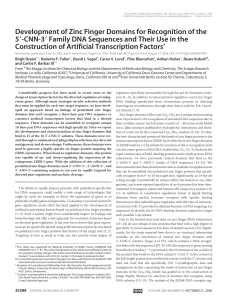
Development of Zinc Finger Domains for Recognition of the 5
... reactions contained 15 kcpm 32P-end-labeled ERBB-2 promoter fragment and 5 mM dithiothreitol, and the protein concentration was varied from 0.1 to 100 nM. Reactions were incubated at 4 °C for 12–18 h. Digestion of DNA was performed using DNase I (Roche Diagnostics) as has been described (34). Sample ...
... reactions contained 15 kcpm 32P-end-labeled ERBB-2 promoter fragment and 5 mM dithiothreitol, and the protein concentration was varied from 0.1 to 100 nM. Reactions were incubated at 4 °C for 12–18 h. Digestion of DNA was performed using DNase I (Roche Diagnostics) as has been described (34). Sample ...
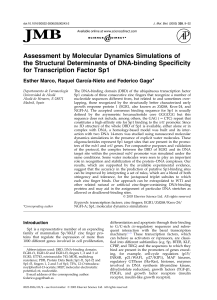
Assessment by Molecular Dynamics Simulations of the Structural
... of the bound protein. In addition, when residue 2 of the helix is aspartic acid, an extra contact can be established with the exocyclic amino group of either adenine or cytosine in the complementary C-rich strand, effectively extending the length of the binding site one nucleotide further outside th ...
... of the bound protein. In addition, when residue 2 of the helix is aspartic acid, an extra contact can be established with the exocyclic amino group of either adenine or cytosine in the complementary C-rich strand, effectively extending the length of the binding site one nucleotide further outside th ...
Genetic and Epigenetic Regulation in Age
... the machinery of epigenetic regulation that is ultimately responsible for the gene expression regulation. The most common DNA methylation form is the 5¶ methylcytosine. It occurs predominantly in the symmetric CG context. Approximately 70% to 80% of CG dinucleotides of the genome are normally methyl ...
... the machinery of epigenetic regulation that is ultimately responsible for the gene expression regulation. The most common DNA methylation form is the 5¶ methylcytosine. It occurs predominantly in the symmetric CG context. Approximately 70% to 80% of CG dinucleotides of the genome are normally methyl ...
Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of another variant of the
... SSC/O.l%SDS at 42 "C and two 15 min washes with a solution of 0.1 x SSC/O.l% SDS at 65 "C. Membranes for hybridization with oligonucleotide probes were prehybridized in 6 x SSC, 5 x Denhardt's solution, 0.05 % sodium pyrophosphate, 0-5% SDS, with denatured salmon sperm at a concentration of 100 pg m ...
... SSC/O.l%SDS at 42 "C and two 15 min washes with a solution of 0.1 x SSC/O.l% SDS at 65 "C. Membranes for hybridization with oligonucleotide probes were prehybridized in 6 x SSC, 5 x Denhardt's solution, 0.05 % sodium pyrophosphate, 0-5% SDS, with denatured salmon sperm at a concentration of 100 pg m ...
Unit 3 Solutions - Manning`s Science
... molecules (“handrails”), nucleotide base pairing (“rungs”), and directionality of both strands and resemble the close up of Figure 5.7 on page 213 of the student textbook. 8. a. Levene proposed that DNA was composed of nucleotides, and that each of the four types of nucleotides contained one of fo ...
... molecules (“handrails”), nucleotide base pairing (“rungs”), and directionality of both strands and resemble the close up of Figure 5.7 on page 213 of the student textbook. 8. a. Levene proposed that DNA was composed of nucleotides, and that each of the four types of nucleotides contained one of fo ...
NIH Public Access
... specifically removes 5-methylcytosine from DNA [5••,18]. DNA glycosylases are repair enzymes that initiate the base excision repair by removing damaged or mismatched bases [19]. DNA glycosylase activity of DME is required for removal of cytosine methylation both in vivo and in vitro [5••,20]. Only t ...
... specifically removes 5-methylcytosine from DNA [5••,18]. DNA glycosylases are repair enzymes that initiate the base excision repair by removing damaged or mismatched bases [19]. DNA glycosylase activity of DME is required for removal of cytosine methylation both in vivo and in vitro [5••,20]. Only t ...
A structural determinant in the uracil DNA glycosylase superfamily
... analysis presented here demonstrates that a K68N substitution not only allows E. coli MUG to act on A/U base pairs, but also increases its catalytic efficiency on all other double-stranded uracil-containing DNA. Binding analysis shows that the substitution enhances the binding affinity of K68N to al ...
... analysis presented here demonstrates that a K68N substitution not only allows E. coli MUG to act on A/U base pairs, but also increases its catalytic efficiency on all other double-stranded uracil-containing DNA. Binding analysis shows that the substitution enhances the binding affinity of K68N to al ...
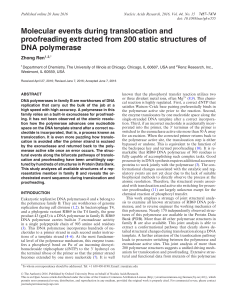
Molecular events during translocation and proofreading extracted
... Structural meta-analysis based on singular value decomposition (SVD) of interatomic distance matrices has enabled a large-scale joint analysis of related protein structures (12–14). This computational method of structural analysis takes advantage of a mathematical, yet practical, definition of confo ...
... Structural meta-analysis based on singular value decomposition (SVD) of interatomic distance matrices has enabled a large-scale joint analysis of related protein structures (12–14). This computational method of structural analysis takes advantage of a mathematical, yet practical, definition of confo ...
Nonconventional Initiation Complex Assembly by STAT and NF
... A. Macrophages with IFN-I + hkL -> increase of histone acetylation at both the proximal and distal promoter locations B. Treatment with IFN-I -> increase of H4 acetylation at the distal IFN response region C. hkL treatment -> increase in H4 acetylation at the proximal NF-κB element ISGF3 and NF-κB ...
... A. Macrophages with IFN-I + hkL -> increase of histone acetylation at both the proximal and distal promoter locations B. Treatment with IFN-I -> increase of H4 acetylation at the distal IFN response region C. hkL treatment -> increase in H4 acetylation at the proximal NF-κB element ISGF3 and NF-κB ...
Adherin - Semantic Scholar
... removal of adherin to and from chromosomes are coordinated with replication origin licensing and mitotic entry, which ensures that cohesion and loss of cohesion are properly synchronized with DNA replication and chromosome segregation. This also means, however, that cohesin is bound to chromosomes t ...
... removal of adherin to and from chromosomes are coordinated with replication origin licensing and mitotic entry, which ensures that cohesion and loss of cohesion are properly synchronized with DNA replication and chromosome segregation. This also means, however, that cohesin is bound to chromosomes t ...
Export To Word
... opinion data about the use of genetically modified foods In this lesson, students will analyze an informational text that addresses the release of genetically modified mosquitoes in Brazil to reduce the transmission of dengue fever. The male mosquitoes were modified so that when they reproduce, thei ...
... opinion data about the use of genetically modified foods In this lesson, students will analyze an informational text that addresses the release of genetically modified mosquitoes in Brazil to reduce the transmission of dengue fever. The male mosquitoes were modified so that when they reproduce, thei ...
Nucleosome

A nucleosome is a basic unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes, consisting of a segment of DNA wound in sequence around eight histone protein cores. This structure is often compared to thread wrapped around a spool.Nucleosomes form the fundamental repeating units of eukaryotic chromatin, which is used to pack the large eukaryotic genomes into the nucleus while still ensuring appropriate access to it (in mammalian cells approximately 2 m of linear DNA have to be packed into a nucleus of roughly 10 µm diameter). Nucleosomes are folded through a series of successively higher order structures to eventually form a chromosome; this both compacts DNA and creates an added layer of regulatory control, which ensures correct gene expression. Nucleosomes are thought to carry epigenetically inherited information in the form of covalent modifications of their core histones.Nucleosomes were observed as particles in the electron microscope by Don and Ada Olins and their existence and structure (as histone octamers surrounded by approximately 200 base pairs of DNA) were proposed by Roger Kornberg. The role of the nucleosome as a general gene repressor was demonstrated by Lorch et al. in vitro and by Han and Grunstein in vivo.The nucleosome core particle consists of approximately 147 base pairs of DNA wrapped in 1.67 left-handed superhelical turns around a histone octamer consisting of 2 copies each of the core histones H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. Core particles are connected by stretches of ""linker DNA"", which can be up to about 80 bp long. Technically, a nucleosome is defined as the core particle plus one of these linker regions; however the word is often synonymous with the core particle. Genome-wide nucleosome positioning maps are now available for many model organisms including mouse liver and brain.Linker histones such as H1 and its isoforms are involved in chromatin compaction and sit at the base of the nucleosome near the DNA entry and exit binding to the linker region of the DNA. Non-condensed nucleosomes without the linker histone resemble ""beads on a string of DNA"" under an electron microscope.In contrast to most eukaryotic cells, mature sperm cells largely use protamines to package their genomic DNA, most likely to achieve an even higher packaging ratio. Histone equivalents and a simplified chromatin structure have also been found in Archea, suggesting that eukaryotes are not the only organisms that use nucleosomes.