Chapter 13 Viruses
... Either have DNA or RNA Surrounded by a protein coat (capsid). Envelope – proteins, carbohydrates, lipids. Obligate intracellular parasites ...
... Either have DNA or RNA Surrounded by a protein coat (capsid). Envelope – proteins, carbohydrates, lipids. Obligate intracellular parasites ...
Slide 1
... • Disulfide bonds can form between two cysteine side chains in proteins. • The 5’end of RNA is capped by the addition of 7-methylguanosine . • Nucleotides are joined together by phosphodiester linkage between 5’and 3’ carbon atoms to form nucleic acids. ...
... • Disulfide bonds can form between two cysteine side chains in proteins. • The 5’end of RNA is capped by the addition of 7-methylguanosine . • Nucleotides are joined together by phosphodiester linkage between 5’and 3’ carbon atoms to form nucleic acids. ...
Protein Synthesis Notes
... specific amino acids from the cytoplasm and attaches to the mRNA strand. ...
... specific amino acids from the cytoplasm and attaches to the mRNA strand. ...
A1981KX02600001
... bands or spots. The turning point in this work came one morning when Barrell showed me a film he had developed that contained a large number of clear, well-defined spots. This was what we had been looking for and the twodimensional fractionation we had used formed the basis of the method described i ...
... bands or spots. The turning point in this work came one morning when Barrell showed me a film he had developed that contained a large number of clear, well-defined spots. This was what we had been looking for and the twodimensional fractionation we had used formed the basis of the method described i ...
SB2a Build DNA using the Nucleotides Then Print
... 2. Arrange the DNA nucleotides so that it is unzipped or pulled apart without the DNA helicase molecules (scissors) present. 3. Leave enough room in between the top and bottom DNA strand to place the RNA nucleotides. 4. Copy and paste the RNA nucleotides next to the bottom DNA strand on this slide t ...
... 2. Arrange the DNA nucleotides so that it is unzipped or pulled apart without the DNA helicase molecules (scissors) present. 3. Leave enough room in between the top and bottom DNA strand to place the RNA nucleotides. 4. Copy and paste the RNA nucleotides next to the bottom DNA strand on this slide t ...
DNA - Gulf Coast State College
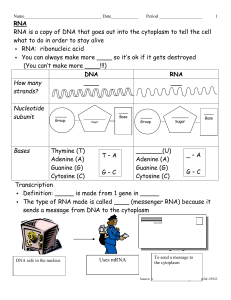
... RNA is a copy of DNA that goes out into the cytoplasm to tell the cell what to do in order to stay alive RNA: ribonucleic acid You can always make more ____ so it’s ok if it gets destroyed (You can’t make more ____!!!) DNA RNA How many ____ ___ strands? Nucleotide subunit ...
... RNA is a copy of DNA that goes out into the cytoplasm to tell the cell what to do in order to stay alive RNA: ribonucleic acid You can always make more ____ so it’s ok if it gets destroyed (You can’t make more ____!!!) DNA RNA How many ____ ___ strands? Nucleotide subunit ...
Mutations and Their Significance
... • 1. RNA Polymerase binds to DNA and separates the DNA strands • 2. RNA polymerase uses one strand of DNA as a template to assemble nucleotides into a strand of RNA • 3. Sequences of DNA that are not involved in coding for proteins are introns • 4. The DNA sequences that code for proteins are called ...
... • 1. RNA Polymerase binds to DNA and separates the DNA strands • 2. RNA polymerase uses one strand of DNA as a template to assemble nucleotides into a strand of RNA • 3. Sequences of DNA that are not involved in coding for proteins are introns • 4. The DNA sequences that code for proteins are called ...
20141203103493
... Acetylation of histone tails promotes loose chromatin structure that permits transcription ...
... Acetylation of histone tails promotes loose chromatin structure that permits transcription ...
Pengaturan Ekspresi gen 1. Struktur gen prokaryot dan eukaryot
... final level of a protein in the cell depends on the efficiency of each step and on the rates of degradation of the RNA and protein molecules. (A) In eucaryotic cells the RNA molecule produced by transcription alone (sometimes referred to as the primary transcript) would contain both coding (exon) an ...
... final level of a protein in the cell depends on the efficiency of each step and on the rates of degradation of the RNA and protein molecules. (A) In eucaryotic cells the RNA molecule produced by transcription alone (sometimes referred to as the primary transcript) would contain both coding (exon) an ...
abstract
... past geochemical processes. Messenger RNA (mRNA) and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) are relatively labile molecules that are rich in biological information, and thus can serve as useful proxies for reconstructing present microbial activities. I will present examples of studies utilizing RNA proxies which inve ...
... past geochemical processes. Messenger RNA (mRNA) and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) are relatively labile molecules that are rich in biological information, and thus can serve as useful proxies for reconstructing present microbial activities. I will present examples of studies utilizing RNA proxies which inve ...
Jeopardy, cells part 2 review
... Which of the following may alter mitosis and cause mutations of DNA. A)medications B) chemical exposture C) radiation D) all of the above ...
... Which of the following may alter mitosis and cause mutations of DNA. A)medications B) chemical exposture C) radiation D) all of the above ...
Molecular Basis for Relationship between Genotype and Phenotype
... Anticodon of a tRNA molecule recognizes and pairs with an mRNA codon. tRNA contains modified bases: pseudouridine, methylguanosine, dimethylguanosine, ...
... Anticodon of a tRNA molecule recognizes and pairs with an mRNA codon. tRNA contains modified bases: pseudouridine, methylguanosine, dimethylguanosine, ...
Black with Gold - Cloudfront.net
... in the decomposition of matter and absorb water. Both then were available to plants. Many plants today are associated with fungi at their roots. ...
... in the decomposition of matter and absorb water. Both then were available to plants. Many plants today are associated with fungi at their roots. ...
L 04 _transcription
... II. Types of RNA (by function) messenger RNA. DNA is in the nucleus, but protein synthesis occurs in the cytoplasm. The DNA sequence of a gene is copied into an RNA sequence by transcription; the RNA copy of a gene is the mRNA. About 2-3% of the total RNA in a cell. transfer RNA. There is no chemica ...
... II. Types of RNA (by function) messenger RNA. DNA is in the nucleus, but protein synthesis occurs in the cytoplasm. The DNA sequence of a gene is copied into an RNA sequence by transcription; the RNA copy of a gene is the mRNA. About 2-3% of the total RNA in a cell. transfer RNA. There is no chemica ...
Section 4.3 – DNA
... Stored in cells that have a nucleus 1952 – Rosalind Franklin discovered that DNA is 2 chains in a spiral -‐ 1953 – Watson and Crick made a DNA model o DNA is made of deoxyribose (sugar) ...
... Stored in cells that have a nucleus 1952 – Rosalind Franklin discovered that DNA is 2 chains in a spiral -‐ 1953 – Watson and Crick made a DNA model o DNA is made of deoxyribose (sugar) ...
Study Guide for Understanding the Concept of Protein Synthesis
... Transfer RNA (tRNA) acts as a "taxi" by which the "escort" ribosomes take the amino acids and position them into place as Ribosomal RNA (rRNA). Step #5: Ribosomes: From the rRNA, the amino acids continue their journey within the cytoplasm, resting on "floating" ribosomes or on the Rough ER. These ri ...
... Transfer RNA (tRNA) acts as a "taxi" by which the "escort" ribosomes take the amino acids and position them into place as Ribosomal RNA (rRNA). Step #5: Ribosomes: From the rRNA, the amino acids continue their journey within the cytoplasm, resting on "floating" ribosomes or on the Rough ER. These ri ...
Chapter 3, Section 4 The DNA Connection
... • The order of the nitrogen bases along a gene forms a genetic code that specifies what type of protein will be produced. • In the genetic code, a group of 3 bases code for the attachment of a specific amino acid. • The order of these bases determine the type of protein. ...
... • The order of the nitrogen bases along a gene forms a genetic code that specifies what type of protein will be produced. • In the genetic code, a group of 3 bases code for the attachment of a specific amino acid. • The order of these bases determine the type of protein. ...
Origin of Life
... as a template for specific proteins. • Since RNA may assume different shapes, some RNA molecules may behave like proteins and catalyze chemical reactions. • A ribosome can act as an enzyme and may have the ability to replicate itself. • Since RNA plays a vital role in the replication of DNA, self-re ...
... as a template for specific proteins. • Since RNA may assume different shapes, some RNA molecules may behave like proteins and catalyze chemical reactions. • A ribosome can act as an enzyme and may have the ability to replicate itself. • Since RNA plays a vital role in the replication of DNA, self-re ...
Chapter 11 Concept Check Questions
... 3. Desribe the experimental design that allowed Hershey and Chase to distinguish between the two options for genetic material. ...
... 3. Desribe the experimental design that allowed Hershey and Chase to distinguish between the two options for genetic material. ...
DNA and RNA review
... How do the purines and pyrimidines differ structurally? What type of bond holds the 2 strands of DNA together? Describe this type of bond. Explain the complementary base pairing of the nitrogen bases in DNA. What is produced in DNA replication? Why is DNA replication necessary? What important roles ...
... How do the purines and pyrimidines differ structurally? What type of bond holds the 2 strands of DNA together? Describe this type of bond. Explain the complementary base pairing of the nitrogen bases in DNA. What is produced in DNA replication? Why is DNA replication necessary? What important roles ...