Introduction to Epigenetics - BITS Embryo
... • Tight control for maintaining gene silencing (vertebrate genes are less “leaky” compared to bacterial) • Transcriptional silencing of transposons (‘genome ...
... • Tight control for maintaining gene silencing (vertebrate genes are less “leaky” compared to bacterial) • Transcriptional silencing of transposons (‘genome ...
Microarrays - TeacherWeb
... chromosome in every cell. • Some genes are active only in certain cells ...
... chromosome in every cell. • Some genes are active only in certain cells ...
i. justification for intensive diabetes control
... The following studies have demonstrated that tight glucose control significantly reduces the presence or progression in microvascular complications of diabetes mellitus. A. Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group: The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and p ...
... The following studies have demonstrated that tight glucose control significantly reduces the presence or progression in microvascular complications of diabetes mellitus. A. Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group: The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and p ...
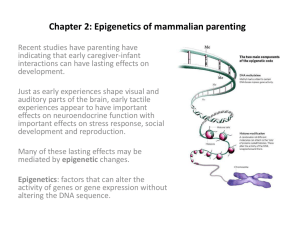
Chapter 2: Epigenetics of mammalian parenting
... • All these effects are traceable to changes in neurotransmitter receptor and activity levels in the brain. ...
... • All these effects are traceable to changes in neurotransmitter receptor and activity levels in the brain. ...
EPIGENETICS Textbook
... – Found in 5’ promoter areas – NOT methylated on active and silent genes – EXCEPTIONS: • Silencing on X chromosome • When cells differentiate • Pathological processes, e.g., inactivation of tumor suppressor genes in some cancers ...
... – Found in 5’ promoter areas – NOT methylated on active and silent genes – EXCEPTIONS: • Silencing on X chromosome • When cells differentiate • Pathological processes, e.g., inactivation of tumor suppressor genes in some cancers ...
outline3985
... 3. INITIAL T(x) for acute : RAISE GLUCOSE LEVELS One cannot determine whether a patient is hypoglycemic or hyperglycemic during an acute attack unless blood tests are performed. Therefore, the initial treatment for an unknown acute attack is to raise glucose levels. Raising glucose levels in a hyper ...
... 3. INITIAL T(x) for acute : RAISE GLUCOSE LEVELS One cannot determine whether a patient is hypoglycemic or hyperglycemic during an acute attack unless blood tests are performed. Therefore, the initial treatment for an unknown acute attack is to raise glucose levels. Raising glucose levels in a hyper ...
AP Biology
... 18. What are key differences between an inducible system and a repressible system in prokaryotic gene expression? ...
... 18. What are key differences between an inducible system and a repressible system in prokaryotic gene expression? ...
Breanna Perreault D145 Presentation 2/23/17 Background
... CpGs: Consecutive C and G nucleotides, sequence that can be directly methylated ...
... CpGs: Consecutive C and G nucleotides, sequence that can be directly methylated ...
Guidelines and Assignments
... 1. (MT1) A. How is the 5-mC distributed within the human genome? B. Do all human genes have CpG island at their promoters? C. How bisulfite treatment may affect the CpG methylation status? D. What methods can be used to detect the methylation status of DNA? Please describe at least four different me ...
... 1. (MT1) A. How is the 5-mC distributed within the human genome? B. Do all human genes have CpG island at their promoters? C. How bisulfite treatment may affect the CpG methylation status? D. What methods can be used to detect the methylation status of DNA? Please describe at least four different me ...
Guidelines and Assignments
... 1. (MT1) A. How is the 5-mC distributed within the human genome? B. Do all human genes have CpG island at their promoters? C. How bisulfite treatment may affect the CpG methylation status? D. What methods can be used to detect the methylation status of DNA? Please describe at least four different me ...
... 1. (MT1) A. How is the 5-mC distributed within the human genome? B. Do all human genes have CpG island at their promoters? C. How bisulfite treatment may affect the CpG methylation status? D. What methods can be used to detect the methylation status of DNA? Please describe at least four different me ...
AP Biology Chapter 18, 19, 27 Study Guide Chapter 18: Regulation
... 4. At which stages can gene expression be regulated? Which is the most commonly regulated stage? ...
... 4. At which stages can gene expression be regulated? Which is the most commonly regulated stage? ...
What is the most likely path of inheritance?
... Paula and Bernie have a child named Liz. Paula is A – and Liz is B +. What are the possible blood phenotypes for Bernie? Genotypes for all? ...
... Paula and Bernie have a child named Liz. Paula is A – and Liz is B +. What are the possible blood phenotypes for Bernie? Genotypes for all? ...
Genetic Engineering
... • Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt): a bacterium that produces a caterpillar toxin • The gene for this toxin has been inserted into this corn’s genome, which causes it to produce the toxin ...
... • Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt): a bacterium that produces a caterpillar toxin • The gene for this toxin has been inserted into this corn’s genome, which causes it to produce the toxin ...
98學年度轉學考試題(周世認)
... population to stop the spread of disease. (15 points) 2. Explain why, if sickle-cell anemia is fatal, natural selection has not eliminated it. (15 points) 3. Describe the creation vs. evolution debate. (10 points) 4. Outline four separate reasons for preserving biodiversity. (10 points) 5. If the co ...
... population to stop the spread of disease. (15 points) 2. Explain why, if sickle-cell anemia is fatal, natural selection has not eliminated it. (15 points) 3. Describe the creation vs. evolution debate. (10 points) 4. Outline four separate reasons for preserving biodiversity. (10 points) 5. If the co ...
Endocrine Disorders
... Caused by prolonged exposure of the body’s tissues to high levels of the hormone cortisol. ...
... Caused by prolonged exposure of the body’s tissues to high levels of the hormone cortisol. ...
Chapter 19: Control of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
... 9.) What is a transcriptional enhancer? How enhancers in the DNA work from such far distances? Lecture 26 “Control of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes: Part 2” PPT Review 1.) Is the final mature mRNA transcript composed of exons or introns? What occurs during splicing of primary mRNAs? 2.) What is alte ...
... 9.) What is a transcriptional enhancer? How enhancers in the DNA work from such far distances? Lecture 26 “Control of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes: Part 2” PPT Review 1.) Is the final mature mRNA transcript composed of exons or introns? What occurs during splicing of primary mRNAs? 2.) What is alte ...
dna methylation
... Calorie consumption dropped from 2,000 to 500 per day for 4.5 million. Children born or raised in this time were small, short in stature and had many diseases including, edema, anemia, diabetes and depression. The Dutch Famine Birth Cohort study showed that women living during this time had children ...
... Calorie consumption dropped from 2,000 to 500 per day for 4.5 million. Children born or raised in this time were small, short in stature and had many diseases including, edema, anemia, diabetes and depression. The Dutch Famine Birth Cohort study showed that women living during this time had children ...
dna methylation
... Calorie consumption dropped from 2,000 to 500 per day for 4.5 million. Children born or raised in this time were small, short in stature and had many diseases including, edema, anemia, diabetes and depression. The Dutch Famine Birth Cohort study showed that women living during this time had children ...
... Calorie consumption dropped from 2,000 to 500 per day for 4.5 million. Children born or raised in this time were small, short in stature and had many diseases including, edema, anemia, diabetes and depression. The Dutch Famine Birth Cohort study showed that women living during this time had children ...
The Code of Life: Topic 3
... DNA is negatively charged (phosphate groups) Histone proteins are positively charged This makes the DNA wrap around groups (8-9) of histones Each wrapped group is called a nucleosome The string then coils due to further charged-region interactions ...
... DNA is negatively charged (phosphate groups) Histone proteins are positively charged This makes the DNA wrap around groups (8-9) of histones Each wrapped group is called a nucleosome The string then coils due to further charged-region interactions ...
Chromatin Structure and Gene Regulation
... them to be translated multiple times if necessary – When it is degraded, enzymes shorten the poly-A tale and 5’ Cap, allowing the mRNA to be degraded – There are nucleotide sequences in the poly-A tail that code for how long it will be until it is degraded ...
... them to be translated multiple times if necessary – When it is degraded, enzymes shorten the poly-A tale and 5’ Cap, allowing the mRNA to be degraded – There are nucleotide sequences in the poly-A tail that code for how long it will be until it is degraded ...
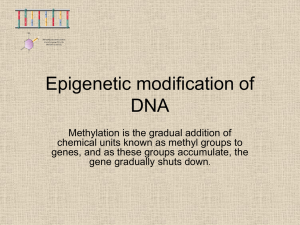
Epigenetic modification of DNA
... importance in the regulation of gene expression during development. ...
... importance in the regulation of gene expression during development. ...
Diabetes handout - City Tech OpenLab
... A. Type I Diabetes Autoimmune destruction of pancreatic beta cells Pancreas produces little or no insulin Genetic and early onset Insulin replacement is needed and is the only effective drug (administered subcutaneously). Insulin can be short/rapid, intermediate, or long acting B. Type II Di ...
... A. Type I Diabetes Autoimmune destruction of pancreatic beta cells Pancreas produces little or no insulin Genetic and early onset Insulin replacement is needed and is the only effective drug (administered subcutaneously). Insulin can be short/rapid, intermediate, or long acting B. Type II Di ...
Supplementary information about the five
... positive and negative feedback of gene x1 , the five-gene model showed three behaviors: (i) fixed-point attractor with high expression of pluripotent genes (FP), (ii) fixed-point attractor with high expression of differentiation genes (FD), and (iii) the oscillatory state (O). The five-gene model als ...
... positive and negative feedback of gene x1 , the five-gene model showed three behaviors: (i) fixed-point attractor with high expression of pluripotent genes (FP), (ii) fixed-point attractor with high expression of differentiation genes (FD), and (iii) the oscillatory state (O). The five-gene model als ...
Epigenetics - Hospital Melaka Department of Medicine Haematology
... The $3-billion project was formally founded in 1990 by the US Department of Energy and the National Institutes of Health A 'rough draft' of the genome was finished in 2000, announced jointly by U.S. President Bill Clinton and the British Prime Minister Tony Blair on June 26, ...
... The $3-billion project was formally founded in 1990 by the US Department of Energy and the National Institutes of Health A 'rough draft' of the genome was finished in 2000, announced jointly by U.S. President Bill Clinton and the British Prime Minister Tony Blair on June 26, ...