AP Biology - TeacherWeb
... 12. Explain how RNA processing is a mechanism of post-transcriptional regulation. ...
... 12. Explain how RNA processing is a mechanism of post-transcriptional regulation. ...
No Slide Title
... mRNA- travel from the nucleus to the ribosome to direct synthesis of specific proteins. rRNA- proteins to form ribosome in the cytoplasm. tRNA- transports amino acids to the ribosome. ...
... mRNA- travel from the nucleus to the ribosome to direct synthesis of specific proteins. rRNA- proteins to form ribosome in the cytoplasm. tRNA- transports amino acids to the ribosome. ...
Discovery through RNA-Seq
... • EML4-ALK fusion (non small cell lung cancer) • TMPRSS2-ERG family fusion (prostate cancer) ...
... • EML4-ALK fusion (non small cell lung cancer) • TMPRSS2-ERG family fusion (prostate cancer) ...
Practice Quiz
... 2. ___________________ is the division of the cell cytoplasm and its associated organelles. 3. The metabolic or growth phase of a cell’s life cycle is called ______________. 4. The process of discharging particles from inside the cell to the outside is called _______. 5. A red blood cell would swell ...
... 2. ___________________ is the division of the cell cytoplasm and its associated organelles. 3. The metabolic or growth phase of a cell’s life cycle is called ______________. 4. The process of discharging particles from inside the cell to the outside is called _______. 5. A red blood cell would swell ...
Slide 1
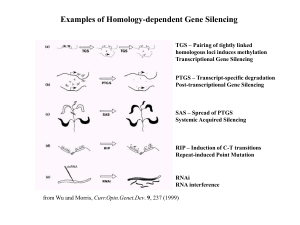
... Figure 1 Genes used to study RNA-mediated genetic interference in C.elegans. Intron–exon structure for genes used to test RNA-mediated inhibition are shown (grey and filled boxes, exons; open boxes, introns; patterned and striped boxes, 5' and 3' untranslated regions. unc-22. ref. 9, unc-54, ref. 1 ...
... Figure 1 Genes used to study RNA-mediated genetic interference in C.elegans. Intron–exon structure for genes used to test RNA-mediated inhibition are shown (grey and filled boxes, exons; open boxes, introns; patterned and striped boxes, 5' and 3' untranslated regions. unc-22. ref. 9, unc-54, ref. 1 ...
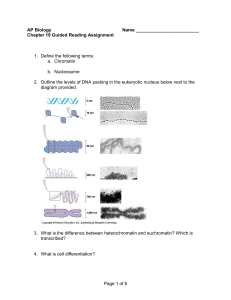
AP Biology Study Guide Key Chapter 18
... a. Repressible enzymes usually function in anabolic pathways. The pathway’s product serves as a corepressor to activate the repressor and turn off enzyme synthesis and prevent overproduction of the product of the pathway. Genes for repressible enzymes are usually switched on and the repressor is syn ...
... a. Repressible enzymes usually function in anabolic pathways. The pathway’s product serves as a corepressor to activate the repressor and turn off enzyme synthesis and prevent overproduction of the product of the pathway. Genes for repressible enzymes are usually switched on and the repressor is syn ...
The Origins of Life
... cenancestor . …. or …. • If it occurs in two of the domains but not the 3rd , we can infer that the trait occurred in the most recent common ancestor and was lost in one of the lineages. • Otherwise the trait would have had to arise 2 or 3 different times which is much less likely because it would r ...
... cenancestor . …. or …. • If it occurs in two of the domains but not the 3rd , we can infer that the trait occurred in the most recent common ancestor and was lost in one of the lineages. • Otherwise the trait would have had to arise 2 or 3 different times which is much less likely because it would r ...
RNA Metabolism Summary Slides as Questions
... Regulation of mRNA concentration within the cell. In bacteria, mRNA halflife is a few minutes; in eukaryotes, can be a few minutes or up to a day. Without degradation, the mRNA concentraion would be out of control.**Bacterial mRNA is degraded by an endoribonuclease followed by 3' to 5' exoribonuclea ...
... Regulation of mRNA concentration within the cell. In bacteria, mRNA halflife is a few minutes; in eukaryotes, can be a few minutes or up to a day. Without degradation, the mRNA concentraion would be out of control.**Bacterial mRNA is degraded by an endoribonuclease followed by 3' to 5' exoribonuclea ...
Protein Synthesis
... Genes code for EVERYTHING our body needs and does (saliva, bones, eye shape) Because DNA is so large, it is stuck inside the nucleus It needs a messenger to move the information from nucleus to protein production locations (ribosomes!) ...
... Genes code for EVERYTHING our body needs and does (saliva, bones, eye shape) Because DNA is so large, it is stuck inside the nucleus It needs a messenger to move the information from nucleus to protein production locations (ribosomes!) ...
AGO1-IP approach to small RNA target discovery in Arabidopsis
... A drawback of the method is its intrinsic reliance on sufficient VSR expression levels in the tissues of interest. This may partly explain its poor performances in roots (Figure S5), where the 35S promoter is reputed to be only weakly active in several cell layers. Constitutive VSR expression might ...
... A drawback of the method is its intrinsic reliance on sufficient VSR expression levels in the tissues of interest. This may partly explain its poor performances in roots (Figure S5), where the 35S promoter is reputed to be only weakly active in several cell layers. Constitutive VSR expression might ...
No Slide Title
... 2) An enzyme “slices” the DNA, making it single stranded. 3) Another enzyme (polymerase) synthesizes a strand of RNA using one of the DNA strands as a template. ...
... 2) An enzyme “slices” the DNA, making it single stranded. 3) Another enzyme (polymerase) synthesizes a strand of RNA using one of the DNA strands as a template. ...
401Lecture5sp2013post
... Each probe specific for sequences separated by known distances in linear Fig. 6-35 Lodish et al. 2013 DNA What result would you expect if DNA exists in loops? Would you expect loops to be present at all stages of cell cycle? ...
... Each probe specific for sequences separated by known distances in linear Fig. 6-35 Lodish et al. 2013 DNA What result would you expect if DNA exists in loops? Would you expect loops to be present at all stages of cell cycle? ...
RNA
... First genes were RNA molecules that polymerized abiotically and replicated themselves autocatalytically ...
... First genes were RNA molecules that polymerized abiotically and replicated themselves autocatalytically ...
Eukaryotes - Alice Pevyhouse
... The Origins of Life on Earth What is the bare minimum for “life”? • RNA – some molecule complex enough to carry genetic blueprints for the organism. • Cell wall – something to protect the RNA from the raw environment and contain replication • A rich organic soup of less complex molecules to ...
... The Origins of Life on Earth What is the bare minimum for “life”? • RNA – some molecule complex enough to carry genetic blueprints for the organism. • Cell wall – something to protect the RNA from the raw environment and contain replication • A rich organic soup of less complex molecules to ...
Transcription & Translation
... a. AGC TAA CCG (DNA) UCG AUU GGC (RNA) 3. RNA strand breaks free, leaves nucleus, heads to ribosome ...
... a. AGC TAA CCG (DNA) UCG AUU GGC (RNA) 3. RNA strand breaks free, leaves nucleus, heads to ribosome ...
Unit 9 Completed Vocabulary - WAHS
... transformation – process in which one strain of bacteria is changed by a gene or genes from another strain of bacteria. bacteriophage – a virus that infects bacteria. nucleotide – monomer of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. base pairing – principl ...
... transformation – process in which one strain of bacteria is changed by a gene or genes from another strain of bacteria. bacteriophage – a virus that infects bacteria. nucleotide – monomer of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. base pairing – principl ...
Final Exam Study Guide Ms. Thomas Spring 2011
... 13. Draw and label a DNA nucleotide. 14. Draw and label the major parts of a flower. Describe the function of each part. 15. Draw and label the stages of meiosis. 16. Draw the following cycles and define each process within the cycle: a. Water b. Carbon c. Nitrogen 17. How many chromosomes are prese ...
... 13. Draw and label a DNA nucleotide. 14. Draw and label the major parts of a flower. Describe the function of each part. 15. Draw and label the stages of meiosis. 16. Draw the following cycles and define each process within the cycle: a. Water b. Carbon c. Nitrogen 17. How many chromosomes are prese ...
3687317_mlbio10_Ch13_TestA_3rd.indd
... d. proteins 4. During eukaryotic transcription, the molecule that is formed is a. complementary to both strands of DNA. b. identical to an entire single strand of DNA. c. double-stranded and inside the nucleus. d. complementary to part of one strand of DNA. 5. There are 64 codons and 20 amino acids. ...
... d. proteins 4. During eukaryotic transcription, the molecule that is formed is a. complementary to both strands of DNA. b. identical to an entire single strand of DNA. c. double-stranded and inside the nucleus. d. complementary to part of one strand of DNA. 5. There are 64 codons and 20 amino acids. ...
Chapter 6 From DNA to Protein: How Cell Read the Genome
... To begin transcription, eucaryotic RNA polymerase II requires a set of general transcriptional factors ...
... To begin transcription, eucaryotic RNA polymerase II requires a set of general transcriptional factors ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... consists of three consecutive nucleotides that specify a single amino acid that is to be added to a polypeptide. ...
... consists of three consecutive nucleotides that specify a single amino acid that is to be added to a polypeptide. ...