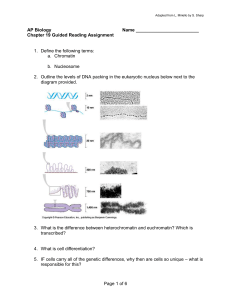
The process represented in the diagram below occurs in many cells
... (1) selective breeding (3) cloning ...
... (1) selective breeding (3) cloning ...
Letter to the Editor
... level increases in parallel with the degree of oxidative stress and it is responsible for oxidative lesions affecting DNA and proteins having a major role in the pathogenesis of many diseases (tumors, coronary artery disease, diabetes mellitus). Renal involvement is preceded by an imbalance between ...
... level increases in parallel with the degree of oxidative stress and it is responsible for oxidative lesions affecting DNA and proteins having a major role in the pathogenesis of many diseases (tumors, coronary artery disease, diabetes mellitus). Renal involvement is preceded by an imbalance between ...
國立嘉義大學九十七學年度
... (3) Which of the following statements are correct? For the incorrect statements, correct them specifically (hint: the correction should not be simply from “can” to “cannot”, or from “is” to “isn’t”). (10%) (i) Restriction endonucleases cut DNA at specific sites that always located between genes. (ii ...
... (3) Which of the following statements are correct? For the incorrect statements, correct them specifically (hint: the correction should not be simply from “can” to “cannot”, or from “is” to “isn’t”). (10%) (i) Restriction endonucleases cut DNA at specific sites that always located between genes. (ii ...
Gene Regulation - Eukaryotic Cells
... Epigenetics • Epigenetics refers to processes that influence gene expression or function without changing the underlying DNA sequence. 1. Acetylation 2. Methylation ...
... Epigenetics • Epigenetics refers to processes that influence gene expression or function without changing the underlying DNA sequence. 1. Acetylation 2. Methylation ...
Chapter 19 - Biology Junction
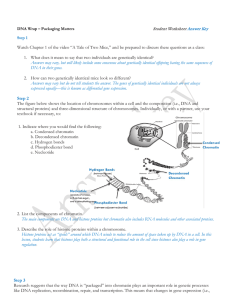
... 23. What is the difference between transposons and retrotransposons. Use the diagram below to help you answer the question. ...
... 23. What is the difference between transposons and retrotransposons. Use the diagram below to help you answer the question. ...
Interspersed Repetitive Noncoding DNA
... “Homolgous knockout of DNA methyltransferase in mice leads to embryonic lethality.” ...
... “Homolgous knockout of DNA methyltransferase in mice leads to embryonic lethality.” ...
SI Worksheet 12
... a. operators....promoters b. exons....introns c. silencers....enhancers d. introns....exons e. promoters....operators 4. Which of the following mechanisms of gene regulation operates after mRnA transcription but before translation of mRNA into protein? a. mRNA splicing b. DNA packing c. repressors a ...
... a. operators....promoters b. exons....introns c. silencers....enhancers d. introns....exons e. promoters....operators 4. Which of the following mechanisms of gene regulation operates after mRnA transcription but before translation of mRNA into protein? a. mRNA splicing b. DNA packing c. repressors a ...
Genome variation informatics: SNP discovery
... vectors in the data set so that similar patterns are together ...
... vectors in the data set so that similar patterns are together ...
Answer Key
... transcribed into mRNA and then translated (conversion of mRNA sequence into amino acids) into a protein. An individual’s environment, even in the womb, can influence these factors and permanently alter the expression of genes in the adult. Alterations in epigenetic mechanisms lead to development of ...
... transcribed into mRNA and then translated (conversion of mRNA sequence into amino acids) into a protein. An individual’s environment, even in the womb, can influence these factors and permanently alter the expression of genes in the adult. Alterations in epigenetic mechanisms lead to development of ...
Genetic Engineering Short Notes
... can replicate independantly of the main chromosome 5. Vector- something used to carry the gene of interest into another cell ...
... can replicate independantly of the main chromosome 5. Vector- something used to carry the gene of interest into another cell ...
Epigenetics Glossary FINAL
... Histone Modifications: Post-translational addition or subtraction of any one of several chemical groups to an individual amino acid of a histone. Depending on the chemical group involved, the modification is called methylation (addition of a methyl group), acetylation (addition of an acetyl group), ...
... Histone Modifications: Post-translational addition or subtraction of any one of several chemical groups to an individual amino acid of a histone. Depending on the chemical group involved, the modification is called methylation (addition of a methyl group), acetylation (addition of an acetyl group), ...
Whole Genome Scale DNA Methylation Differences in
... initiated 1) a discovery programme to identify DNA methylation variable positions (MVPs) in diseaserelevant tissues; 2) a development programme to define MVPs in disease relevant tissues when DNA amount is limited; 3) a development programme to collect thymus and obtain DNA/RNA from it. Methods: In ...
... initiated 1) a discovery programme to identify DNA methylation variable positions (MVPs) in diseaserelevant tissues; 2) a development programme to define MVPs in disease relevant tissues when DNA amount is limited; 3) a development programme to collect thymus and obtain DNA/RNA from it. Methods: In ...
Presentation 1
... Goals should be individualized based on: ● duration of diabetes ● pregnancy status ● age ● co-morbid conditions ● hypoglycemia unawareness ● individual patient considerations ...
... Goals should be individualized based on: ● duration of diabetes ● pregnancy status ● age ● co-morbid conditions ● hypoglycemia unawareness ● individual patient considerations ...
The Major Transitions in Evolution
... • A naturally occurring mutant of Linaria vulgaris, originally described more than 250 years ago by Linnaeus, in which the fundamental symmetry of the flower is changed from bilateral to radial. • The mutant carries a defect in Lcyc, a homologue of the cycloidea gene which controls dorsoventral asym ...
... • A naturally occurring mutant of Linaria vulgaris, originally described more than 250 years ago by Linnaeus, in which the fundamental symmetry of the flower is changed from bilateral to radial. • The mutant carries a defect in Lcyc, a homologue of the cycloidea gene which controls dorsoventral asym ...
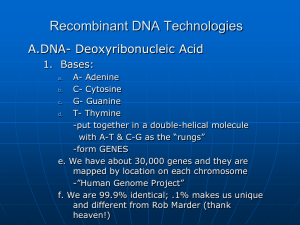
Recombinant DNA Technologies
... d. T- Thymine -put together in a double-helical molecule with A-T & C-G as the “rungs” -form GENES e. We have about 30,000 genes and they are mapped by location on each chromosome -”Human Genome Project” f. We are 99.9% identical; .1% makes us unique and different from Rob Marder (thank heaven!) a. ...
... d. T- Thymine -put together in a double-helical molecule with A-T & C-G as the “rungs” -form GENES e. We have about 30,000 genes and they are mapped by location on each chromosome -”Human Genome Project” f. We are 99.9% identical; .1% makes us unique and different from Rob Marder (thank heaven!) a. ...
On the Origin of Language
... Space of functional segment polarity networks • 22 parameters out of 48 are shown • Gray polygons yield functional networks • Kxy: concentration of X at which activity of y is half maximal, etc.. • Mean and standard variation for polygons are shown ...
... Space of functional segment polarity networks • 22 parameters out of 48 are shown • Gray polygons yield functional networks • Kxy: concentration of X at which activity of y is half maximal, etc.. • Mean and standard variation for polygons are shown ...
Ch. 18 - ltcconline.net
... operator, repressor, and corepressor. 3. Distinguish between structural and regulatory genes. 4. Describe how the lac operon functions and provide details on the role of the inducer, allolactose. 5. Explain how repressible and inducible enzymes differ and how those differences reflect differences in ...
... operator, repressor, and corepressor. 3. Distinguish between structural and regulatory genes. 4. Describe how the lac operon functions and provide details on the role of the inducer, allolactose. 5. Explain how repressible and inducible enzymes differ and how those differences reflect differences in ...
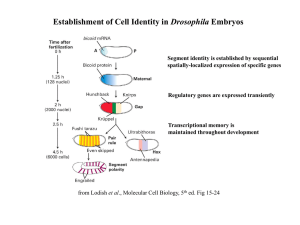
Establishment of Cell Identity in Drosophila Embryos
... DNA methylation patterns are re-established by de novo DNMTs at the blastocyst stage Primordial germ cells are demethylated through a TET-independent and a TET-mediated oxidative pathway ...
... DNA methylation patterns are re-established by de novo DNMTs at the blastocyst stage Primordial germ cells are demethylated through a TET-independent and a TET-mediated oxidative pathway ...
Epigenetics - BLI-Research-Synbio-2014-session-1
... • Along with the many controls we discussed in gene expression, the epigenome also influences gene expression. • The term epigenome refers to modifications in chromatin structures which do not involve mutations. • In biology, and specifically genetics, epigenetics is the study of inherited changes i ...
... • Along with the many controls we discussed in gene expression, the epigenome also influences gene expression. • The term epigenome refers to modifications in chromatin structures which do not involve mutations. • In biology, and specifically genetics, epigenetics is the study of inherited changes i ...
Supplementary Fig S7: A Schematic Figure of the Key Driver Analysis
... Supplementary Fig S7: A Schematic Figure of the Key Driver Analysis (KDA). In order to test if gene G (shown in red) is a KD or not, the subnetwork of G is first extracted by retrieving its 1st to 3rdlayer neighbor genes in the network. Subsequently, the enrichment of genes in a given BP gene set (s ...
... Supplementary Fig S7: A Schematic Figure of the Key Driver Analysis (KDA). In order to test if gene G (shown in red) is a KD or not, the subnetwork of G is first extracted by retrieving its 1st to 3rdlayer neighbor genes in the network. Subsequently, the enrichment of genes in a given BP gene set (s ...
Title: P.I.’s :
... phenotypes under different environmental conditions. Genetic differences determine much of this phenotypic variability. It is increasingly becoming clear that this variability cannot be completely explained by genetic mechanisms alone. Recent studies suggest that environmental factors cause epigenet ...
... phenotypes under different environmental conditions. Genetic differences determine much of this phenotypic variability. It is increasingly becoming clear that this variability cannot be completely explained by genetic mechanisms alone. Recent studies suggest that environmental factors cause epigenet ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... II. State whether the following are true or false, if false, give reason ...
... II. State whether the following are true or false, if false, give reason ...
RNA-Seq is a sequencing technique applied to transcript analysis
... microarray (microarray) gene expression data, including the large dynamic range of gene expression values and the low Of the background noise and other characteristics. Therefore, in recent years, high-throughput gene expression studies have changed from microarray technology to RNA-Seq technology. ...
... microarray (microarray) gene expression data, including the large dynamic range of gene expression values and the low Of the background noise and other characteristics. Therefore, in recent years, high-throughput gene expression studies have changed from microarray technology to RNA-Seq technology. ...